Reserpine is an antihypertensive and antipsychotic agent that lowers blood pressure by depleting norepinephrine from nerve endings.
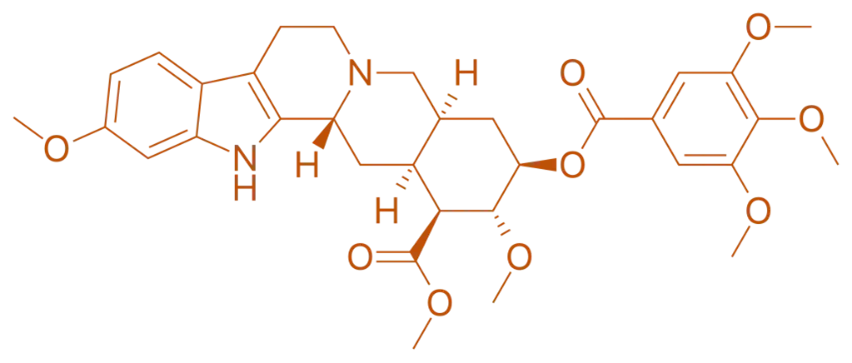
Structure of Reserpine
- Reserpine is an indole alkaloid derived from the Rauwolfia serpentina plant, featuring a complex structure with an indole ring and multiple alkyl side chains.
- Chemical Formula: C₂₂H₂₄N₂O
Advertisements
Mode of Action
- Sympathetic Inhibition: Depletes catecholamines (norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin) from sympathetic nerve endings by irreversibly binding to VMAT (vesicular monoamine transporter).
- Vasodilation: Reduces sympathetic tone, leading to decreased peripheral vascular resistance and lowered blood pressure.
- Sedative Effects: Decreases central nervous system activity by reducing monoamine levels.
Advertisements
Uses
- Hypertension: Historically used as an antihypertensive agent by reducing sympathetic outflow.
- Psychiatric Disorders: Employed in the past for schizophrenia and mania due to its monoamine-depleting effects.
- Migraine Prophylaxis: Occasionally used to prevent migraine attacks.
- Drug Addiction: Investigated for potential use in managing addiction by reducing craving.
Side Effects of Reserpine
- Depression: Due to depletion of serotonin and norepinephrine.
- Sedation: Excessive drowsiness and fatigue.
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Orthostatic Hypotension: Dizziness upon standing due to vasodilation.
Advertisements