- RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is a single-stranded nucleic acid made up of ribonucleotides, which consist of a ribose sugar, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), or guanine (G).
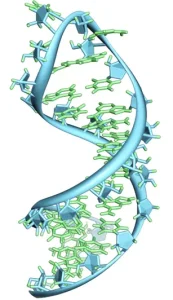
Structure:
1. Single-Stranded of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid):
- RNA is typically single-stranded, but it can form secondary structures by folding upon itself.
- Backbone: Each strand consists of a sugar-phosphate backbone, with the sugar being ribose.
- Bases: RNA contains adenine (A), uracil (U), cytosine (C), and guanine (G), with A pairing with U in complementary base pairing.
- Secondary Structures: RNA can form hairpins, loops, and other complex structures through intramolecular base pairing.
2. Types of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid):
- mRNA (Messenger RNA): Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- tRNA (Transfer RNA): Transfers specific amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis.
- rRNA (Ribosomal RNA): Structural and functional component of ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
- Other RNAs: Includes small nuclear RNA (snRNA), microRNA (miRNA), and others involved in regulation and processing.
Functions of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid):
-
Messenger RNA (mRNA):
- Transcription: mRNA is synthesized from a DNA template during transcription.
- Translation: mRNA is translated into a protein sequence by ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
-
Transfer RNA (tRNA):
- Amino Acid Transport: tRNA molecules transport amino acids to the ribosome.
- Codon-Anticodon Interaction: Each tRNA has an anticodon that pairs with a complementary codon on the mRNA, ensuring the correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain.
-
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA):
- Ribosome Structure: rRNA molecules combine with proteins to form ribosomes.
- Catalysis: rRNA catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids during protein synthesis.
-
Regulatory RNAs:
- miRNA and siRNA: These small RNAs regulate gene expression by degrading mRNA or inhibiting translation.
- snRNA: Involved in splicing pre-mRNA to remove introns and join exons.
Difference between DNA and RNA
| Feature | DNA | RNA |
| Strand Structure | Double-stranded | Single-stranded (usually) |
| Sugar | Deoxyribose | Ribose |
| Bases | Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) | Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) |
| Base Pairing | A-T, C-G | A-U, C-G |
| Functions | Genetic information storage, replication, gene expression regulation | Protein synthesis (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA), gene regulation (miRNA, snRNA) |
| Stability | More stable | Less stable |
| Location | Nucleus (in eukaryotes), mitochondria | Nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes |
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos

