- Definition: Rate depends on either:
-
- Square of one reactant: $\text{Rate} = k[A]^2$
- Product of two reactants: $\text{Rate} = k[A][B]$
- Integrated form (when A = B):
$\tfrac{1}{[A]_t} = \tfrac{1}{[A]_0} + kt$
Derivation:
Separate variables:
$\frac{d[A]}{[A]^2} = -k \, dt$
Advertisements
Integrate both sides:
$\int_{[A]_0}^{[A]} \frac{d[A]}{[A]^2} = -k \int_{0}^{t} dt$
$\left[ -\frac{1}{[A]} \right]_{[A]_0}^{[A]} = -kt$
$- \frac{1}{[A]} + \frac{1}{[A]_0} = -kt$
$\frac{1}{[A]} = \frac{1}{[A]_0} + kt$
- Graph: $\text{Plot of }\frac{1}{[A]}$ vs. time = straight line with slope = k
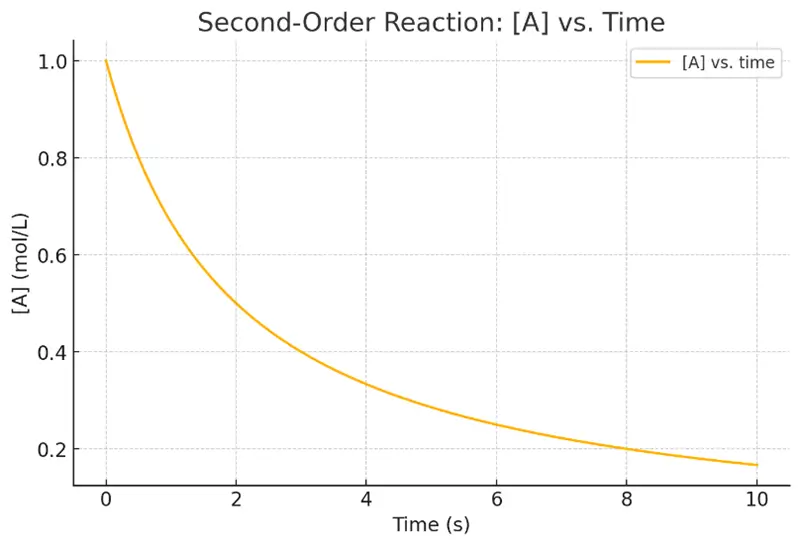
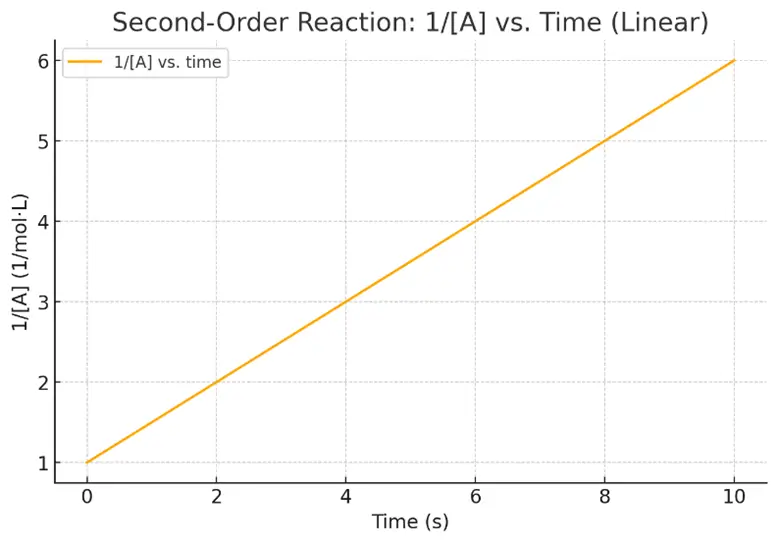
Features:
- Half-life depends on initial concentration:
$t_{1/2} = \frac{1}{k[A]_0}$
- Common in bimolecular reactions