Sotalol is a class III anti-arrhythmic and beta-blocker that treats atrial and ventricular arrhythmias by prolonging repolarization.
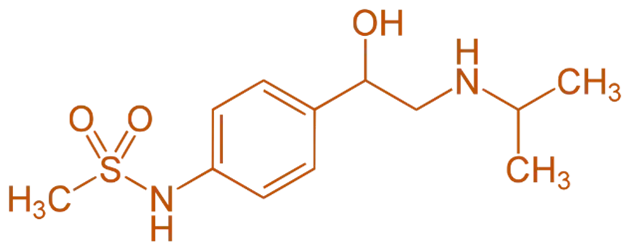
Structure of Sotalol
- Sotalol is a class III antiarrhythmic agent with both beta-blocking (class II) and potassium channel-blocking (class III) properties. It features a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist core linked to a benzothiazole moiety.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₄H₁₆N₂O₃S
Mode of Action
- Class III Antiarrhythmic: Blocks potassium channels, prolonging repolarization, action potential duration, and refractory period.
- Class II Antiarrhythmic: Non-selectively blocks beta-adrenergic receptors, reducing heart rate and myocardial contractility.
- Effect on Heart Rate: Slows heart rate and reduces oxygen demand by the heart.
Advertisements
Uses
- Ventricular Arrhythmias: Treats ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation.
- Atrial Arrhythmias: Manages atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter by maintaining sinus rhythm.
- Post-Myocardial Infarction: Prevents ventricular arrhythmias after myocardial infarction.
- Reentrant Arrhythmias Prevention: Effective in preventing recurrence of various reentrant arrhythmias.
- Long QT Syndrome: Used in specific arrhythmic syndromes involving prolonged QT intervals.
Side Effects of Sotalol
- Proarrhythmic Effects: Risk of torsades de pointes due to QT interval prolongation.
- Bradycardia: Excessive slowing of heart rate, especially in patients with existing conduction system disease.
- Fatigue and Dizziness: Due to beta-blockade effects.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia can increase proarrhythmic risks.
- Bronchospasm: Non-selective beta-blockade can exacerbate asthma or COPD.