Source of Herbs includes wild collection, cultivation, and commercial farming to obtain medicinal plants for therapeutic products.
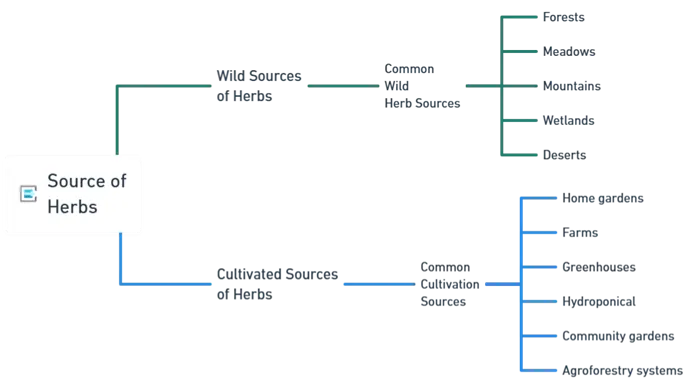
Wild Sources of Herbs
- Wild herbs grow naturally in the environment and are harvested for medicinal or culinary use.
Common Wild Herb Sources:
- Forests – Ginseng, goldenseal, elderberry
- Meadows – Chamomile, yarrow
- Mountains – Ginkgo, ginseng, echinacea
- Wetlands – Cattails, marshmallow, willow
- Deserts – Sage, juniper, chaparral
Advantages:
- Rich Biodiversity – Provides diverse plant species beneficial for health.
- Potency & Freshness – Harvested directly from nature.
- Cost-Effective – Often free or low-cost.
- Traditional Knowledge – Used for centuries in traditional medicine.
- Cultural Significance – Deeply tied to local traditions.
Disadvantages:
- Overharvesting – Can lead to species depletion.
- Habitat Destruction – Unregulated collection harms ecosystems.
- Quality Control Issues – Exposure to contaminants.
- Misidentification Risks – Can lead to toxic plant consumption.
- Legal Restrictions – Some areas regulate wild plant harvesting.
Cultivated Sources of Herbs
- Cultivated herbs are intentionally grown for use in medicine, cooking, and industry.
Common Cultivation Sources:
- Home gardens – Ensures freshness and quality.
- Farms – Commercial-scale herb production.
- Greenhouses – Controlled environment for year-round growth.
- Hydroponics – Grows herbs without soil.
- Community gardens – Shared spaces for herb cultivation.
- Agroforestry systems – Integrated farming for sustainability.
Advantages:
- Consistency & Quality – Controlled environment ensures purity.
- Year-Round Availability – Unlike seasonal wild herbs.
- Lower Contamination Risk – Grown in regulated conditions.
- Higher Yield – Meets increasing demand.
- Economic Benefits – Supports job creation and local economies.
Disadvantages:
- Reduced Genetic Diversity – Over-reliance on single varieties.
- Synthetic Inputs – Pesticides and fertilizers may be used.
- Soil Degradation – Intensive farming depletes nutrients.
- High Water Demand – Problematic in water-scarce areas.
- Competition with Native Plants – Can disrupt local ecosystems.