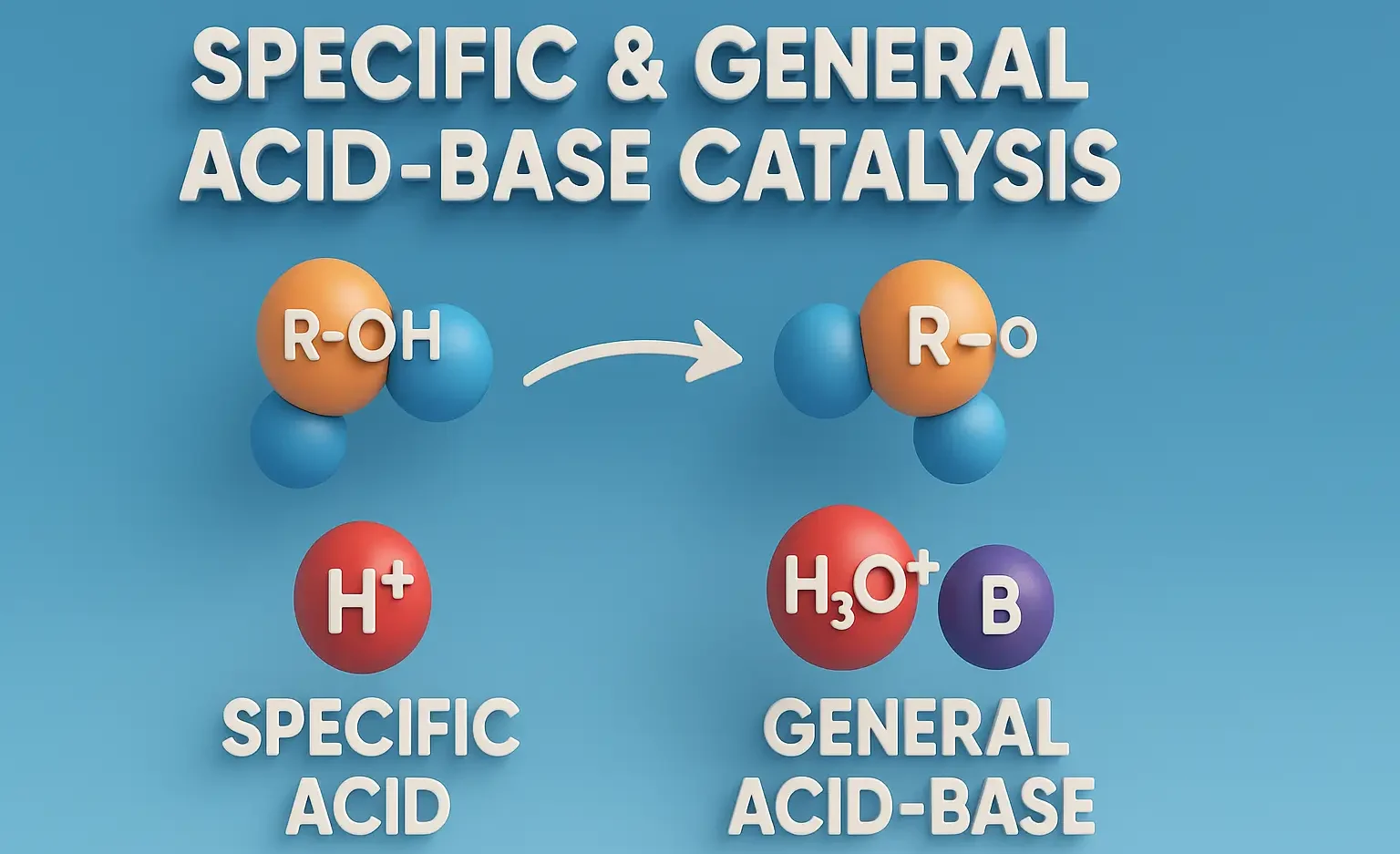
Specific Acid/Base Catalysis:
- Catalysis by hydronium (H₃O⁺) or hydroxide (OH⁻) only.
- Rate is pH-dependent.
Rate law:
\(\text{Rate} = k_H [H_3O^+] + k_{OH} [OH^-]\)
General Acid/Base Catalysis:
- Catalysis by any proton donor (acid) or proton acceptor (base), e.g., acetate, phosphate, ammonia.
- Buffers can contribute to catalysis.
Rate law (general form):
$\text{Rate} = k + k_{AH}[AH] + k_{A^-}[A^-]$
Advertisements
- Where:
- AH: general acid
- A−: conjugate base