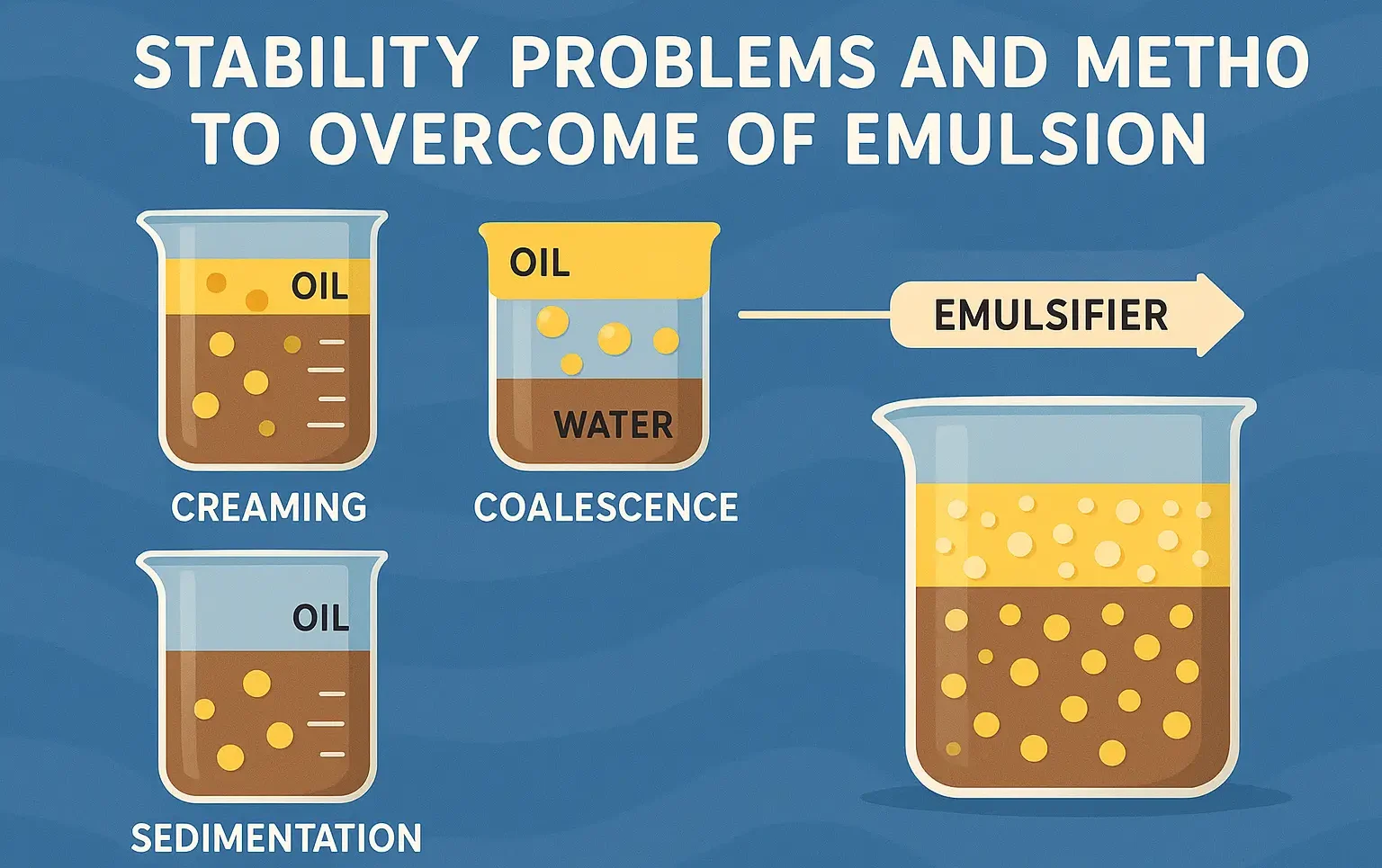
- Emulsions can encounter several stability issues due to the immiscible nature of their components.
- Common problems include creaming, flocculation, coalescence, and phase separation.
- Below, we discuss these issues and provide methods to overcome them.

1. Creaming
Definition:
- Creaming occurs when the dispersed droplets in an emulsion migrate toward the top or bottom of the system due to differences in density between the phases, leading to a concentrated layer.
- Creaming does not necessarily indicate emulsion breakdown but can lead to coalescence and phase separation if left unchecked.
Methods to Overcome Creaming:
-
Reduce droplet size:
- Smaller droplets have lower settling velocities, which reduces the rate of creaming.
- Homogenization or high-shear processes can be used to create smaller droplets.
-
Increase emulsion viscosity:
- A higher viscosity in the continuous phase slows down droplet movement.
- Thickening agents like gums, polymers, or colloidal particles can be added to increase viscosity.
2. Flocculation
Definition:
- Flocculation refers to the aggregation of droplets within the emulsion, leading to the formation of larger clusters.
- While flocculation alone may not break an emulsion, it often leads to creaming, coalescence, and eventually phase separation.
Methods to Overcome Flocculation:
-
Optimize emulsifier concentration:
- Using the appropriate concentration of emulsifying agent helps prevent droplet aggregation and stabilizes the emulsion.
-
Employ electrostatic stabilization:
- Charged emulsifiers or stabilizers can induce electrostatic repulsion between droplets, preventing flocculation.
3. Coalescence
Definition:
- Coalescence is the merging of dispersed droplets into larger droplets, which ultimately leads to the breakdown of the emulsion.
- It typically occurs due to droplet collisions, insufficient emulsifying agents, or the breakdown of the protective film around droplets.
Methods to Overcome Coalescence:
-
Use adequate emulsifiers:
- Ensure sufficient quantities of an appropriate emulsifying agent to cover the surface area of all droplets effectively.
-
Increase emulsion viscosity:
- A higher viscosity in the continuous phase reduces droplet collisions and helps prevent coalescence.
4. Phase Separation
Definition:
- Phase separation is the complete breakdown of the emulsion, where the oil and water phases separate into distinct layers.
- It is often a result of unresolved issues like creaming, flocculation, or coalescence.
Methods to Overcome Phase Separation:
-
Use multiple emulsifiers:
- A combination of emulsifiers with varying properties can create a more robust and stable emulsion.
-
Optimize formulation:
- Adjust the oil-to-water ratio, emulsifier concentration, and other formulation parameters to enhance emulsion stability.