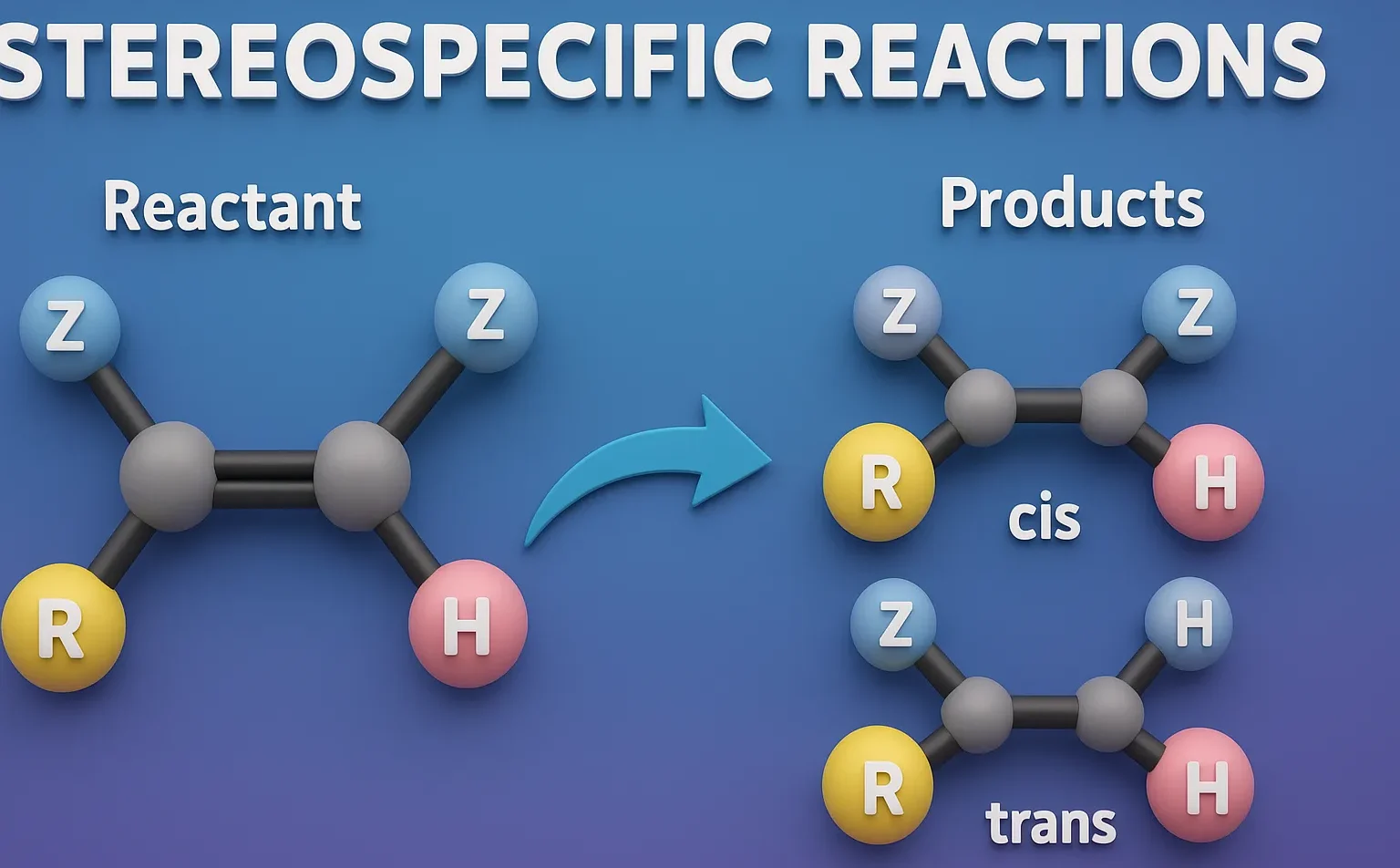
Stereospecific Reactions are chemical reactions where a specific stereoisomer of the reactant always leads to a specific stereoisomer of the product.
Definition of Stereospecific Reactions:
- A stereospecific reaction is one where the stereochemistry of the reactant completely determines the stereochemistry of the product.
- Each stereoisomeric reactant leads to a different stereoisomeric product.
- The reaction mechanism is such that it requires specific spatial arrangements of atoms.
Advertisements
Key Characteristics:
- The reaction is not just selective, it is deterministic: different stereoisomers of the reactant give distinct products.
- Only one product is formed from a given stereoisomer of the starting material.
Example:
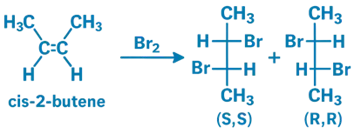
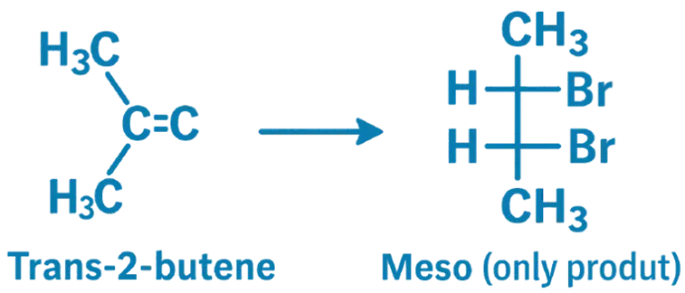
Bromination of 2-Butene
- When 2-butene is treated with Br₂, the reaction proceeds via an anti-addition mechanism, and the stereochemistry of the alkene determines the stereochemistry of the dibromide product.
- Reactions:
- Cis-2-butene + Br₂ → Produces a racemic mixture of enantiomers:
- (S,S)-2,3-dibromobutane
- (R,R)-2,3-dibromobutane

- Trans-2-butene + Br₂ → Produces only the meso form:
- meso-2,3-dibromobutane

- Cis-2-butene + Br₂ → Produces a racemic mixture of enantiomers:
Advertisements