Definition of Suppositories
- Suppositories are solid dosage forms intended for insertion into body cavities, such as the rectum, vagina, or urethra, where they melt, soften, or dissolve to release the active pharmaceutical ingredient(s).
- They are typically made from a base material that is either lipophilic (fat-soluble) or hydrophilic (water-soluble).
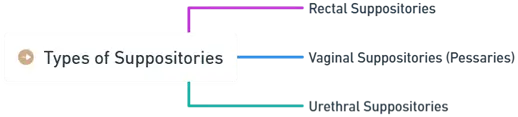
Types of suppositories:
-
Rectal suppositories:
- These are the most common type of suppositories and are intended for insertion into the rectum.
- They are usually cone- or torpedo-shaped and are used for local or systemic drug delivery.
-
Vaginal suppositories (pessaries):
- These suppositories are inserted into the vagina and used to treat local infections or to deliver hormones for contraceptive purposes.
- They are usually oval or globular in shape.
-
Urethral suppositories:
- These are less common and are intended for insertion into the male or female urethra.
- They are typically used for local anaesthesia or the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
Advantages of suppositories:
-
Bypass first-pass metabolism:
- Drugs administered via suppositorie can avoid first-pass metabolism in the liver, which may improve bioavailability for certain drugs.
-
Alternative route for patients with difficulty swallowing:
- Suppositorie are useful for patients who have difficulty swallowing oral medications, such as young children, the elderly, or those with swallowing disorders.
-
Suitable for unconscious or nauseous patients:
- Suppositorie can be administered to patients who are unconscious or experiencing nausea and vomiting, making them a practical alternative to oral medications.
-
Local treatment:
- Suppositorie can deliver drugs directly to the site of action for local treatment, such as treating haemorrhoids or vaginal infections.
Disadvantages of suppositorie:
-
Patient acceptability:
- Some patients may be reluctant to use suppositorie due to the invasive nature of the administration route or cultural factors.
-
Limited drug absorption:
- The absorption of certain drugs may be limited or erratic in the rectal or vaginal mucosa, which can affect their efficacy.
-
Melting and leakage:
- Suppositorie can melt or leak at body temperature, causing discomfort and messiness.
-
Incompatibility with certain drugs:
- Some drugs may be incompatible with suppository bases or may have poor stability at the melting point of the base.

