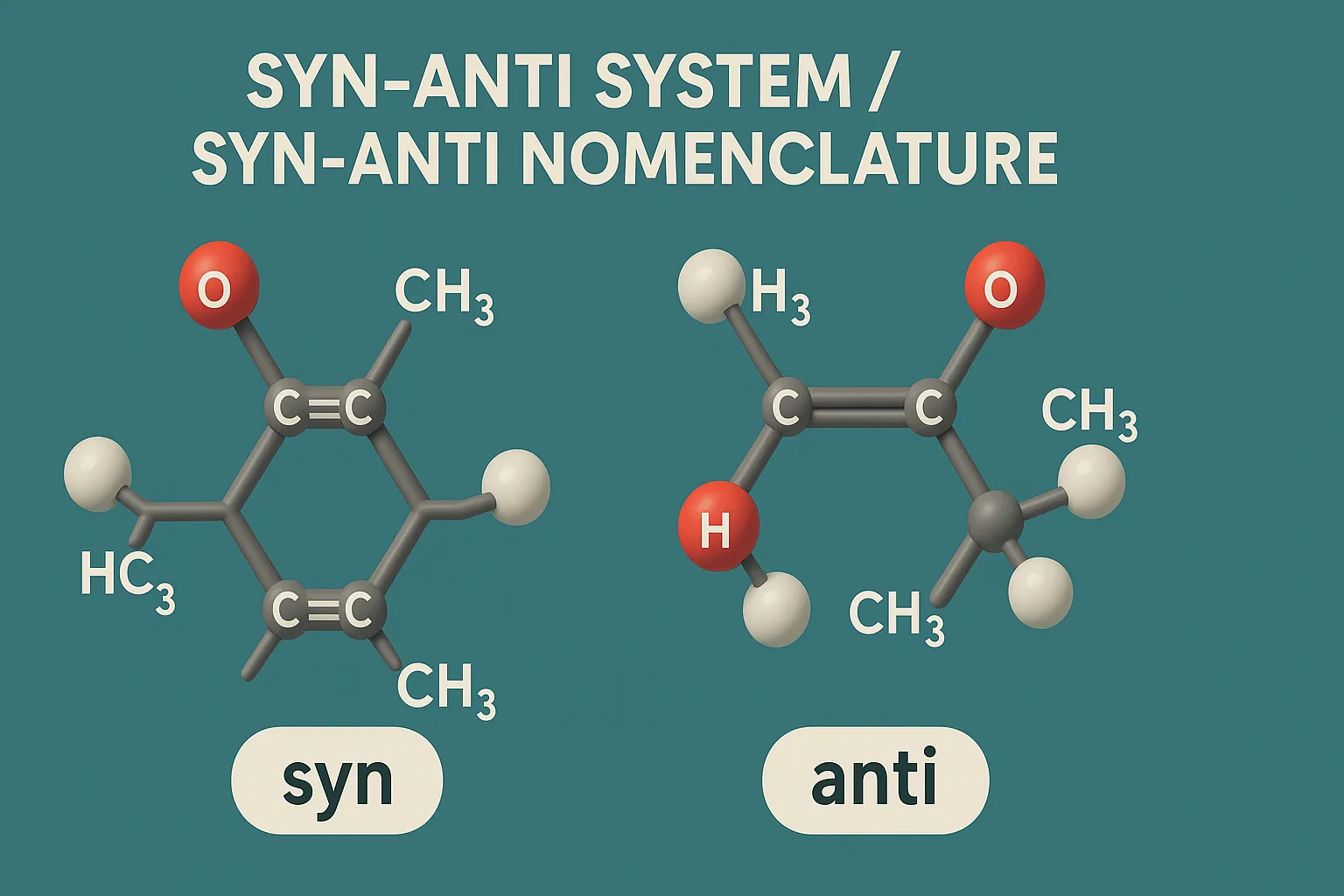
Syn-Anti System (Syn-Anti Nomenclature) describes stereoisomers by the relative positions of substituents on adjacent atoms or double bonds.
Applicability:
- This system is less commonly used for simple alkenes and more common in:
- Cyclic compounds
- Organic reaction mechanisms (especially eliminations and additions)
- Carbohydrate and organometallic chemistry
Rules and Definitions of Syn-Anti System
-
Syn:
- Two groups (atoms or substituents) are on the same face (or side) of a double bond or ring system.
-
Anti:
- Two groups are on opposite faces (or sides).
This system is based on spatial orientation, often discussed in 3D molecular structures and conformations.
Usage in Reaction Mechanisms
The Syn–Anti terminology is especially valuable when describing stereochemical outcomes in:
-
Syn Addition:
- Two atoms/groups add to the same side of a double bond.
- Example: Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes.
-
Anti Elimination:
- Two atoms/groups are eliminated from opposite sides of a molecule.
- Example: E2 elimination mechanism.
Examples of Syn-Anti System:
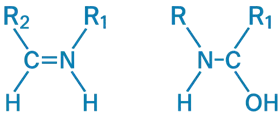
- R1 and R2 on the same side → Syn
- R1 and R2 on opposite sides → Anti
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos