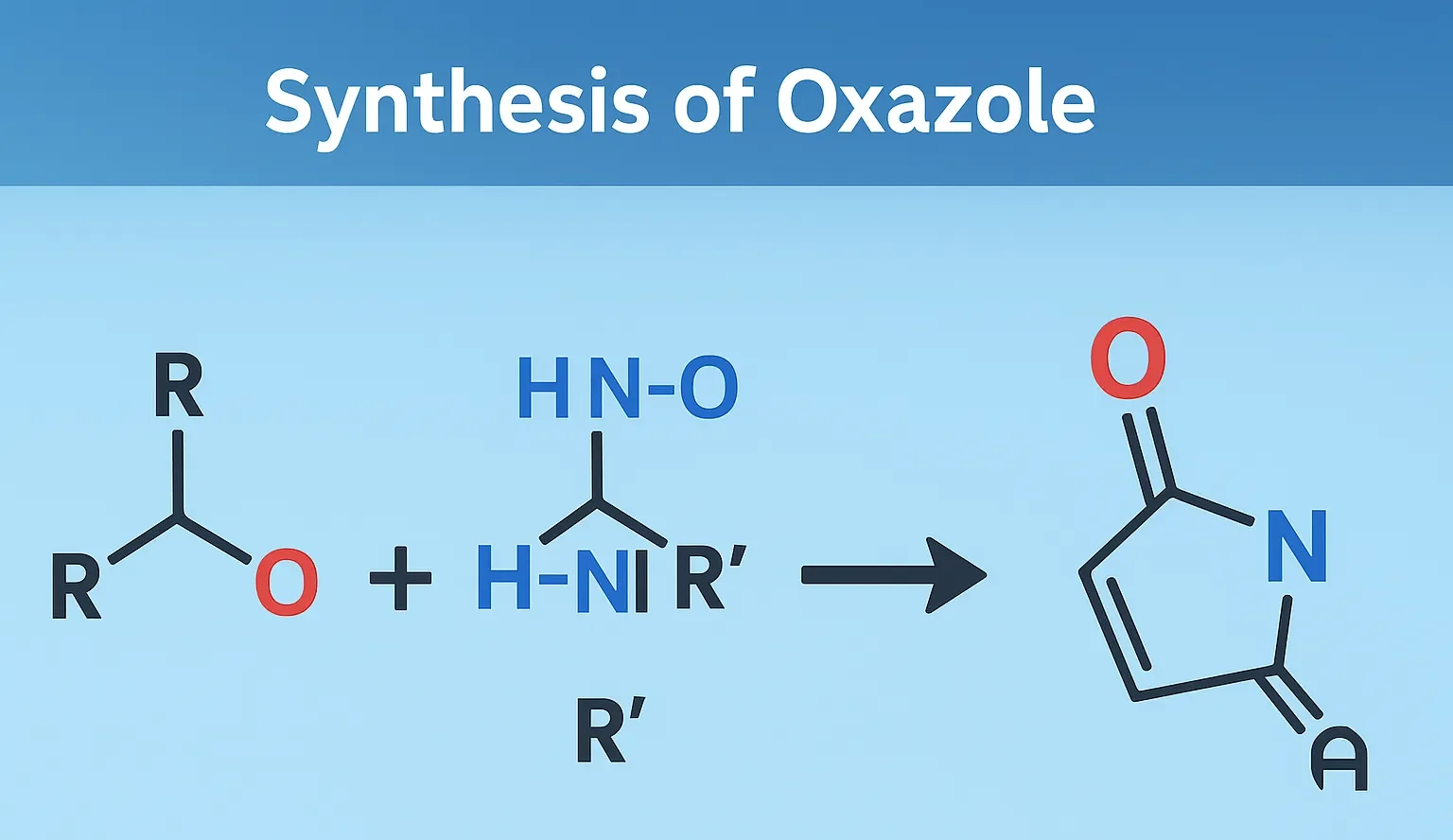
Synthesis of Oxazole involves methods like Robinson-Gabriel synthesis, Fischer oxazole synthesis, and cyclization of α-acylaminoketones.
-
Robinson–Gabriel Synthesis (Classical method)
-
- Reactants: α-acylaminoketones
- Reagents: Acidic dehydrating agents (e.g., P₂O₅, POCl₃)
- Reaction:
- R–CO–CH₂–NH–CO–R’ → Oxazole (via cyclodehydration)
- Mechanism:
- Intramolecular cyclization
- Dehydration
- Aromatization
-
-
Bredereck Synthesis
-
- Reactants: α-haloketone + formamide
- Reaction:
- CH₃COCH₂Cl + HCONH₂ → 2-methyl-oxazole
- Good for substituted oxazoles
-
-
From 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds + Hydroxylamine
- Produces isoxazole as well, depending on structure
- Useful in some functionalized derivatives
-
Cyclization of Acetylenic Ketones and Amides
- Involves oxidative or Lewis acid-assisted cyclization