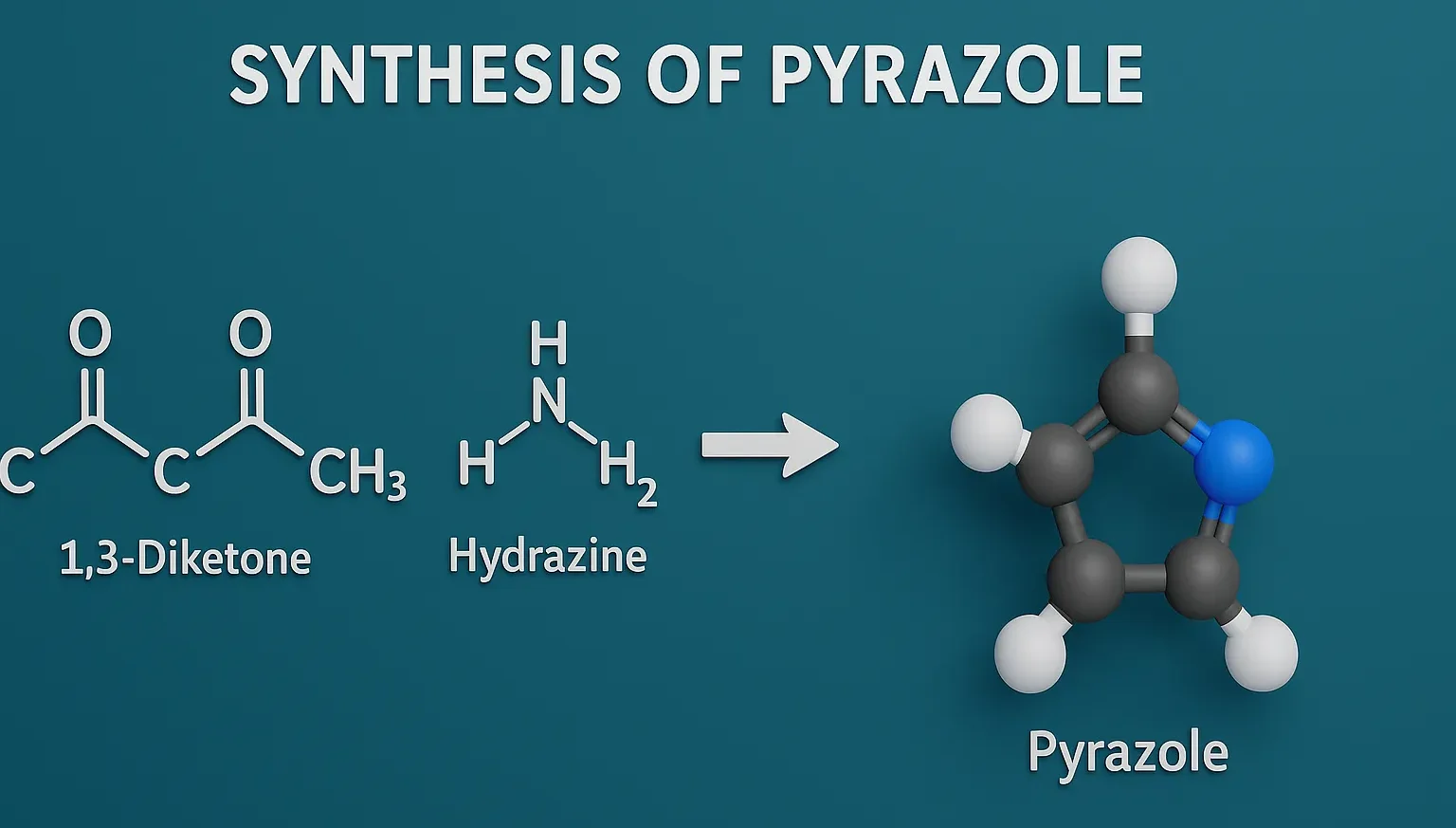
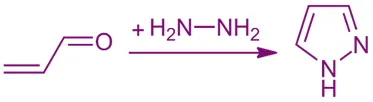Synthesis of Pyrazole involves methods like Knorr synthesis using 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds and hydrazines.
-
Condensation of 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds with Hydrazine (most common method)
-
Reactants:
- 1,3-diketones (e.g., acetylacetone)
- Hydrazine (NH₂NH₂) or substituted hydrazines
-
Reaction:
- CH₃COCH₂COCH₃ + NH₂NH₂ → 3,5-Dimethylpyrazole + H₂O

-
Mechanism:
- Formation of hydrazone at one carbonyl
- Intramolecular cyclization
- Elimination of water → Pyrazole ring
-
Advantages:
- Simple, high-yielding, allows substitution at 3 and 5 positions
-
-
Knorr Pyrazole Synthesis
- Reactants: α-hydrazino ketones + β-ketoesters
- Use: For substituted pyrazoles with varying groups at C-3 and C-5
-
From α,β-unsaturated ketones and hydrazines
- Hydrazine adds to the double bond and then cyclizes.