Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone that regulates muscle mass, libido, and male reproductive functions.
Structure of Testosterone
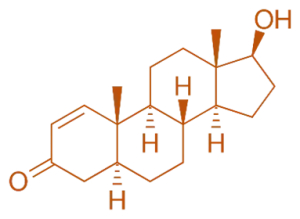
- Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and an anabolic steroid. It features a four-ring cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene structure with hydroxyl and ketone functional groups.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₈H₂₈O₂
Mode of Action
- Androgen Receptor Activation: Testosterone binds to androgen receptors in various tissues, initiating gene transcription that promotes the development and maintenance of male characteristics.
- Anabolic Effects: Stimulates protein synthesis, muscle mass increase, and bone density.
- Sexual Development: Essential for the development of male reproductive tissues, secondary sexual characteristics, and libido.
- Erythropoiesis: Enhances red blood cell production in the bone marrow.
Advertisements
Uses
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): Treats conditions like hypogonadism and delayed puberty in males.
- Anabolic Steroid Therapy: Used (often illicitly) to enhance muscle mass and athletic performance.
- Gender-Affirming Therapy: Assists in masculinizing effects for transgender men.
- Breast Cancer Treatment: Sometimes used in hormone-sensitive breast cancers to inhibit estrogen effects.