- The nervous system introduction is a complex network of nerves, neurons, and supporting cells that coordinate and transmit information throughout the body.
- It is responsible for sensing and responding to various internal and external stimuli, enabling organisms to interact with their environment and maintain homeostasis.
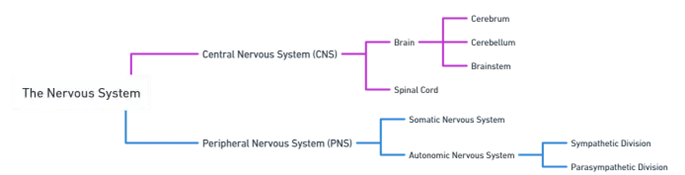
- The nervous system can be divided into two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
1. Central Nervous System (CNS)
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord.
- It acts as the body’s control center and is responsible for processing, integrating, and coordinating sensory information, motor commands, and higher cognitive functions.
Brain:
- The brain is the primary organ of the CNS and is responsible for higher cognitive functions, such as perception, reasoning, decision-making, learning, and memory.
- It has several distinct regions, including the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem, each with specific functions.
Advertisements
Spinal Cord:
- The spinal cord is a long, tubular structure that extends from the brainstem and runs down the vertebral column.
- It serves as a communication pathway between the brain and the PNS, transmitting sensory information to the brain and motor commands from the brain to the body.
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The PNS includes all the nerves and ganglia (clusters of nerve cell bodies) outside the CNS.
- It connects the CNS to the rest of the body, transmitting sensory information from the body to the CNS and motor commands from the CNS to the muscles, glands, and organs.
- The PNS can be further divided into two main subsystems:
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)