- Thiamylal Sodium enhances GABA action in the CNS, producing rapid sedative and hypnotic effects.
- It is a barbiturate used for induction of anesthesia and short surgical procedures.
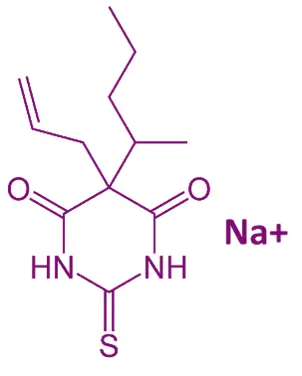
Chemical Formula:
- C₁₁H₁₇N₂NaO₂S
Mechanism of Thiamylal Sodium:
- Potentiates GABA-A receptor
- Highly lipophilic → rapid onset of CNS depression
Advertisements
Uses of Thiamylal Sodium:
- Anesthesia induction
- Brief surgical anesthesia
Side Effects:
- Respiratory depression
- Hypotension
- Reflex tachycardia
- Laryngospasm (esp. in children)