Thioguanine is an anti-neoplastic antimetabolite used in acute leukemia treatment by inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis in cancer cells.
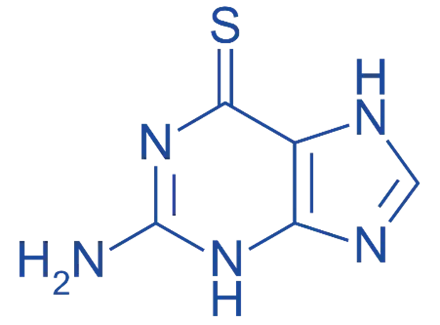
Structure of Thioguanine
- It is also known as 6-thioguanine (6-TG), is a purine analog with the following structural features:
- Purine Base: Similar to guanine.
- Thio Group: Contains a sulfur atom replacing the oxygen at position 6.
- Amino Group: Contains an amino group at position 2.
- Chemical Formula: C₅H₄N₄OS
Mode of Action
- Thioguanine acts as an antimetabolite by:
- Incorporation into DNA and RNA: Disrupts nucleic acid synthesis and function.
- Inhibition of Purine Synthesis Enzymes: Blocks enzymes involved in purine nucleotide synthesis.
- Induction of Apoptosis: Causes cytotoxicity in rapidly dividing cells, particularly in leukemic cells.
Advertisements
Uses
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Often used in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): As part of certain treatment regimens.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (off-label).
- Autoimmune Disorders: Including rheumatoid arthritis (off-label).

