Definition of Thixotropy (Time-Dependent Shear-Thinning):
- Thixotropy (Time-Dependent Shear-Thinning) is a time-dependent shear-thinning behavior.
- When a material is subjected to constant shear, its viscosity decreases over time.
- When the shear is removed, the material slowly regains its original viscosity.
Key Features:
- Viscosity decreases with sustained shear.
- Recovery is reversible but time-dependent.
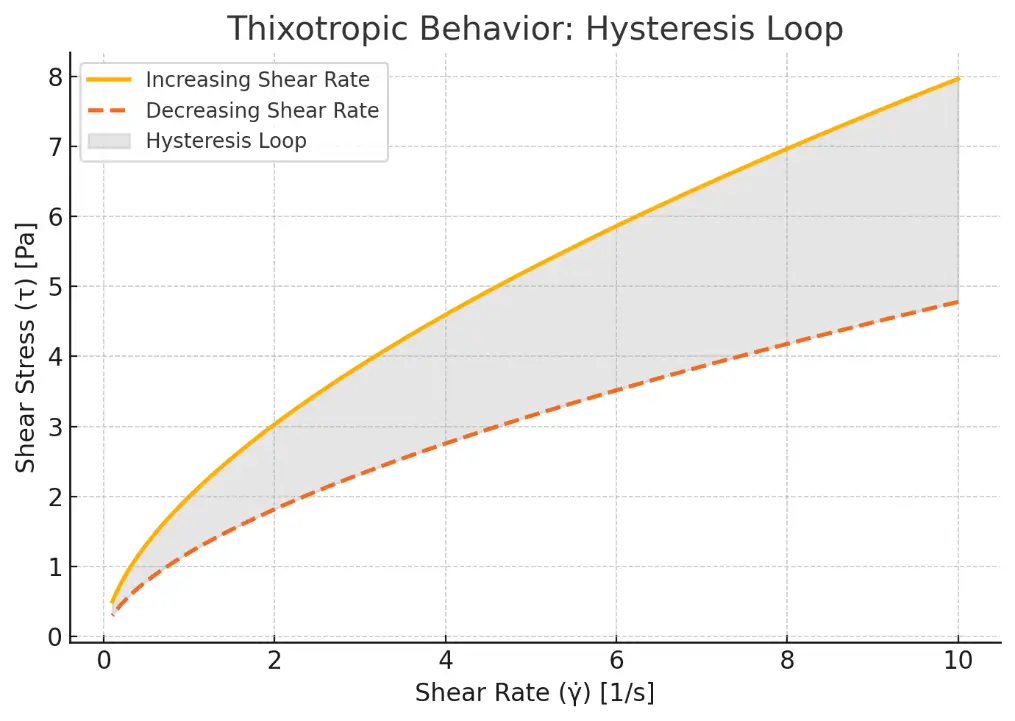
- Exhibits a hysteresis loop in shear stress vs. shear rate plots (up and down curves don’t match).
Advertisements
Mechanism:
- Thixotropy is primarily due to the breakdown of internal structures (such as interparticle networks) when shear is applied.
- Continuous shear causes the material’s microstructure to disassemble, reducing resistance to flow.
- When shear stops, the microstructure reassembles, causing viscosity to increase over time.
Rheogram:
- Shows a hysteresis loop between the upward and downward curves of a shear stress vs. shear rate plot.
- The area of the loop indicates the degree of thixotropy.
Advertisements
Examples:
- Gels (e.g., carbopol gels)
- Creams
- Some injectable suspensions
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements