Timolol is a non-selective beta-blocker used to treat hypertension, angina, and glaucoma by reducing heart rate and intraocular pressure.
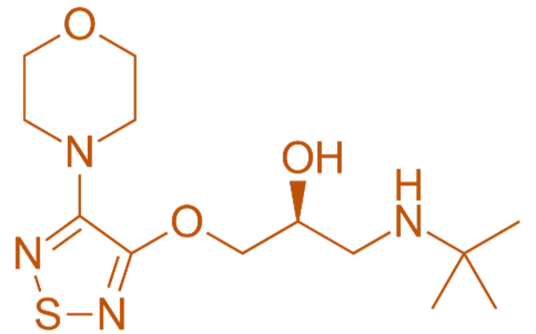
Structure of Timolol
- Timolol is a non-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker featuring a diphenylmethanol structure with a secondary amine.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₅H₂₂N₂O₃
Mode of Action
- Beta-Blockade: Inhibits both β₁ and β₂ adrenergic receptors.
- Cardiac Effects: Reduces heart rate, myocardial contractility, and cardiac output.
- Vascular Effects: Decreases renin release from the kidneys, leading to vasodilation and reduced blood pressure.
- Ocular Effects: Reduces intraocular pressure by decreasing aqueous humor production (used in glaucoma).
Uses
- Hypertension: Lowers blood pressure by decreasing cardiac output and renin release.
- Angina Pectoris: Reduces myocardial oxygen demand by lowering heart rate and contractility.
- Arrhythmias: Manages supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias by slowing AV node conduction.
- Glaucoma: Topically applied to reduce intraocular pressure.
- Migraine Prophylaxis: Prevents migraine attacks by stabilizing vascular tone.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos