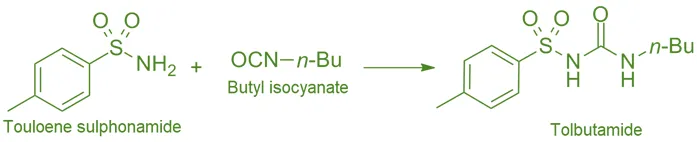Tolbutamide is a first-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic drug that lowers blood sugar by stimulating insulin release from the pancreas.
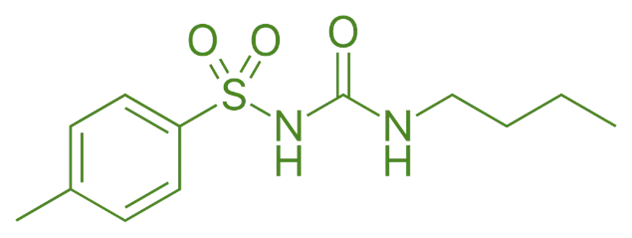
Structure of Tolbutamide
- Tolbutamide is a first-generation sulfonylurea with a benzene ring substituted with a sulfonylurea moiety and butyl side chains.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₆H₂₅N₃O₃S
Mode of Action
- ATP-Sensitive K⁺ Channel Blockade: Inhibits K⁺ channels on pancreatic beta cells, leading to cell membrane depolarization.
- Calcium Influx: Depolarization opens voltage-dependent calcium channels, increasing intracellular calcium.
- Insulin Secretion: Elevated calcium stimulates insulin granule exocytosis, enhancing insulin release.
Uses
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Improves glycemic control by increasing insulin secretion.
- Gestational Diabetes: Used cautiously under medical supervision to manage blood glucose levels.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Sulfonylurea Moiety: Essential for binding to the SUR1 (sulfonylurea receptor 1) subunit of the K⁺
- Alkyl Side Chains: Longer butyl chains enhance lipophilicity and binding affinity.
- Benzene Substitution: Substituents on the benzene ring can affect potency and duration of action.
Synthesis of Tolbutamide