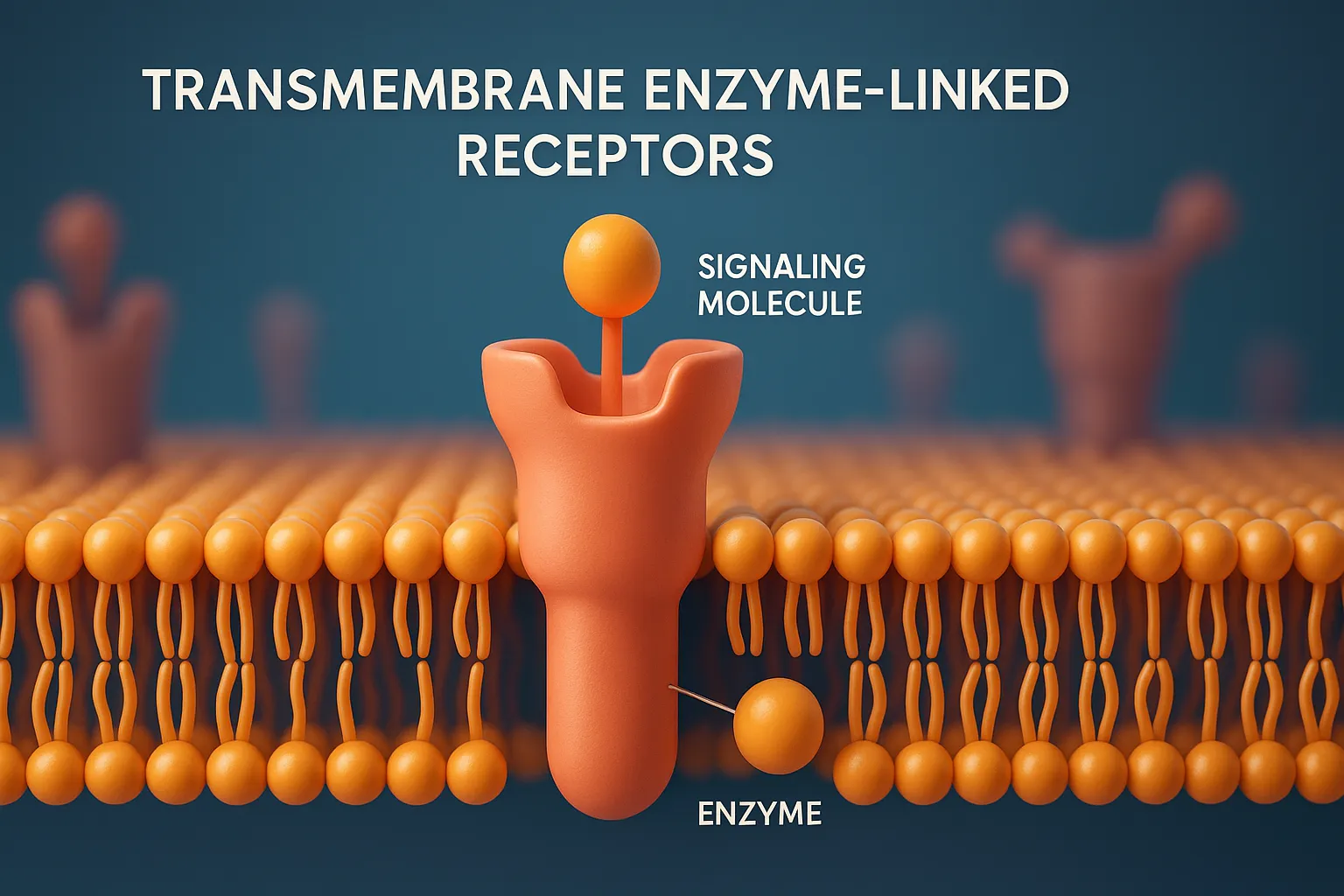
Transmembrane Enzyme-Linked Receptors are cell-surface receptors that activate intracellular enzymes upon ligand binding, regulating growth, metabolism, and cell signaling.
- These receptors have intrinsic enzymatic activity (often kinase activity).
- Most Common Type: Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs)
Structure of Transmembrane Enzyme-Linked Receptors:
- Single transmembrane domain
- Extracellular ligand-binding site
- Intracellular tyrosine kinase domain

Mechanism:
- Ligand binds to the receptor
- Receptors dimerize
- Autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues
- Recruitment and activation of intracellular signaling proteins
- Activation of signaling pathways such as:
- MAP kinase pathway
- PI3K-Akt pathway
Response Time:
- Minutes to hours
Examples:
- Insulin receptor
- Epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor
- Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor