- Typhoid fever is a systemic bacterial infection caused by Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (commonly called Salmonella typhi).
- It primarily affects the gastrointestinal system and can lead to severe complications if untreated.
Signs and Symptoms
-
Early Stage:
- Fever: Starts low and increases daily.
- Weakness: General feeling of malaise.
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort in the abdominal area.
- Headache: Persistent and severe.
- Diarrhea or Constipation: Alternating bowel habits.
- Dry Cough: Non-productive cough.
-
Later Stage:
- High Fever: Peaks at around 104°F (40°C).
- Rash (Rose Spots): Small red spots, usually on the abdomen and chest.
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Intense pain and tenderness.
- Swollen Abdomen: Due to inflamed intestines.
- Severe Fatigue: Profound weakness and lethargy.
- Confusion or Delirium: Mental disturbances, sometimes termed “typhoid state.”
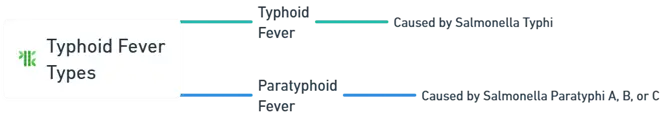
Types of Typhoid Fever
-
Typhoid Fever:
- Caused by Salmonella Typhi.
-
Paratyphoid Fever:
- Caused by Salmonella Para typhi A, B, or C, generally resulting in a milder illness.
Advertisements
Etiology
- Causative Agent: Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (S. Typhi).
- Transmission: Fecal-oral route via contaminated food or water, person-to-person contact.
Pathogenesis
- Entry: Bacteria are ingested, survive stomach acid, and reach the intestines.
- Invasion: They penetrate the intestinal mucosa and are phagocytosed by macrophages.
- Spread: Bacteria survive within macrophages, travel to lymphoid tissues, and disseminate via the bloodstream to various organs.
- Systemic Infection: Results in widespread inflammation and systemic symptoms.
Treatment
-
Antibiotics:
- Ciprofloxacin: Commonly used for adults.
- Ceftriaxone: Effective for severe cases or drug-resistant strains.
- Azithromycin: Used in cases of resistance to other antibiotics.
- Ampicillin/Chloramphenicol: Historically used, now less common due to resistance.
-
Supportive Care:
- Hydration: Oral rehydration solutions or intravenous fluids.
- Nutritional Support: Maintaining adequate nutrition during illness.
- Rest: Ensuring the patient gets enough rest.
Prevention:
- Vaccination: Typhoid vaccines (oral or injectable) are available and recommended for travelers to endemic areas.
- Safe Drinking Water: Ensuring access to clean and safe water.
- Sanitation: Proper disposal of sewage and maintaining clean living environments.
- Hygiene Practices: Regular hand washing and safe food handling practices.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements