- The urea cycle, also known as the ornithine cycle, is a crucial metabolic pathway in the liver that detoxifies ammonia, converting it into urea, which is then excreted by the kidneys.
- This cycle is vital for the removal of excess nitrogen generated during amino acid metabolism.
- Here’s a detailed explanation:
Steps of the Urea Cycle:
-
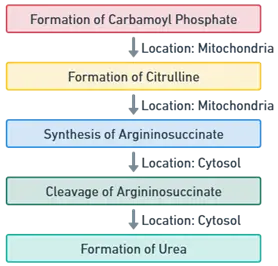
Formation of Carbamoyl Phosphate:
- Location: Mitochondria
- Enzyme: Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)
- Reaction: Ammonia (NH3) combines with bicarbonate (HCO3-) and two ATP molecules to form carbamoyl phosphate.
- Regulation: This is the rate-limiting step and is allosterically activated by N-acetylglutamate.
-
Formation of Citrulline:
- Location: Mitochondria
- Enzyme: Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC)
- Reaction: Carbamoyl phosphate donates its carbamoyl group to ornithine, producing citrulline.
- Transport: Citrulline is then transported from the mitochondria to the cytosol.
-
Synthesis of Argininosuccinate:
- Location: Cytosol
- Enzyme: Argininosuccinate synthetase (ASS)
- Reaction: Citrulline combines with aspartate (donated by the TCA cycle) in the presence of ATP to form argininosuccinate.
-
Cleavage of Argininosuccinate:
- Location: Cytosol
- Enzyme: Argininosuccinate lyase (ASL)
- Reaction: Argininosuccinate is cleaved into arginine and fumarate. Fumarate can enter the TCA cycle, linking the urea and TCA cycles.
-
Formation of Urea:
- Location: Cytosol
- Enzyme: Arginase
- Reaction: Arginine is hydrolyzed to produce urea and ornithine. Ornithine is transported back into the mitochondria to continue the cycle.
Summary of the Urea Cycle:
- NH3 + HCO3- + 2 ATP → Carbamoyl Phosphate (CPS I)
- Carbamoyl Phosphate + Ornithine → Citrulline (OTC)
- Citrulline + Aspartate + ATP → Argininosuccinate (ASS)
- Argininosuccinate → Arginine + Fumarate (ASL)
- Arginine → Urea + Ornithine (Arginase)
Importance of the Urea Cycle:
- Detoxification of Ammonia: Converts toxic ammonia to urea, which is less toxic and easily excreted.
- Nitrogen Balance: Maintains nitrogen homeostasis in the body.
- Interconnection with Other Metabolic Pathways: Links with the TCA cycle through fumarate and aspartate.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos