Urinary System
Definition of Urinary System
- The urinary system (renal system) removes waste, maintains electrolyte balance, regulates blood pressure, and produces hormones.
Anatomy
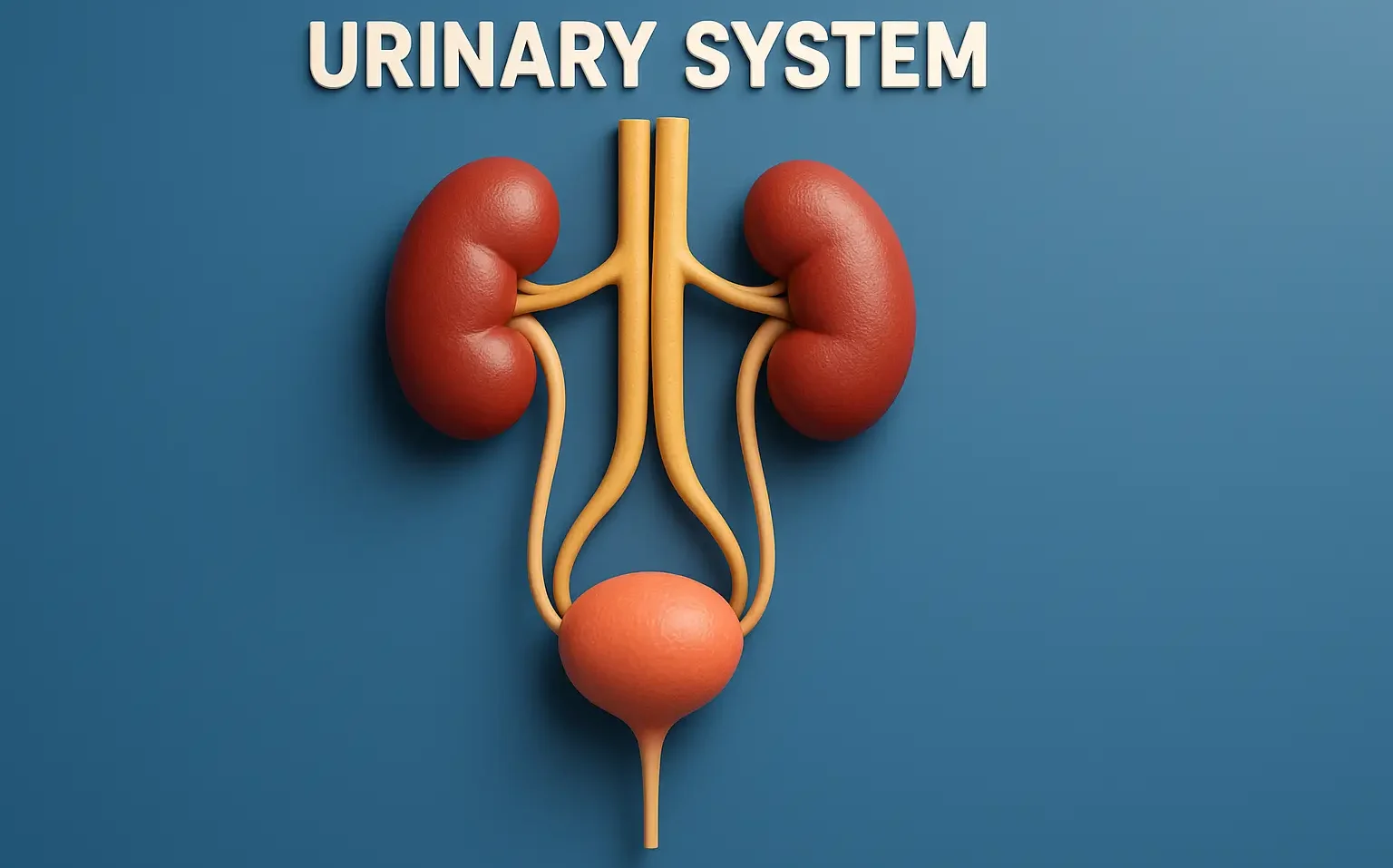
- Kidneys (2): Filter blood, regulate fluid, electrolytes, acid-base balance, and produce hormones (erythropoietin, renin).
- Ureters (2): Transport urine to the bladder via peristalsis.
- Bladder: Stores urine (300–500 mL capacity).
- Urethra: Excretes urine.
- Male (20 cm): Passes through prostate.
- Female (4 cm): Higher UTI risk.
Functions of Urinary System
- Filtration and Excretion: Removes waste (urea, creatinine).
- Balance: Regulates fluids, electrolytes, and pH.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
- Hormone Production:
- Erythropoietin: Stimulates RBC production.
- Vitamin D Activation: Enhances calcium absorption.
- Urine Formation:
- Filtration: Forms filtrate.
- Reabsorption: Recovers water, glucose, and electrolytes.
- Secretion: Eliminates waste.
Common Disorders
-
Kidney Disorders:
- CKD: Gradual loss of function.
- AKI: Sudden decline in function.
- Stones (Nephrolithiasis): Mineral deposits.
- Glomerulonephritis: Glomerular inflammation.
- PKD: Genetic cystic disorder.
-
Bladder Disorders:
- UTI: Bacterial infection.
- Interstitial Cystitis: Chronic inflammation.
- Bladder Cancer: Abnormal growth.
- Incontinence: Loss of control.
-
Urethral Disorders:
- Urethritis: Inflammation, often infection-related.
- Stricture: Narrowing causing urinary difficulty.
Symptoms
- Painful Urination (Dysuria).
- Blood in Urine (Hematuria).
- Frequent Urination (Polyuria/Nocturia).
- Reduced Output (Oliguria/Anuria).
- Proteinuria: Indicates kidney damage.
Diagnosis
- Urinalysis: Detects blood, protein, and infections.
- Blood Tests: BUN, creatinine, electrolytes assess function.
- Imaging: Ultrasound, CT, MRI identify stones or abnormalities.
- Special Tests:
- Cystoscopy: Bladder inspection.
- Biopsy: Kidney tissue analysis.
Treatment
-
Medications:
- Antibiotics:
- Diuretics: Fluid overload.
- Analgesics: Pain relief.
- Antihypertensives: BP control.
- Erythropoietin: Stimulates RBCs.
-
Procedures and Surgery:
- Dialysis: Blood filtration in kidney failure.
- Lithotripsy: Breaks kidney stones.
- Nephrectomy: Kidney removal (cancer).
- Transplant: For end-stage failure.
Prevention
- Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet.
- Avoid smoking and excess alcohol.
- Maintain BP and blood sugar control.
- Practice hygiene to prevent infections.
- Routine check-ups for early detection.
Prognosis
- Acute Disorders: Often reversible.
- Chronic Conditions: May need lifelong management, dialysis, or transplant.
- Early Detection: Improves outcomes and reduces complications.