Warfarin is an oral anticoagulant that prevents blood clots by inhibiting vitamin K–dependent clotting factor synthesis.
Structure of Warfarin
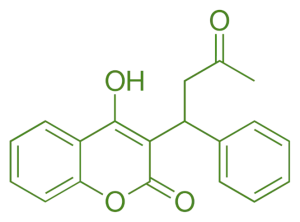
- Warfarin is a synthetic coumarin derivative with a 4-hydroxycoumarin core structure substituted with a 3-phenylpropyl side chain.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₉H₁₆O₄
Mode of Action
- Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Inhibition: Blocks the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase, preventing the regeneration of reduced vitamin K.
- Coagulation Factor Inhibition: Reduces the synthesis of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X.
- Anticoagulant Effect: Prolongs clotting times (INR) to prevent thrombosis and embolism.
Advertisements
Uses
- Prophylaxis and Treatment of Thromboembolic Disorders: Prevents deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and stroke.
- Atrial Fibrillation: Reduces the risk of stroke by preventing clot formation.
- Mechanical Heart Valves: Prevents thrombus formation on artificial valves.
- Myocardial Infarction: Lowers the risk of recurrent heart attacks by preventing clot formation.
Structure-Activity Relationship (SAR)
- Coumarin Core: Essential for binding to vitamin K epoxide reductase.
- 3-Phenylpropyl Side Chain: Enhances binding affinity and specificity for the target enzyme.
- Hydroxyl Group: Increases solubility and facilitates hydrogen bonding with the enzyme.
- Substituents: Modifications on the phenyl ring can affect potency, metabolism, and duration of action.
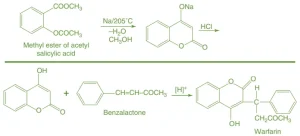
Synthesis of Warfarin