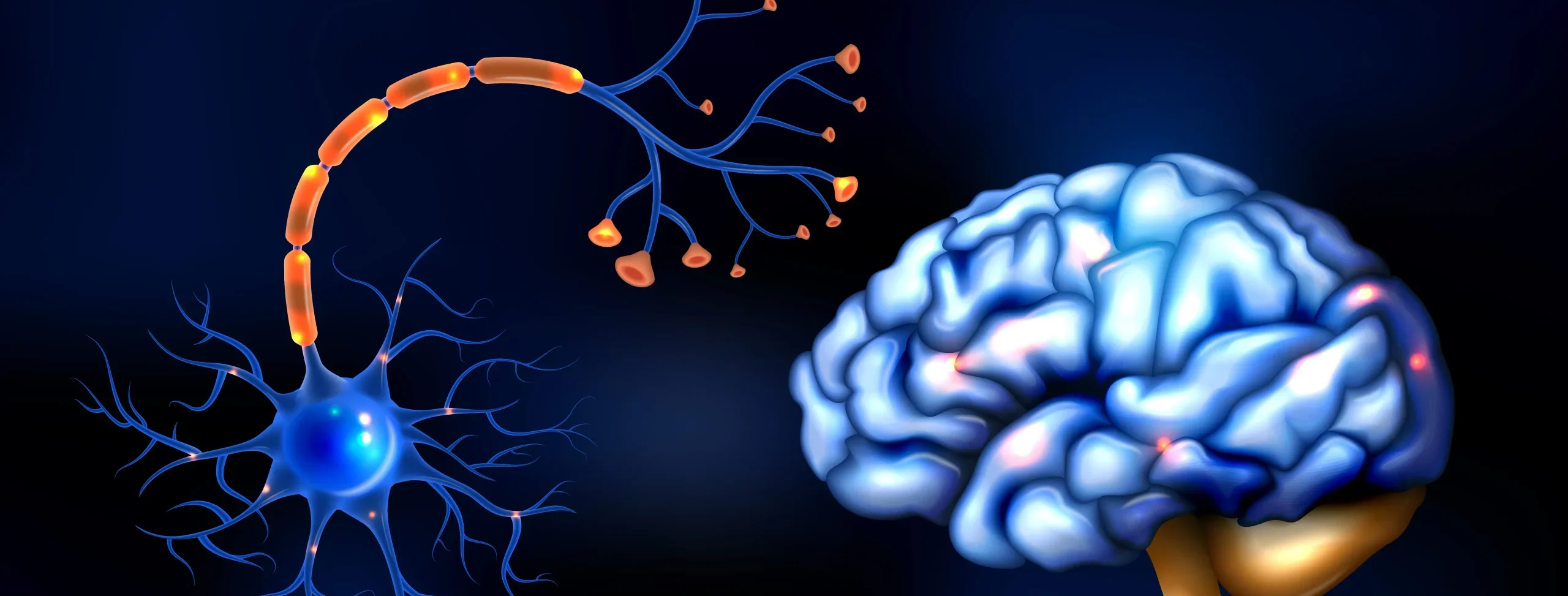
Classification Of Neuron
Classification of Neuron can be based on their structure, function, or the type of neurotransmitters they release. Here’s a brief overview of the Classification of Neuron: 1. Structural classification of Neuron: a. Unipolar neurons: These neurons have a single process extending from the cell body, which later branches into an axon and a dendrite. Unipolar … Read more