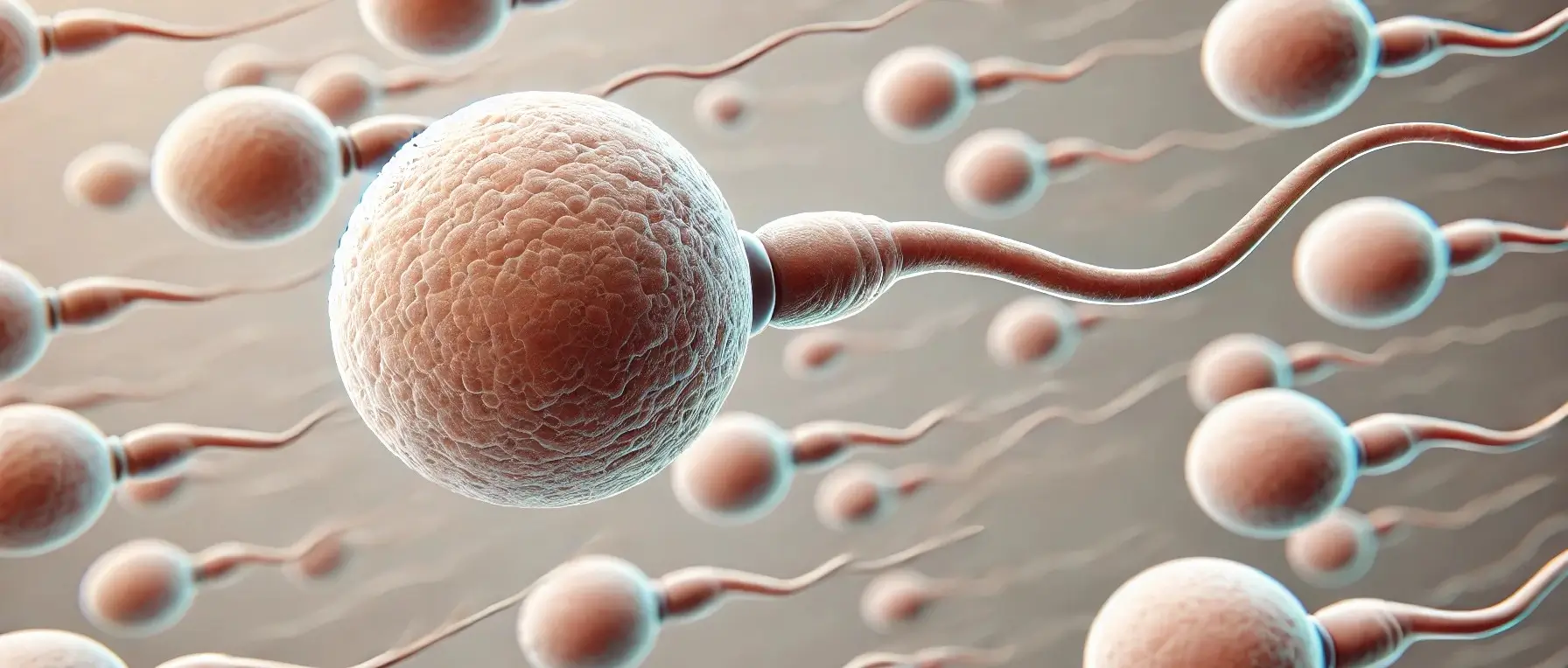
Sperm (Spermatozoa)
Sperm, or spermatozoa, are male reproductive cells that fertilize the female egg (ovum) to create an embryo, leading to the development of a fetus. Structure of Sperm (Spermatozoa) Sperm cells have a specialized structure consisting of three main parts: Head: Contains the nucleus with genetic material (DNA) passed to the offspring. Covered by the acrosome, … Read more