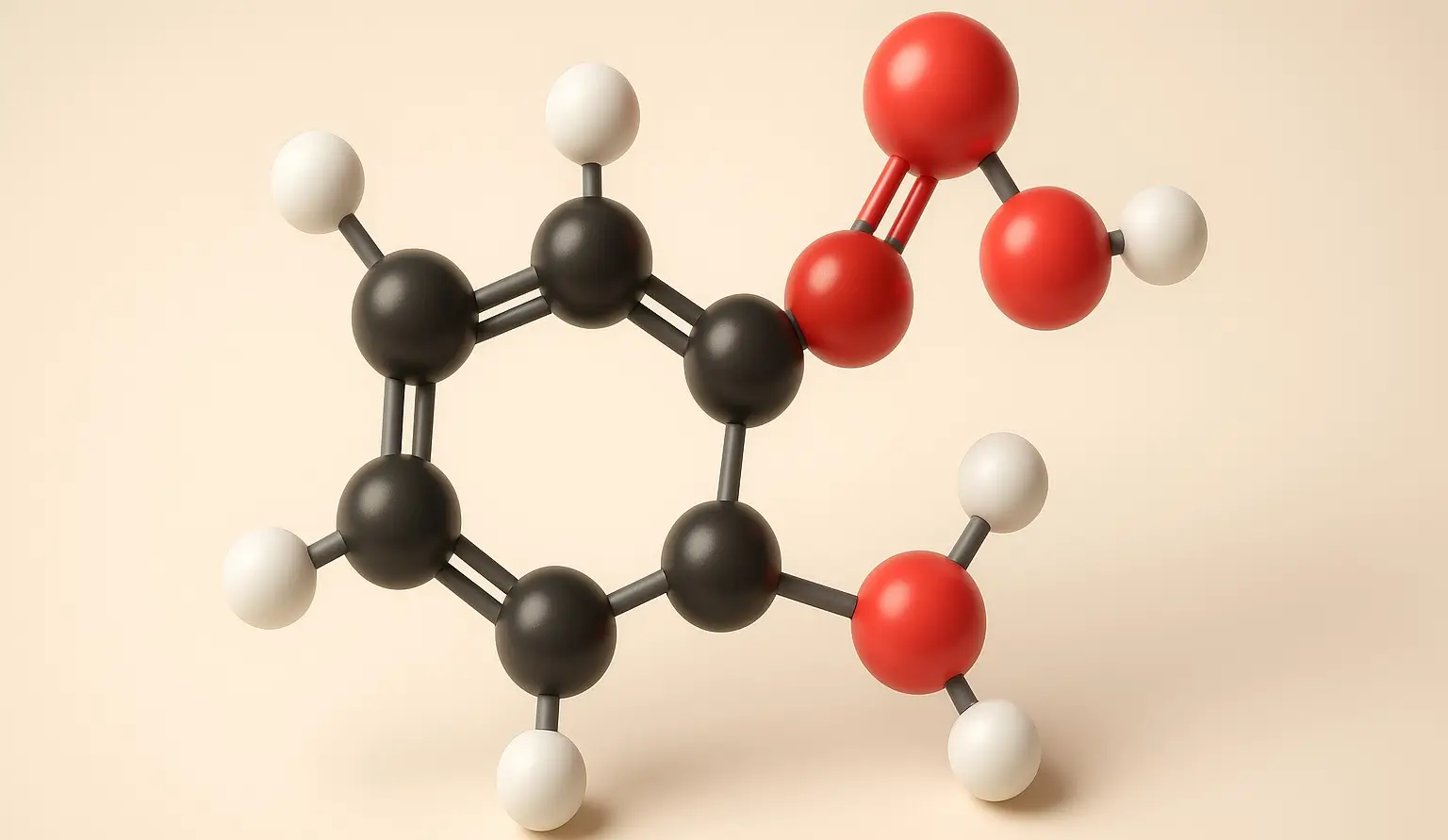
Acetyl Salicylic Acid (Aspirin)
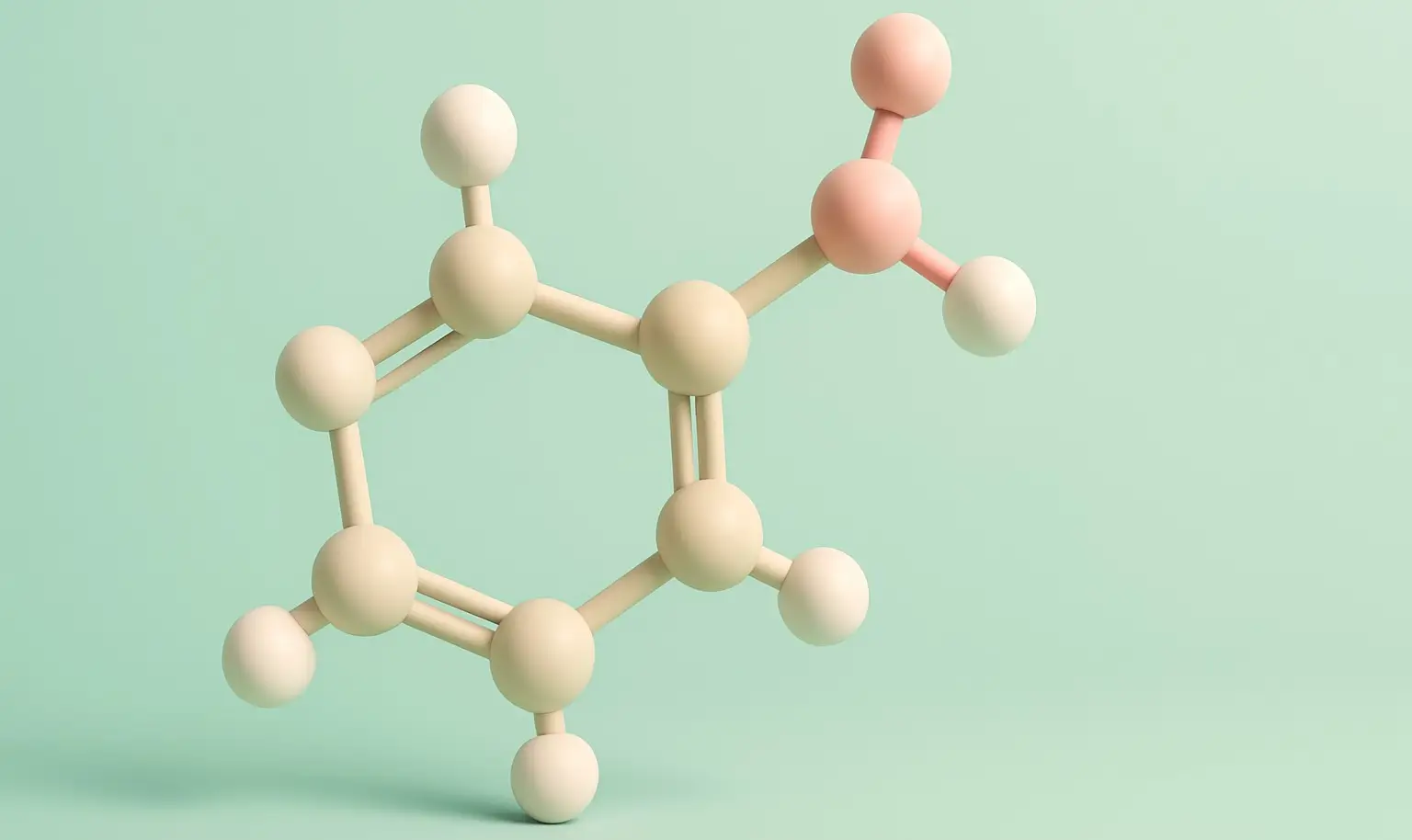
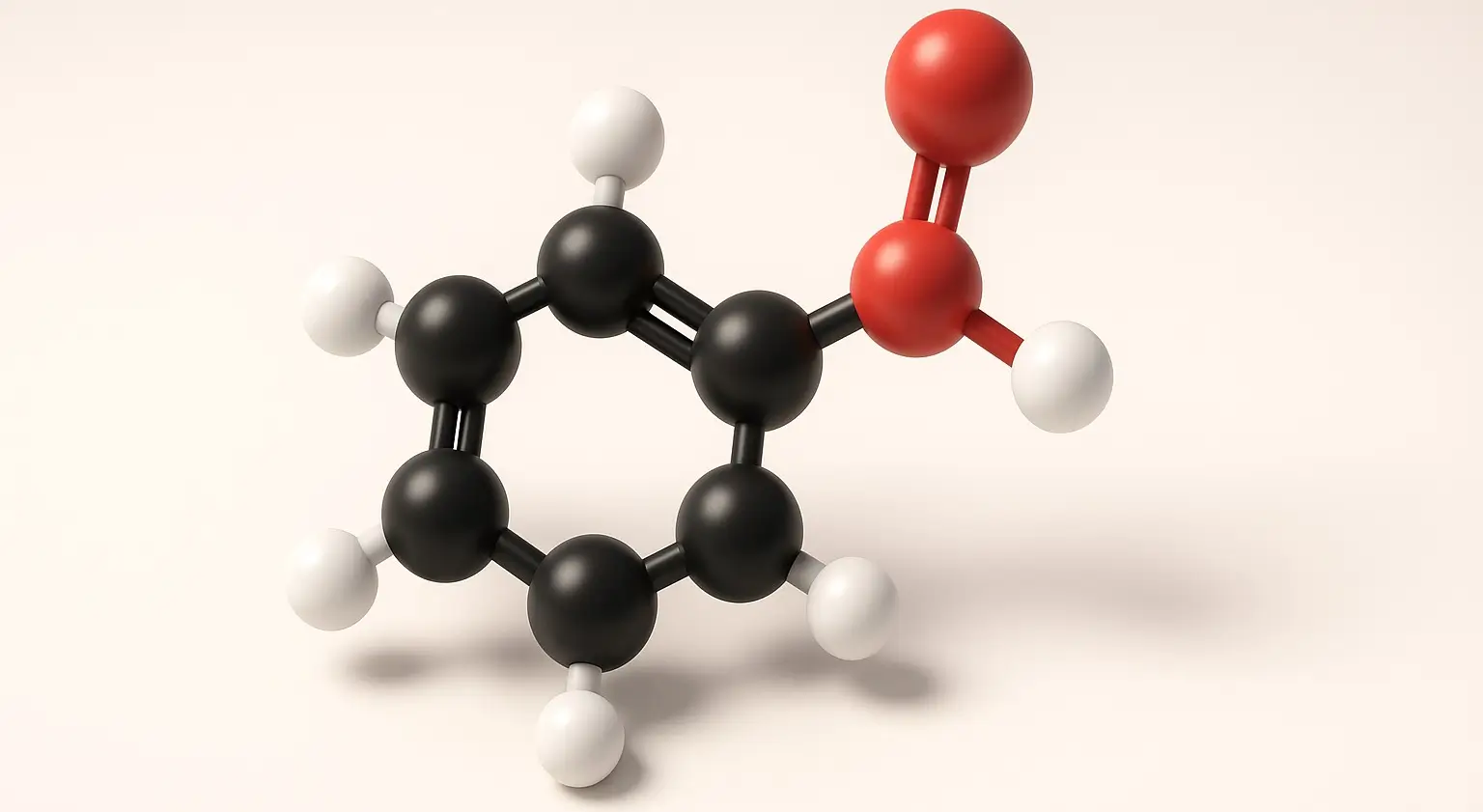
Acetyl Salicylic Acid (Aspirin) Definition Acetyl Salicylic Acid (Aspirin) commonly known as aspirin, is a synthetic derivative of salicylic acid and belongs to the class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It is widely used for its analgesic (pain-relieving), antipyretic (fever-reducing), anti-inflammatory, and antiplatelet (blood-thinning) properties. Structure: Chemical Formula: C₉H₈O₄ Molecular Structure: An ester formed by … Read more