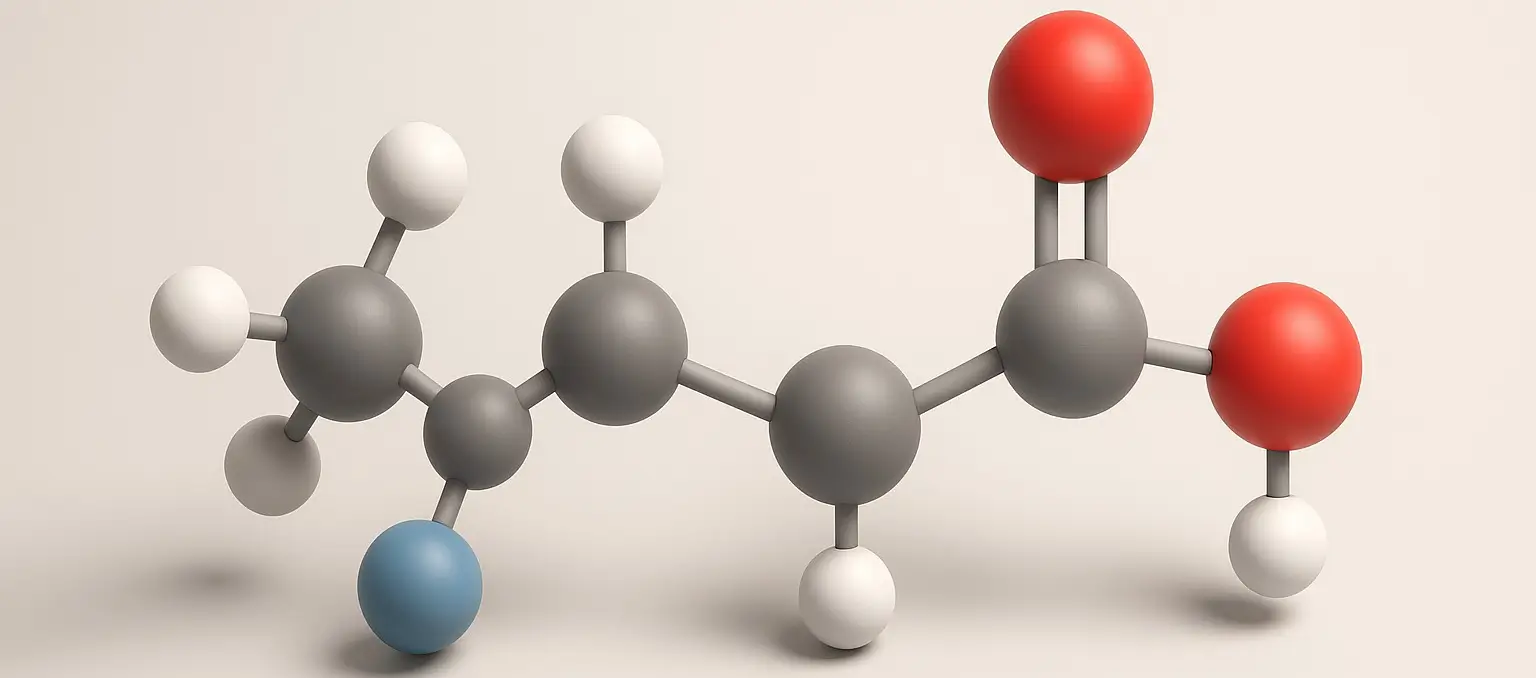
Lactic Acid
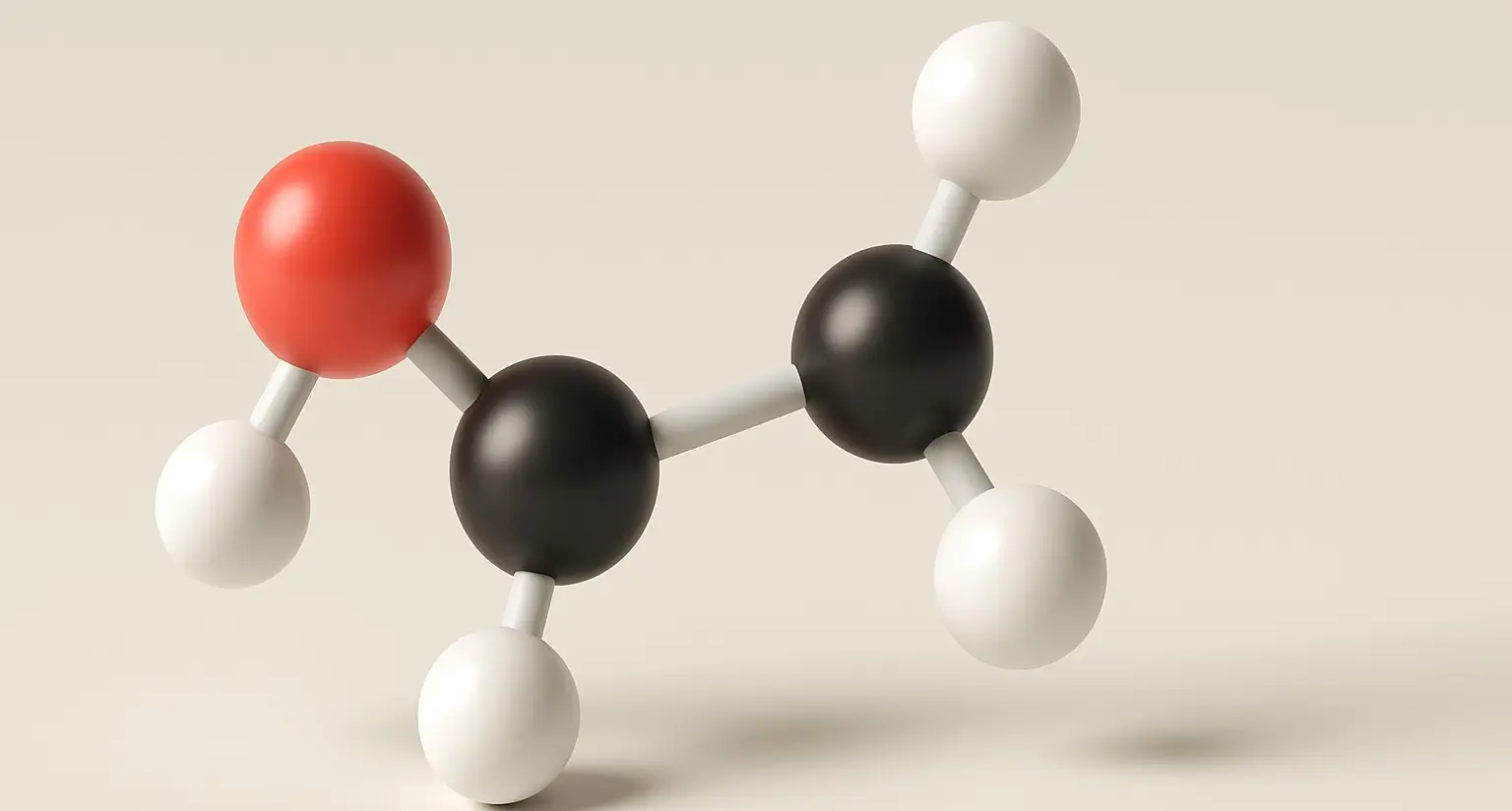
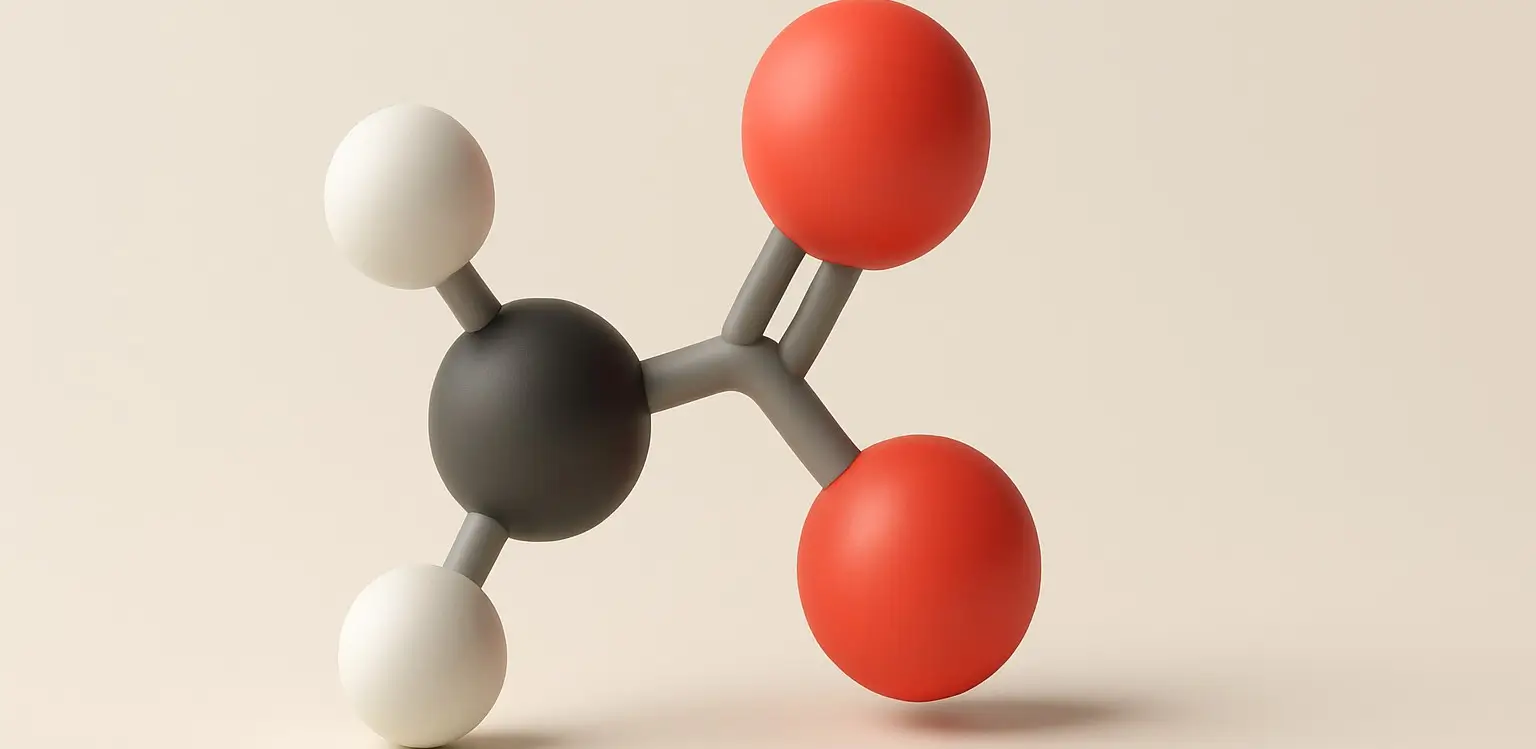
Lactic Acid Definition Lactic acid is an organic compound with the formula C₃H₆O₃, classified as an alpha-hydroxy acid (AHA). It is naturally produced in the body during anaerobic respiration (when oxygen is scarce), especially during intense physical activity. It is also found in fermented foods like yogurt and sourdough. Structure: Chemical Formula: C₃H₆O₃ Molecular Structure: … Read more