Nephron Anatomy
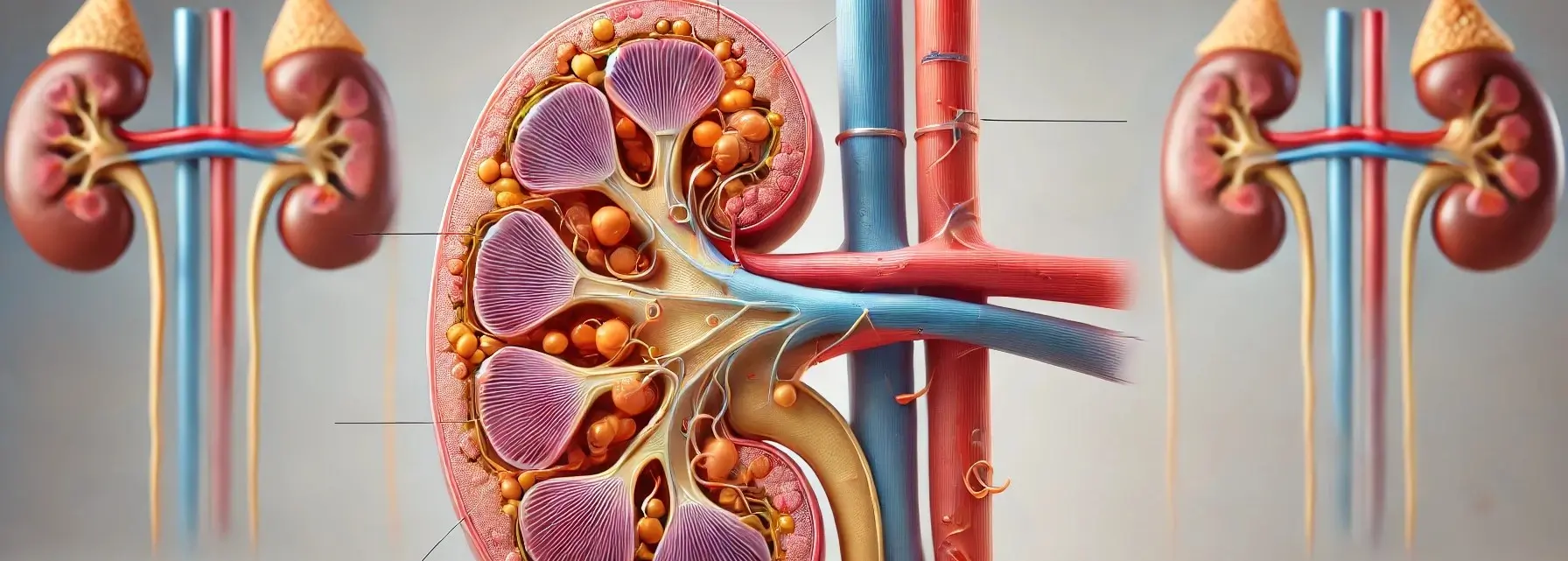
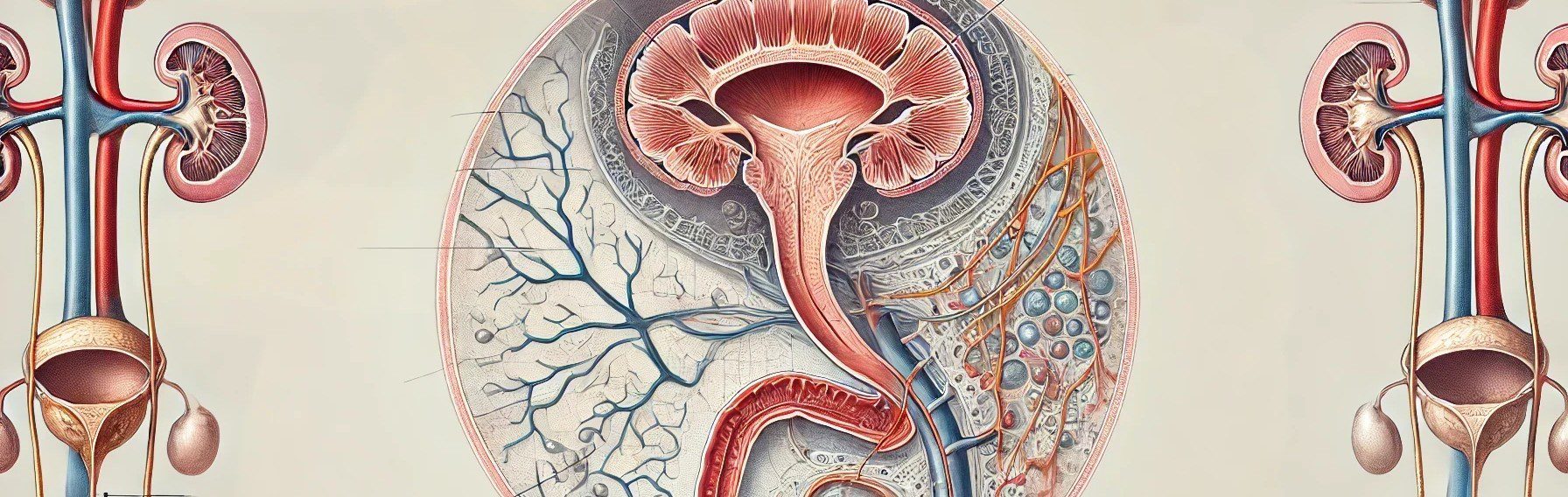
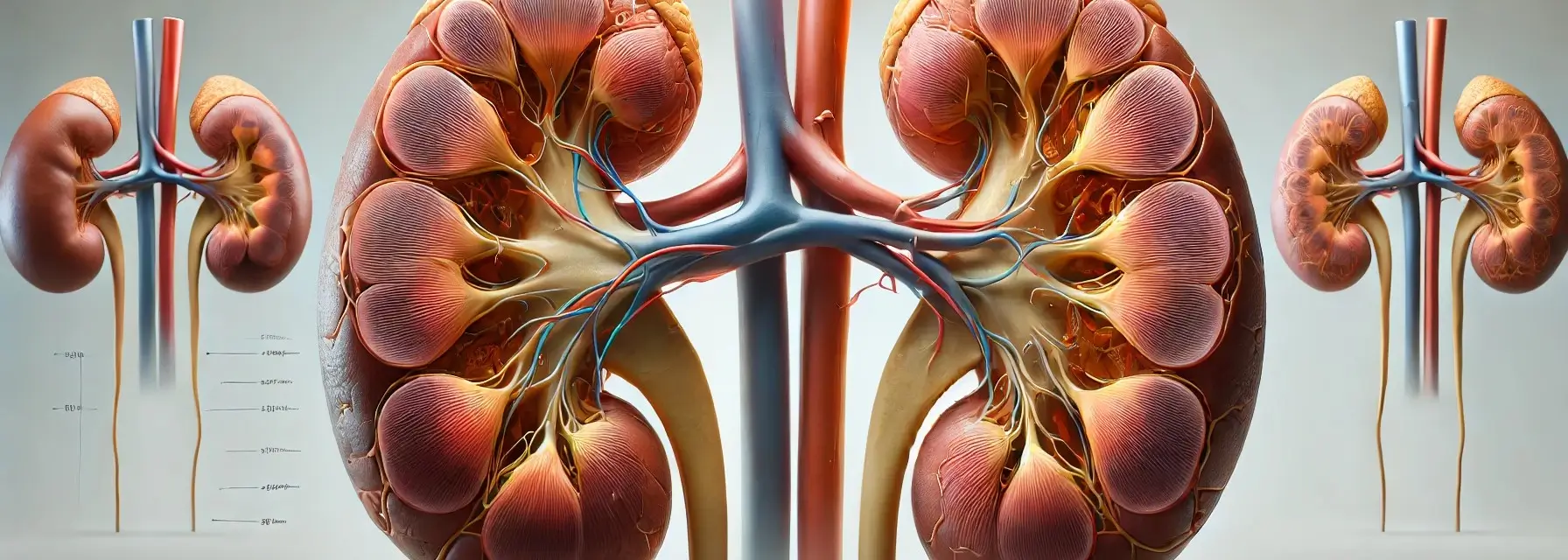
Nephron anatomy are the microscopic structural and functional units of the kidney, crucial for the process of filtering blood, removing waste, and regulating fluid and electrolyte balance. Each kidney contains about 1 million nephrons. A nephron is composed of two main parts: the renal corpuscle and the renal tubule. Renal Corpuscle The renal corpuscle is … Read more