Industrial Production of Artemisinin
Source
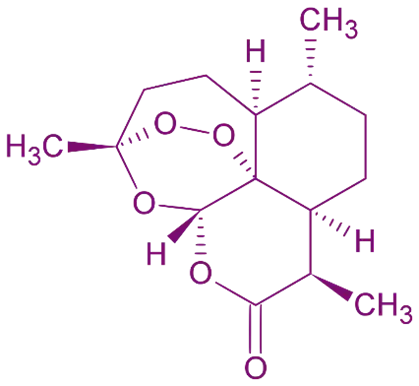
- Artemisinin is a sesquiterpene lactone derived from the sweet wormwood plant, Artemisia annua.

Extraction Process:
- Cultivation: annua is cultivated under controlled conditions to optimize artemisinins yield.
- Harvesting: Leaves and flowering tops are harvested and dried.
- Extraction: Typically involves solvent extraction using hexane or ethanol.
- Isolation: Techniques such as column chromatography are employed to purify artemisinin.
- Refinement: Final purification steps include recrystallization to achieve pharmaceutical-grade artemisinin.
Semi-Synthetic Production:
- Biosynthetic Engineering: Efforts are underway to produce artemisinins semi-synthetically using engineered yeast, enhancing production efficiency and reducing dependency on plant sources.
Advertisements
Estimation
Analytical Techniques:
- HPLC: The principal method for quantifying artemisinin in plant extracts and pharmaceutical formulations.
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS): Used for detailed analysis and confirmation.
- NMR Spectroscopy: Employed for structural verification and purity assessment.
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Utilized for routine monitoring based on absorbance properties.
Utilization
Pharmacological Applications:
- Antimalarial Agent: Artemisinins and its derivatives (e.g., artesunate, artemether) are frontline treatments for Plasmodium falciparum
- Cancer Research: Investigated for potential anticancer properties due to its ability to induce apoptosis in cancer cells.
- Anti-inflammatory and Antiviral Activities: Emerging research explores these additional therapeutic roles.
Other Uses:
- Combination Therapies: Integral to Artemisinins-based Combination Therapies (ACTs) to prevent resistance development in malaria parasites.
- Veterinary Medicine: Used in some regions for treating parasitic infections in animals.