Benzoic Acid
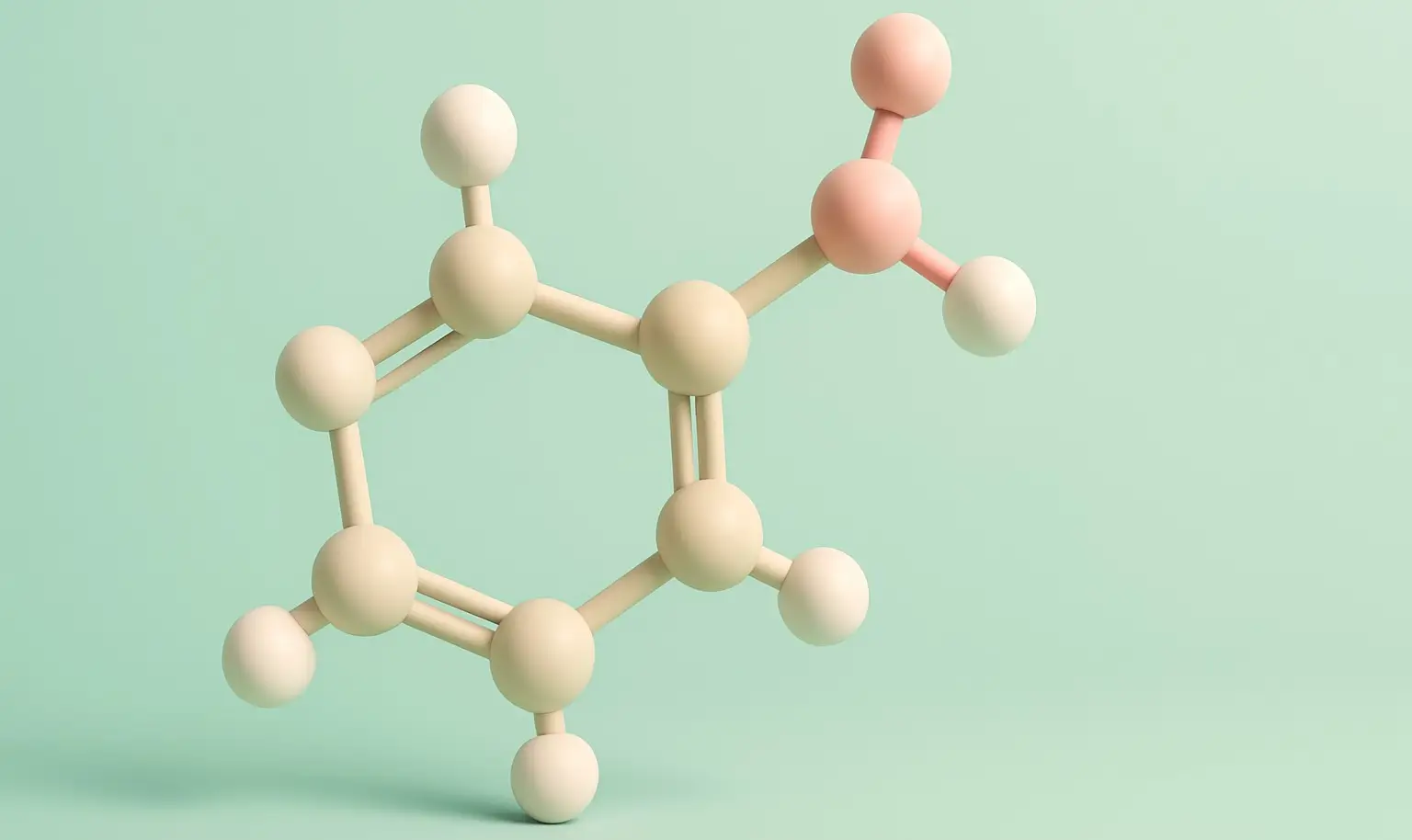
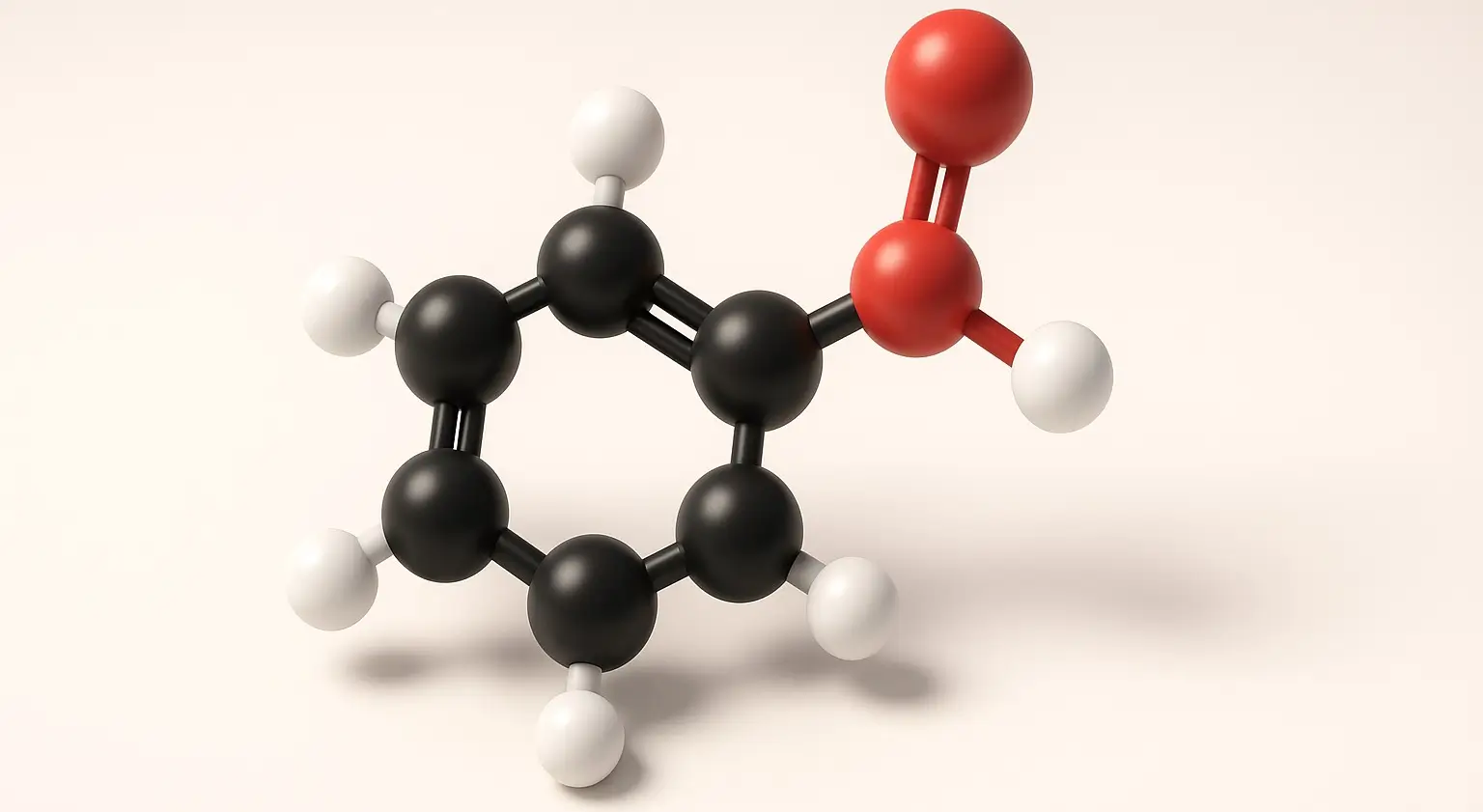
Benzoic Acid Definition Benzoic Acid is a white, crystalline aromatic carboxylic acid with the chemical formula C₆H₅COOH. It consists of a benzene ring attached to a carboxyl group. It is slightly soluble in water and highly soluble in organic solvents. Structure: Chemical Formula: C₇H₆O₂ Molecular Structure: Contains a benzene ring attached to a carboxyl group … Read more