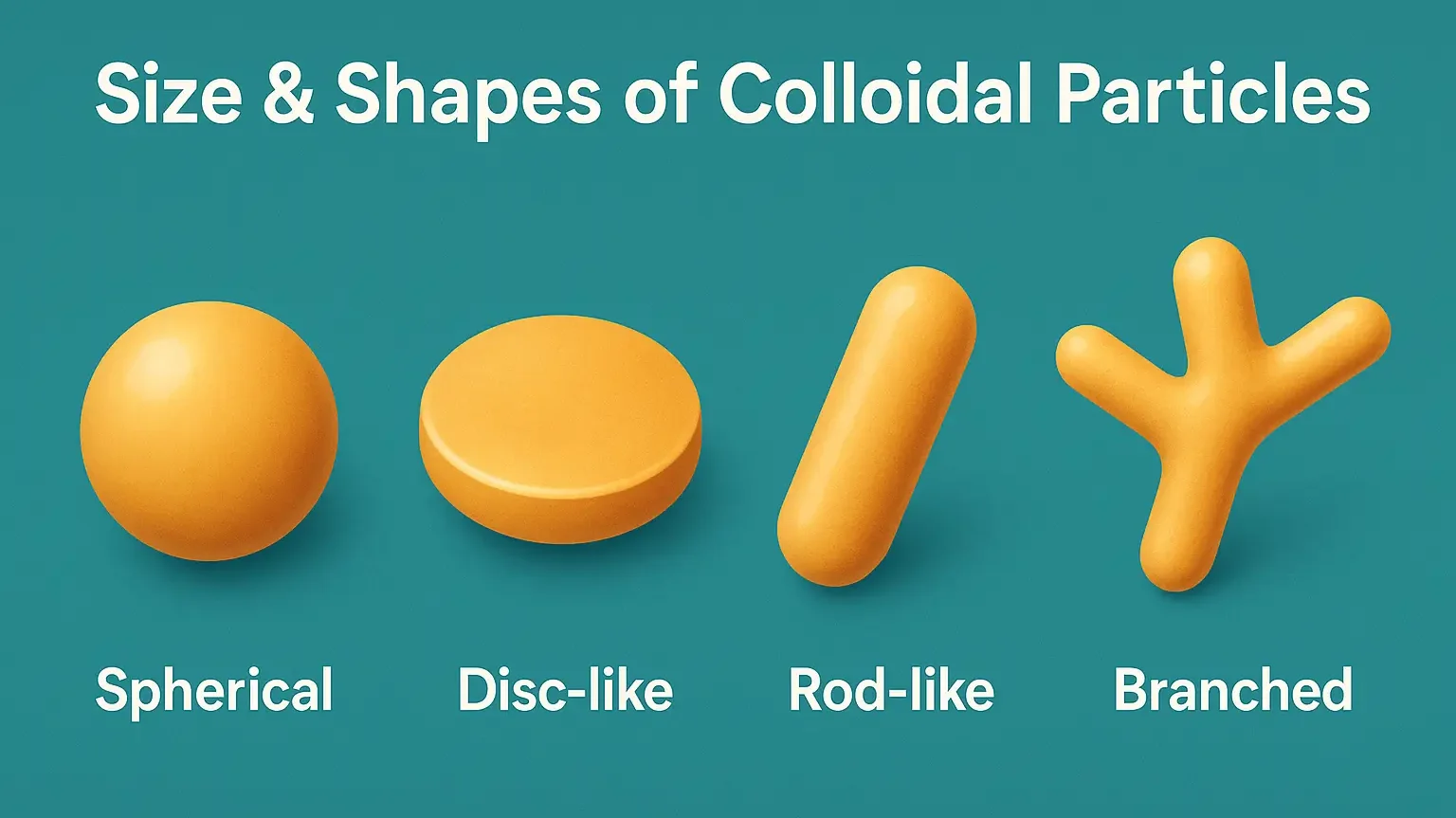
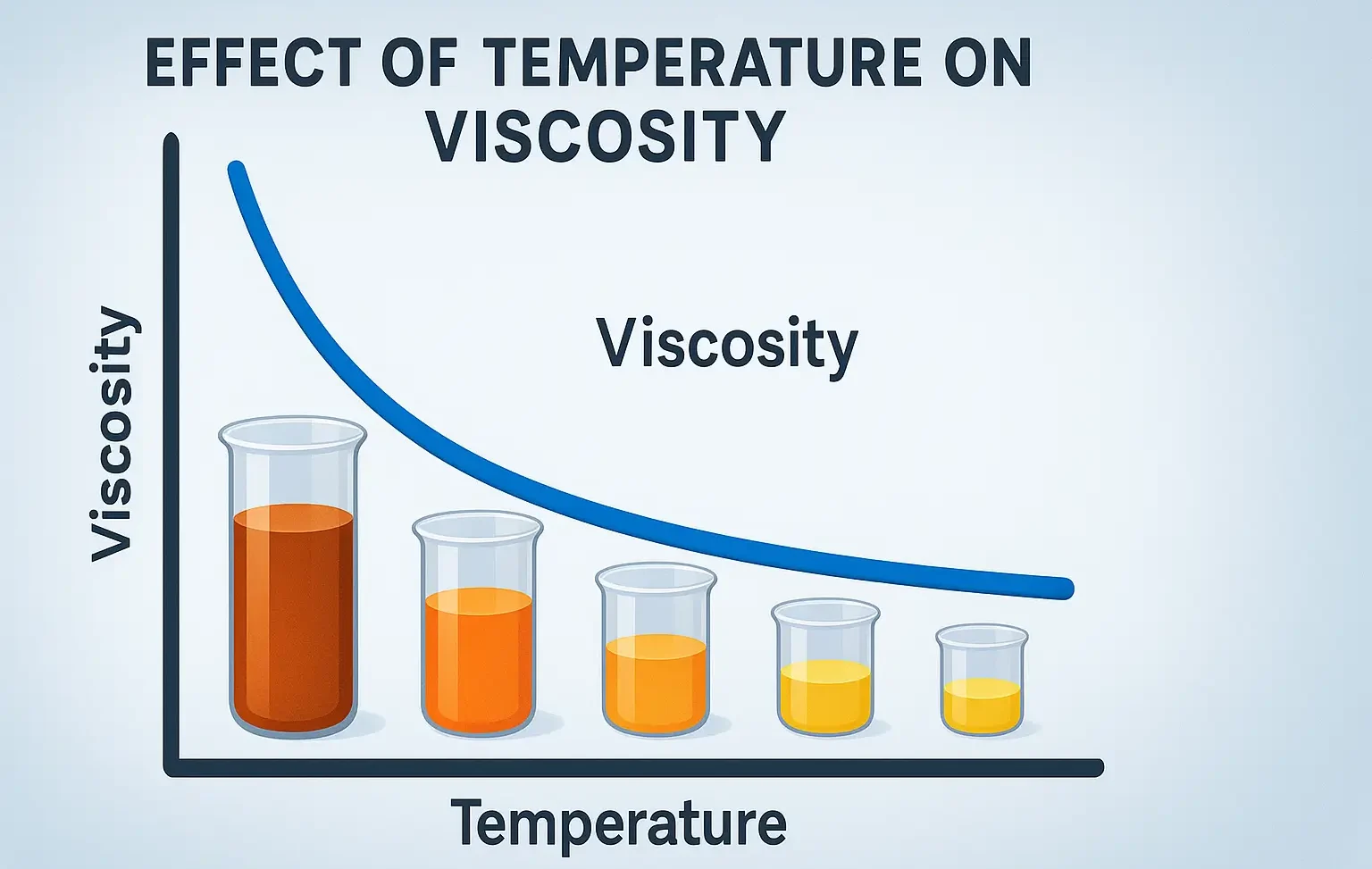
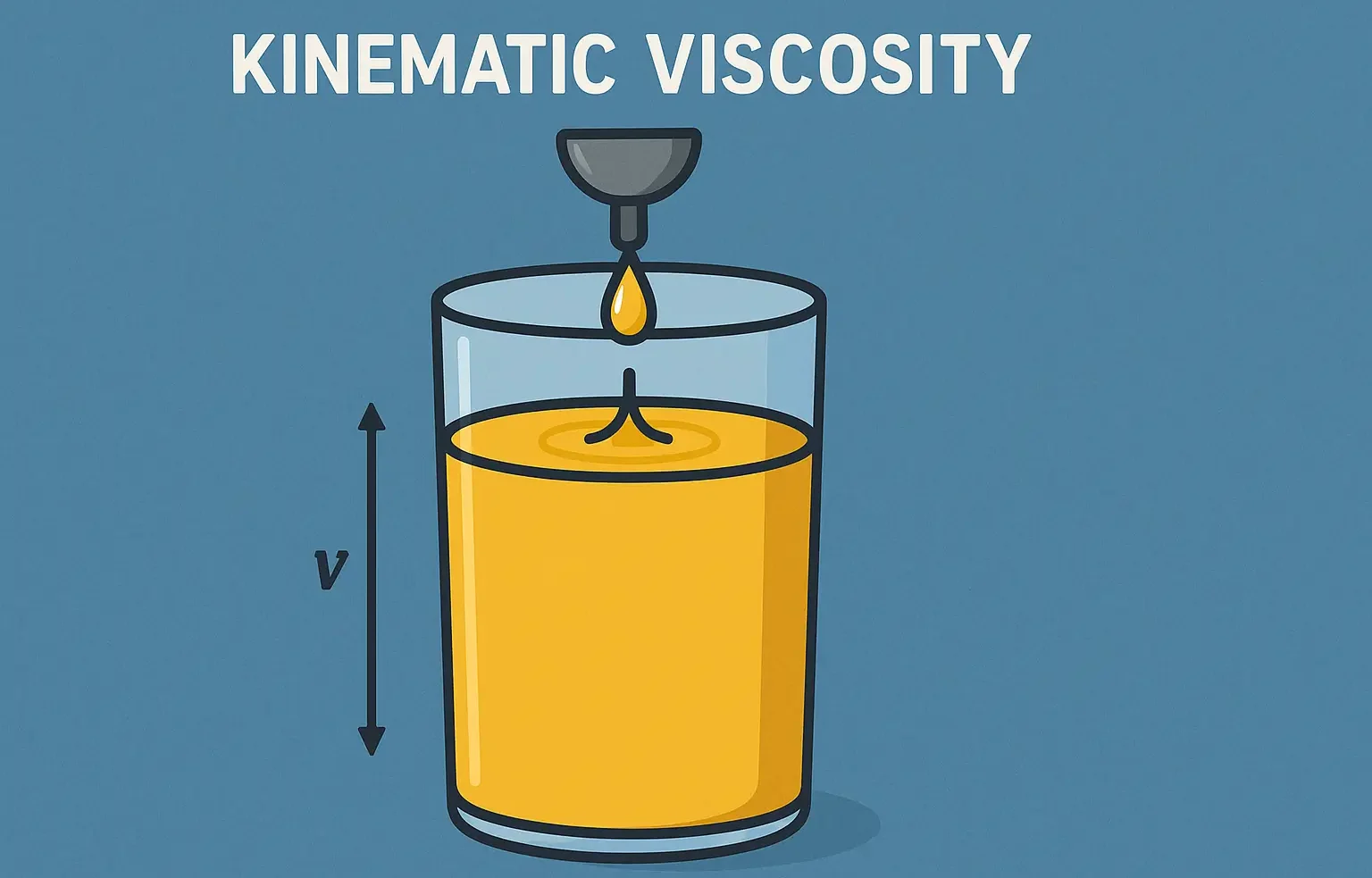
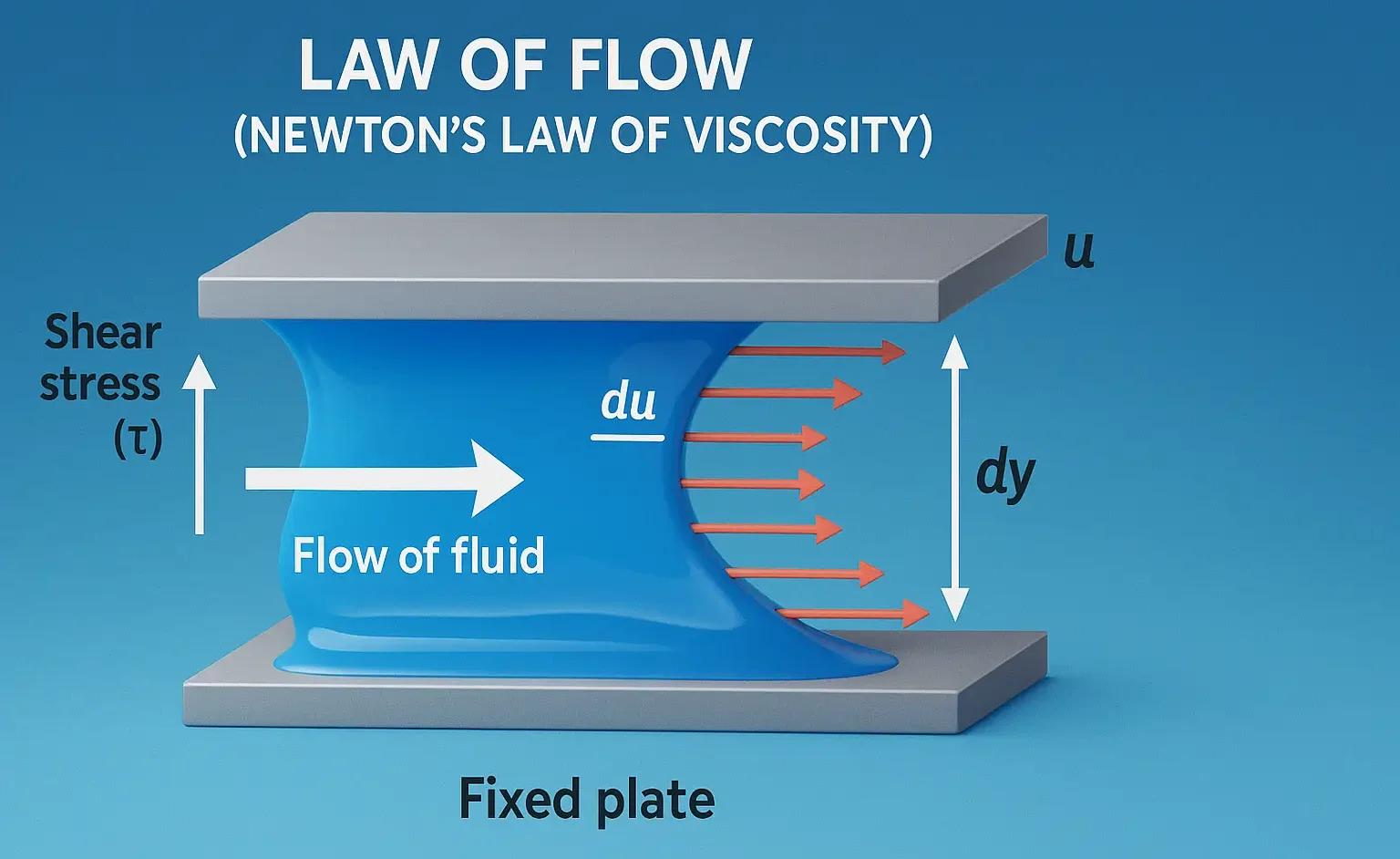
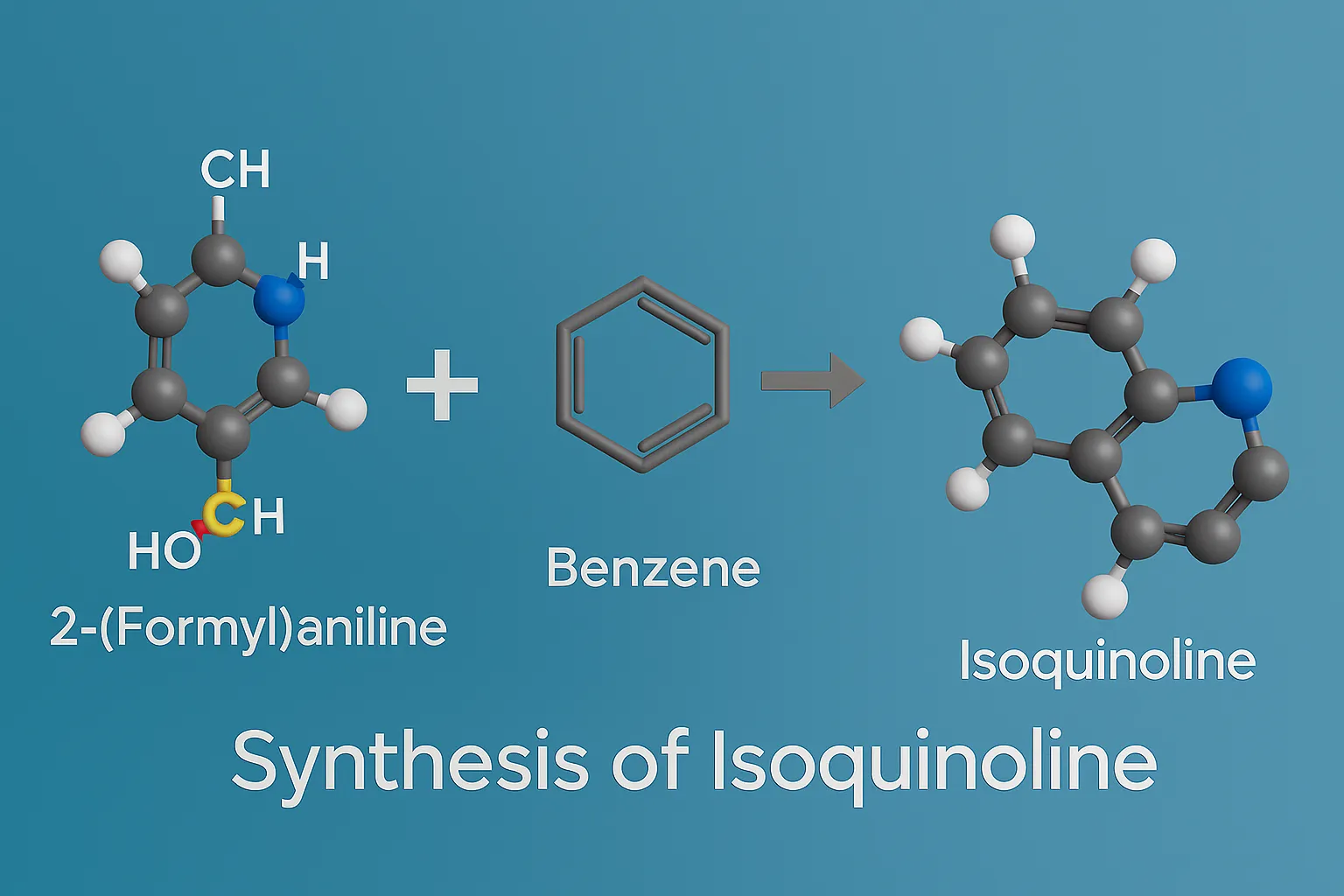
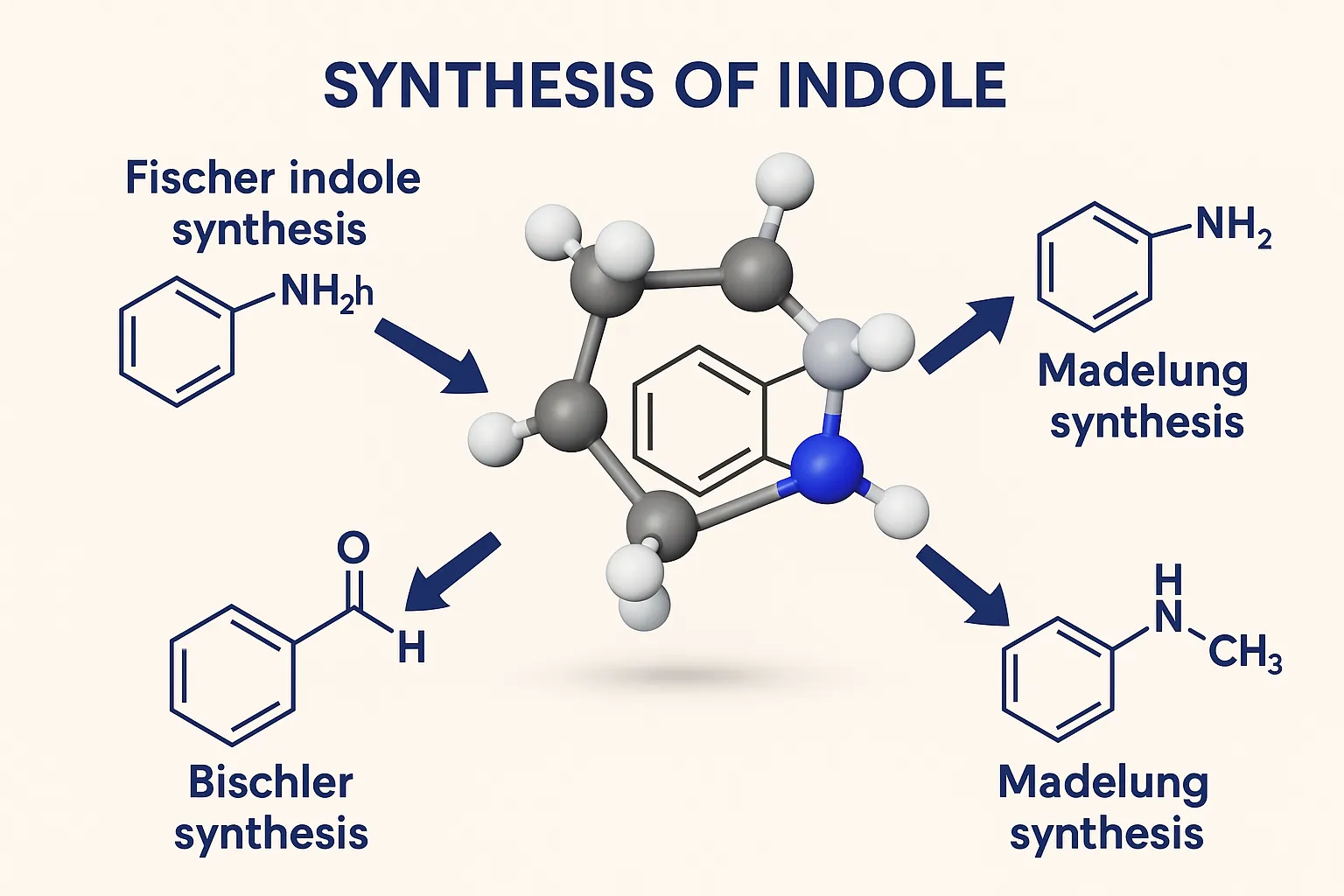
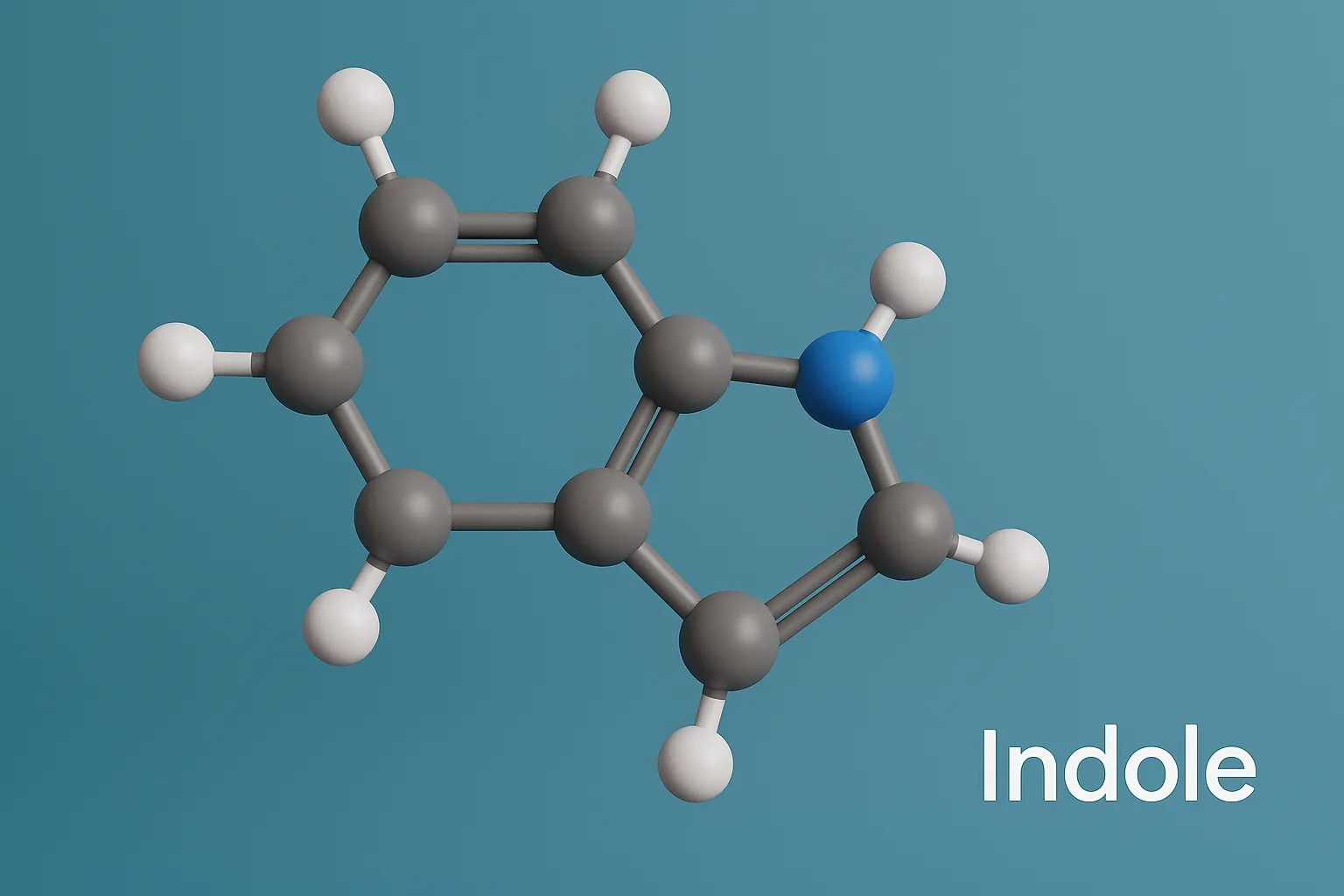
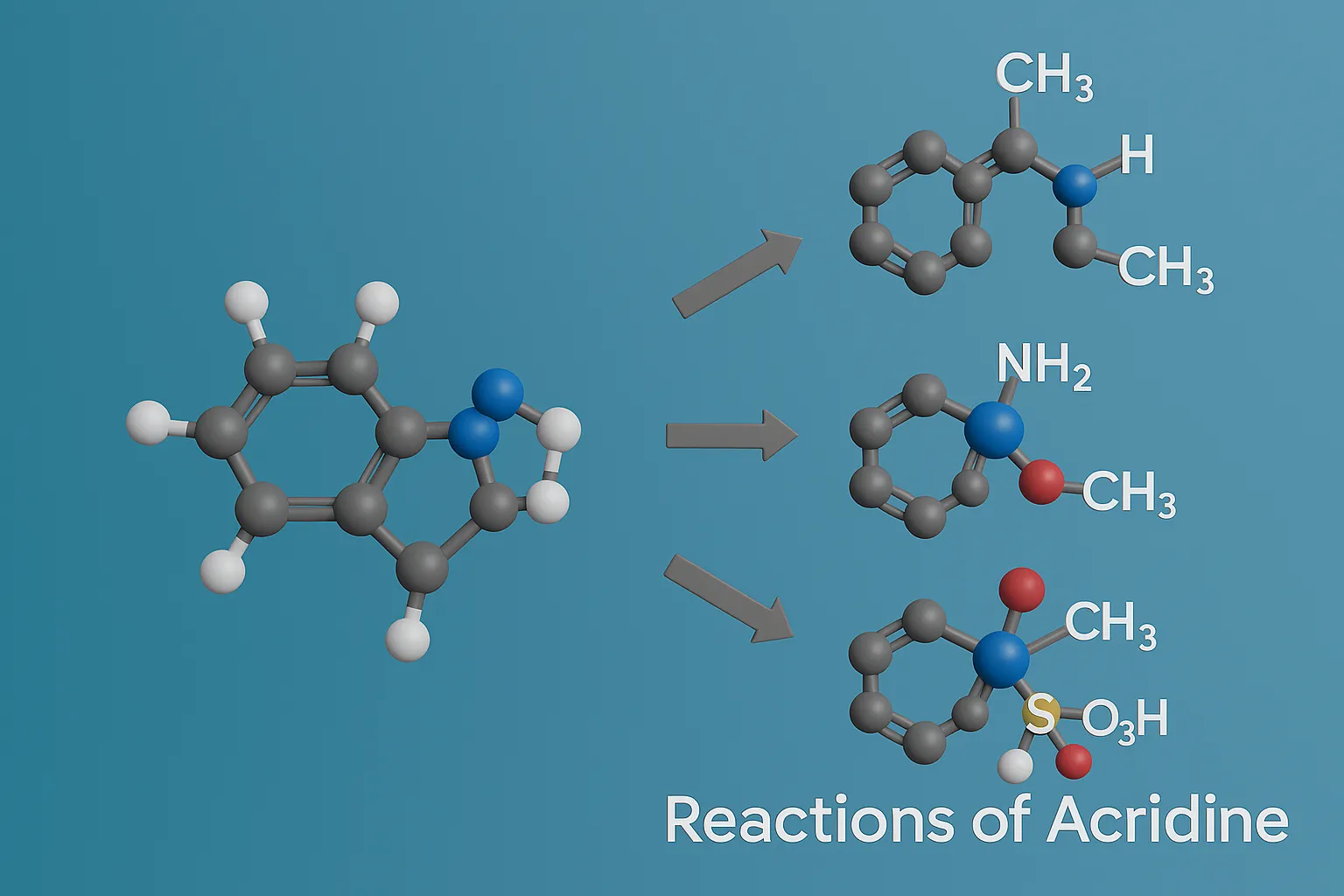
Size & Shapes of Colloidal Particles
Size & Shapes of Colloidal Particles range from 1–1000 nm, influencing stability and optical properties. Size & Shapes of Colloidal Particles include spherical, rod-like, lamellar, and irregular forms. Size of Colloidal Particles: Range: 1 nm to 1000 nm (i.e., 10⁻⁹ m to 10⁻⁶ m). Size influences: Surface area Stability Interaction with biological membranes Drug release … Read more