Benoxinate is an ester local anesthetic mainly used in ophthalmology to numb the eye surface for diagnostic procedures.
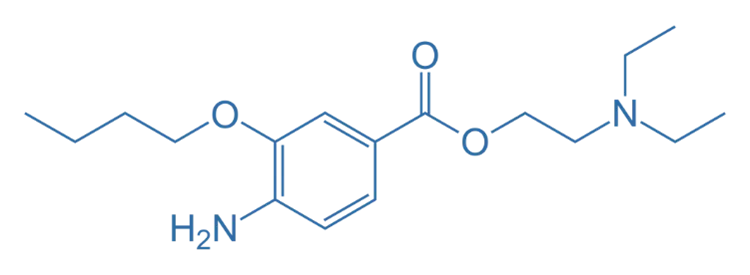
Structure of Benoxinate
- It is an amino benzoic acid derivative with a butyl ester group, primarily used in ophthalmic preparations for its local anesthetic properties.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₂H₂₀N₂O₂
Mode of Action
- Sodium Channel Inhibition: Blocks voltage-gated sodium channels in corneal nerves, preventing pain signal transmission.
- Membrane Stabilization: Reduces nerve excitability by stabilizing nerve membranes.
Uses
- Ophthalmic Anesthesia: Applied as eye drops to numb the cornea before eye surgeries, injections, or diagnostic procedures.
- Minor Eye Procedures: Used in non-surgical interventions requiring temporary corneal numbing.
Side Effects of Benoxinate
- Local Irritation: May cause eye redness, stinging, or discomfort.
- Systemic Absorption: Minimal, but potential for allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.

