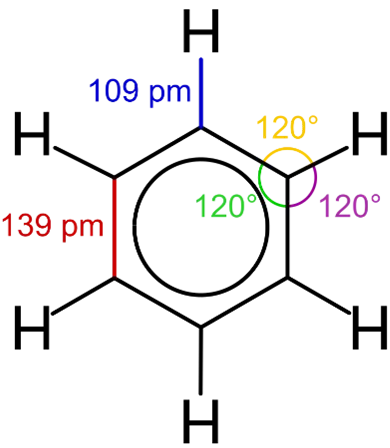
- Benzene (C₆H₆) and its derivatives are simple aromatic hydrocarbons, characterized by a six-carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds.
- The molecule is planar, with each carbon atom bonded to two other carbons and a hydrogen atom.
- Due to the presence of resonance structures, the electrons in the π-bonds are delocalized, which results in the ring having a high degree of stability.
- Benzene and its derivatives form a crucial part of organic chemistry, with applications in many industries.
Advertisements
Derivatives of Benzene
- Benzene derivatives are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by other atoms or functional groups.
- Some common derivatives include:
-
Toluene (C6H5CH3)
- Functional Group: Methyl group (-CH3)
- Uses: Solvent, fuel additive, starting material for synthesizing other chemicals.
-
Aniline (C6H5NH2)
- Functional Group: Amino group (-NH2)
- Uses: Production of dyes, rubber chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
-
Nitrobenzene (C6H5NO2)
- Functional Group: Nitro group (-NO2)
- Uses: Precursor for the synthesis of aniline and other chemicals.
-
Styrene (C6H5CH=CH2)
- Functional Group: Vinyl group (-CH=CH2)
- Uses: Production of polystyrene and other plastics.
-
Xylene (C6H4(CH3)2)
- Functional Group: Two methyl groups (-CH3)
- Uses: Solvent, starting material for the production of polyester fibers and other chemicals.
-
Halo benzenes (C6H5X)
- Functional Group: Halogen atom (X = F, Cl, Br, I)
- Uses: Solvents, intermediates in chemical synthesis, production of pesticides and pharmaceuticals.
-
- These are just a few examples of the wide range of benzene derivatives that play important roles in various industries, from pharmaceuticals to plastics and dyes.
Advertisements