Nose
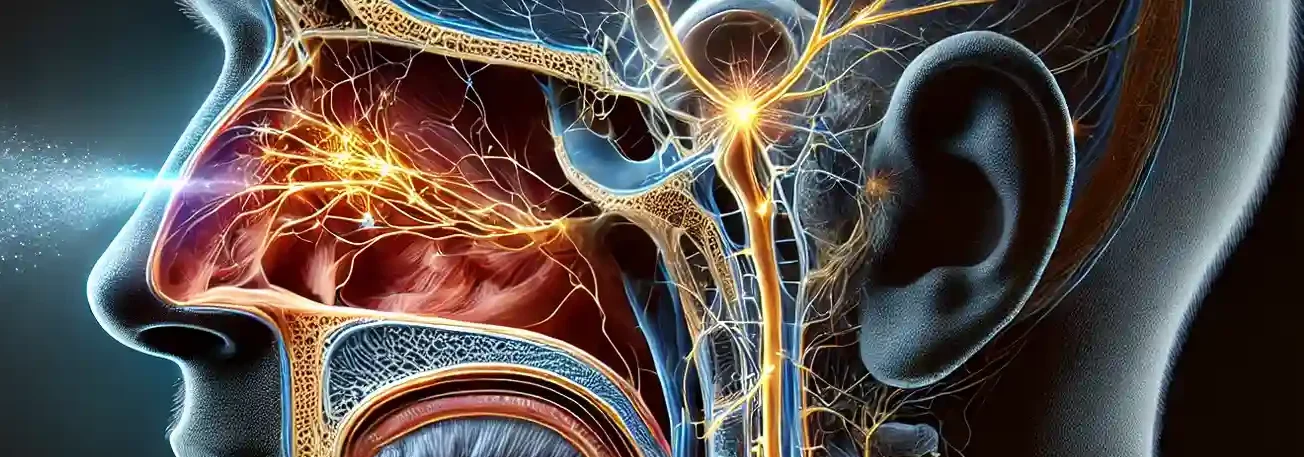
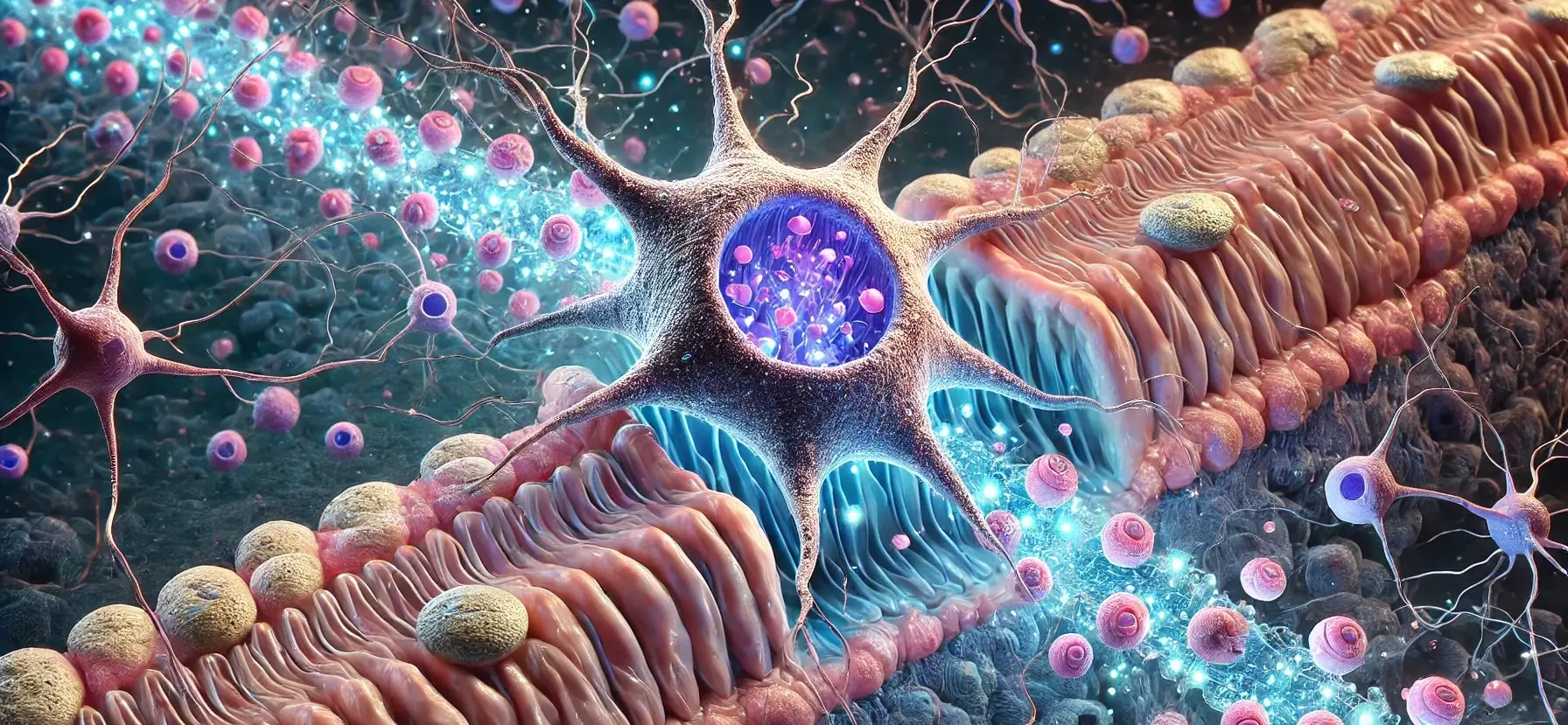
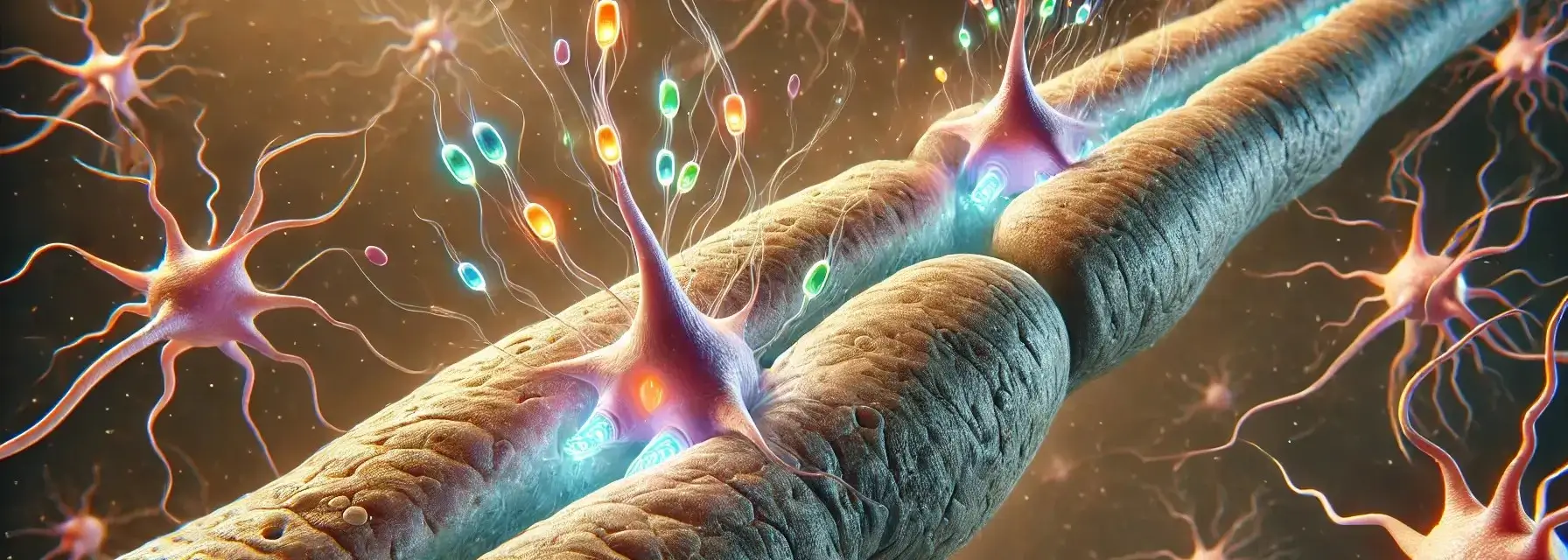
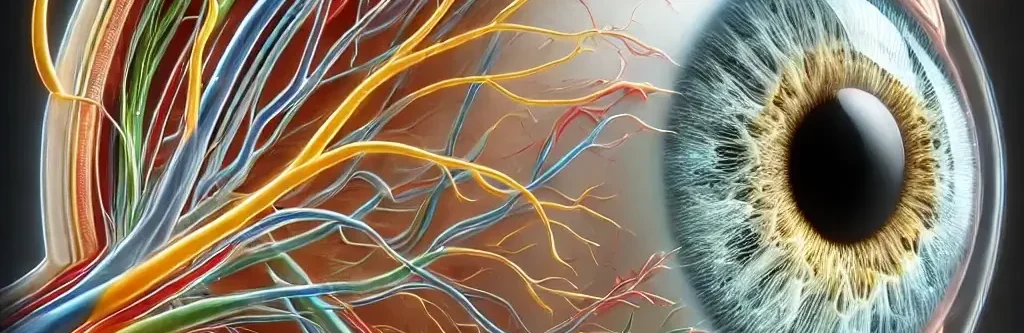
The nose is a sensory organ primarily responsible for the sense of smell (olfaction) and plays a significant role in respiration. It is composed of several structures that work together to detect and process odours and filter, warm, and humidify the air we breathe. Structure of the Nose The nose is a critical organ for … Read more