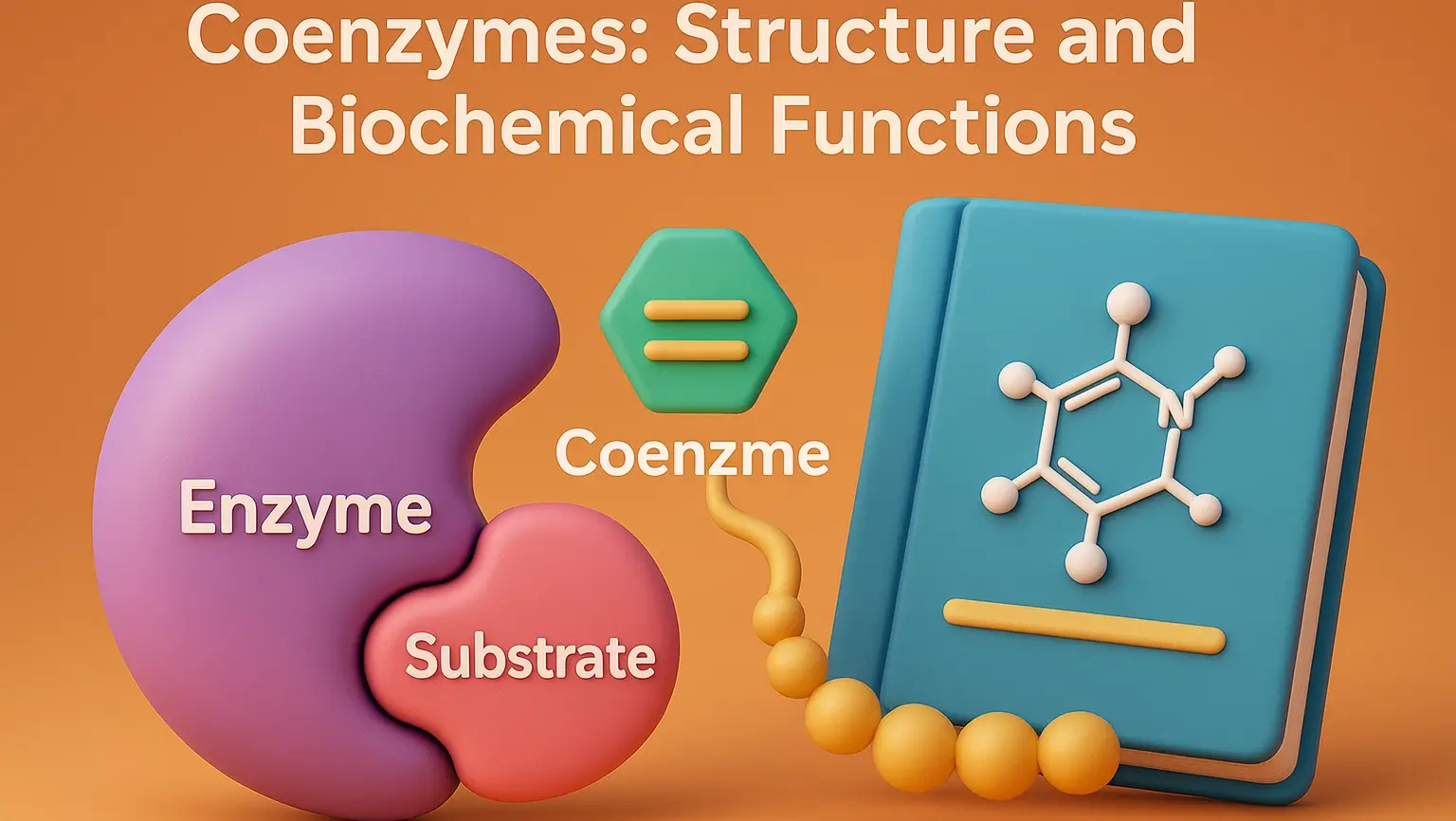
Coenzymes: Structure and Biochemical Functions
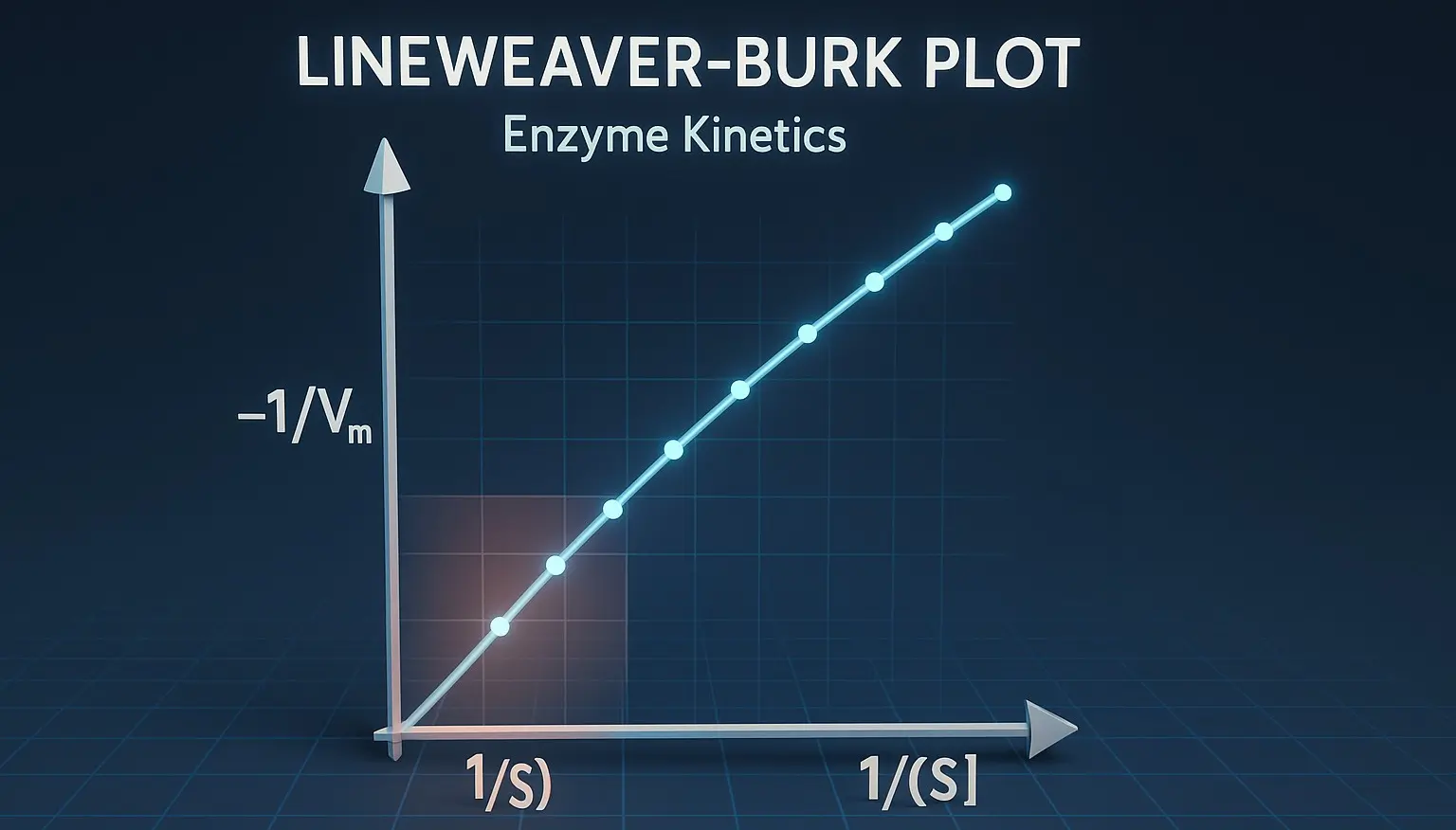
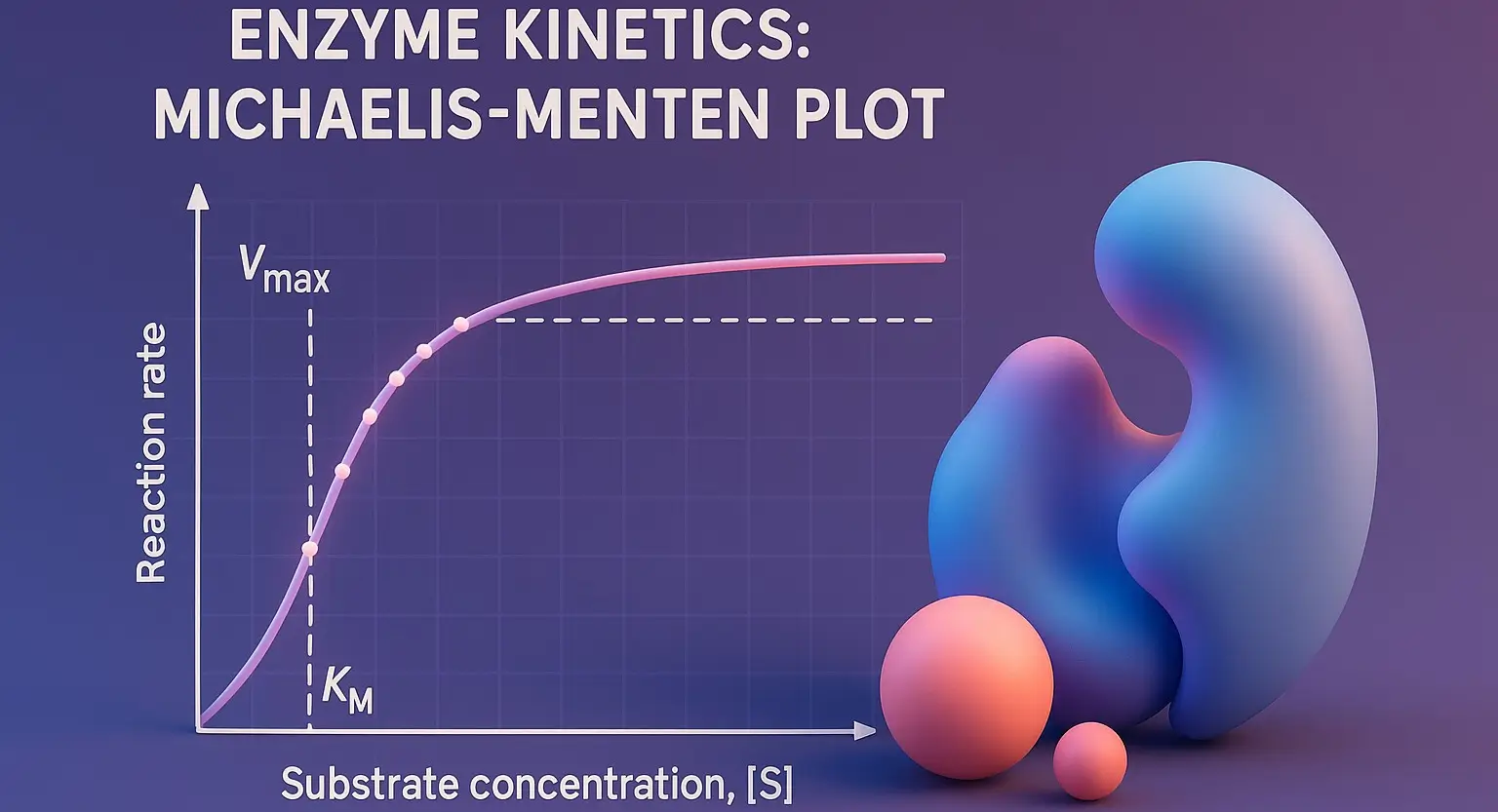
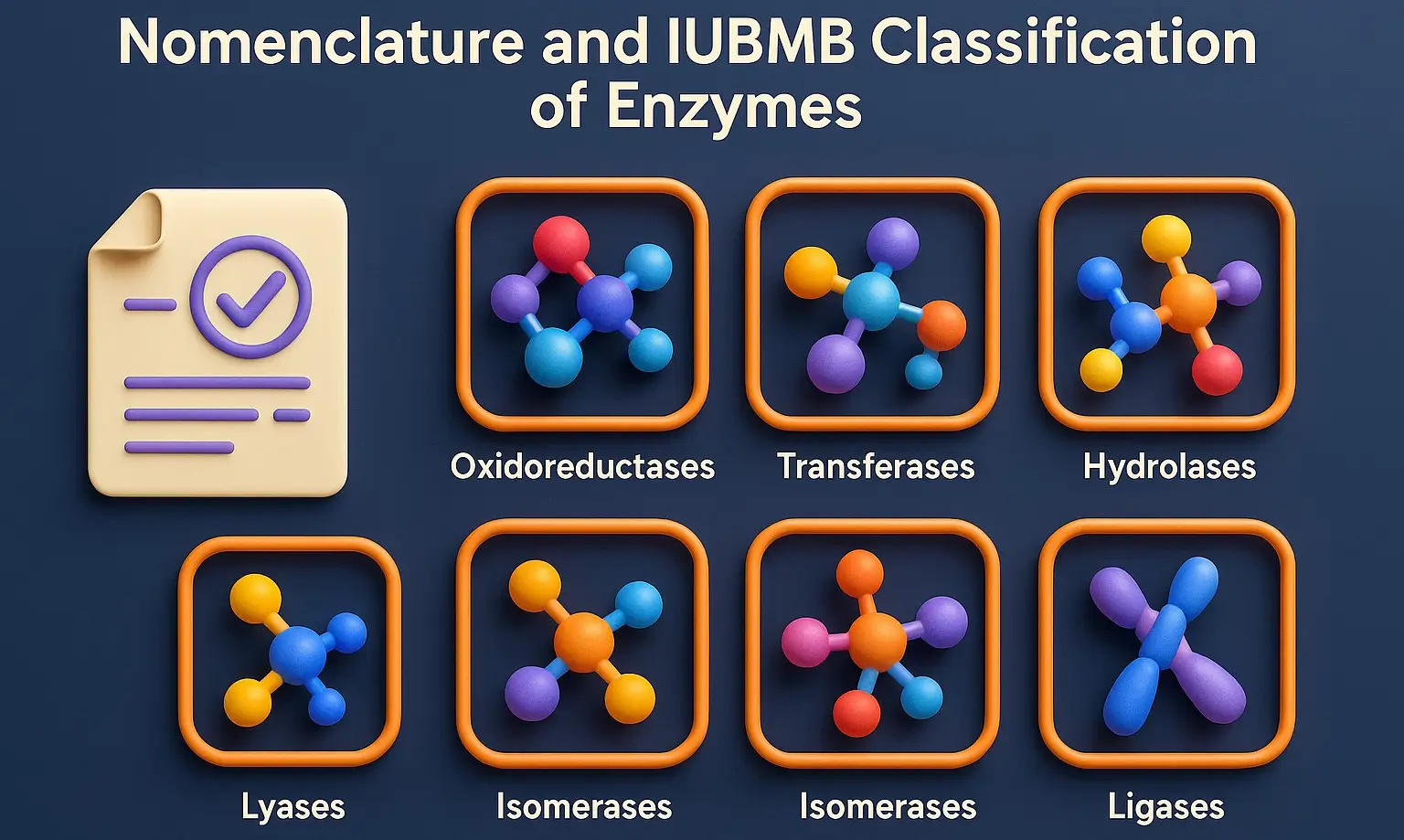
Coenzymes are small, organic molecules that bind to enzymes and are essential for their catalytic activity. Derived from vitamins, they act as carriers for chemical groups or electrons in enzymatic reactions. Structure and Examples of Coenzymes Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD⁺) Structure: Two nucleotides (adenine and nicotinamide) joined by phosphate groups. Function: Electron carrier in redox … Read more