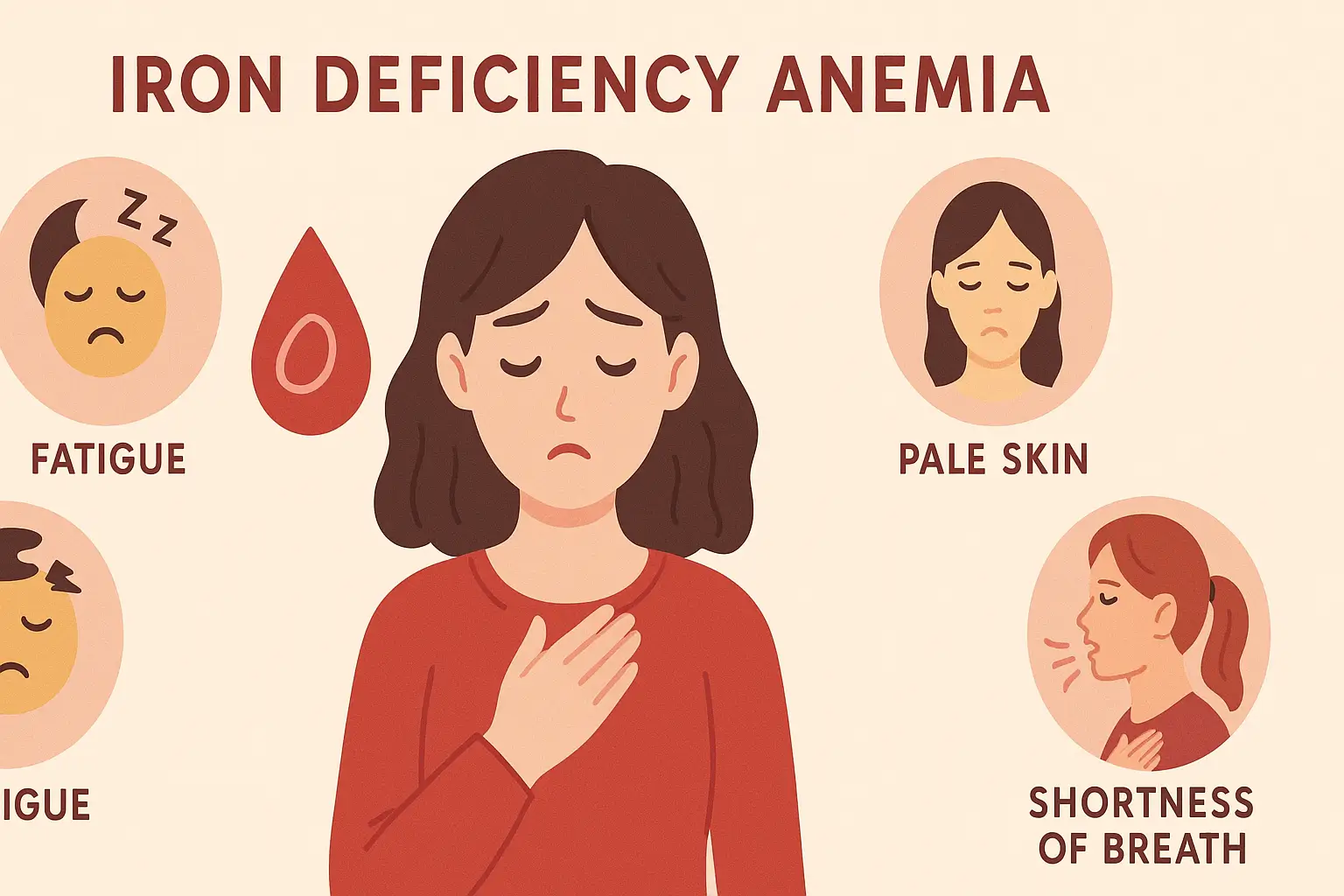
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes Introduction Type 2 diabetes, previously known as adult-onset diabetes or non-insulin-dependent diabetes. The most common form of diabetes. Characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. Causes of Type 2 diabetes Genetic Factors Family history increases risk. Lifestyle Factors Obesity, physical inactivity, poor diet, and aging. Metabolic Syndrome A cluster of conditions: … Read more