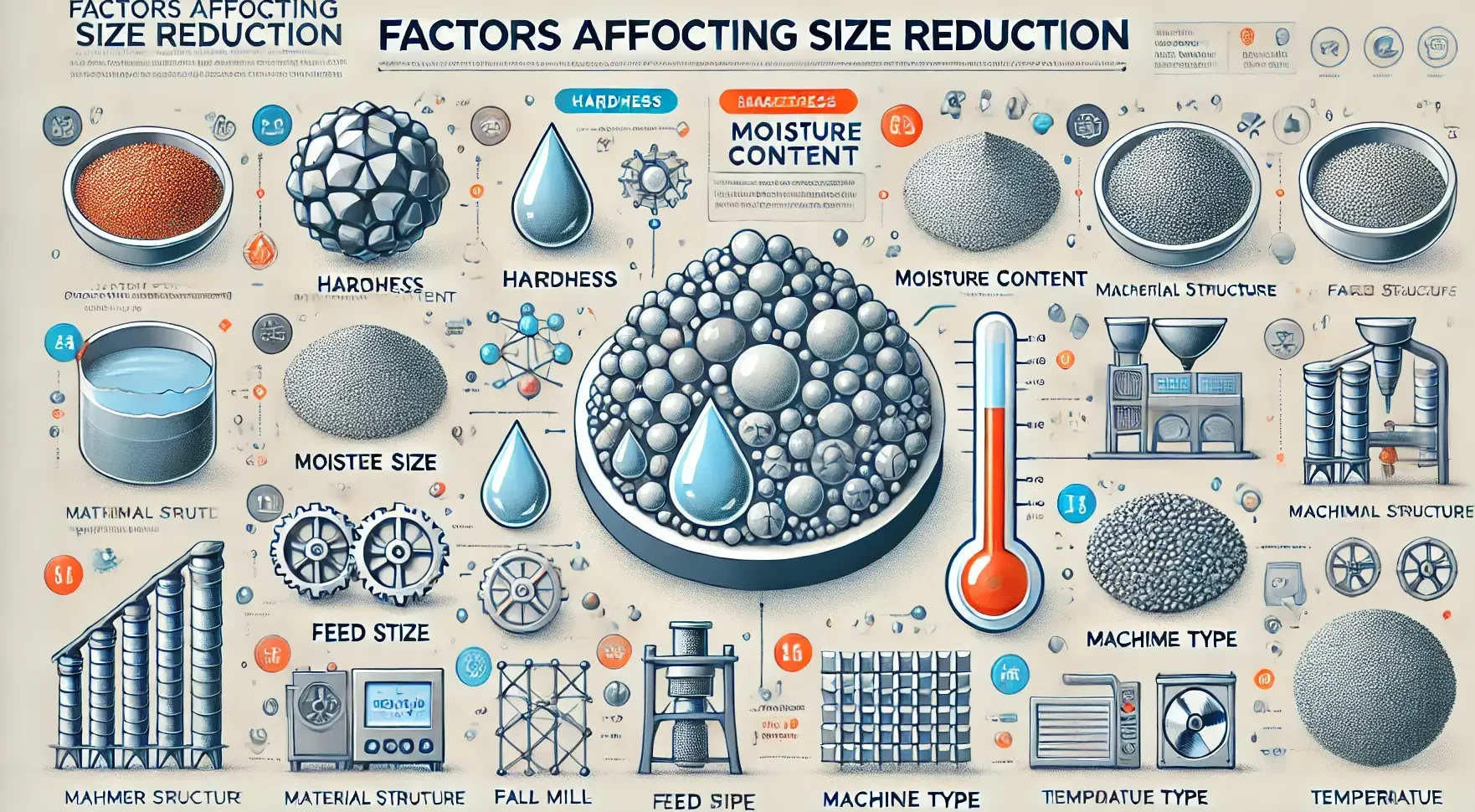
Factors Affecting Size Reduction
Material Characteristics: Hardness: Harder materials require more energy for size reduction. Toughness: Tough materials may deform rather than break. Moisture Content: High moisture content can cause materials to adhere and clog equipment. Friability: Easily crumbled materials require less energy. Type of Equipment: The design and operational parameters of size reduction equipment impact efficiency and effectiveness. … Read more