Organic Compounds Classification
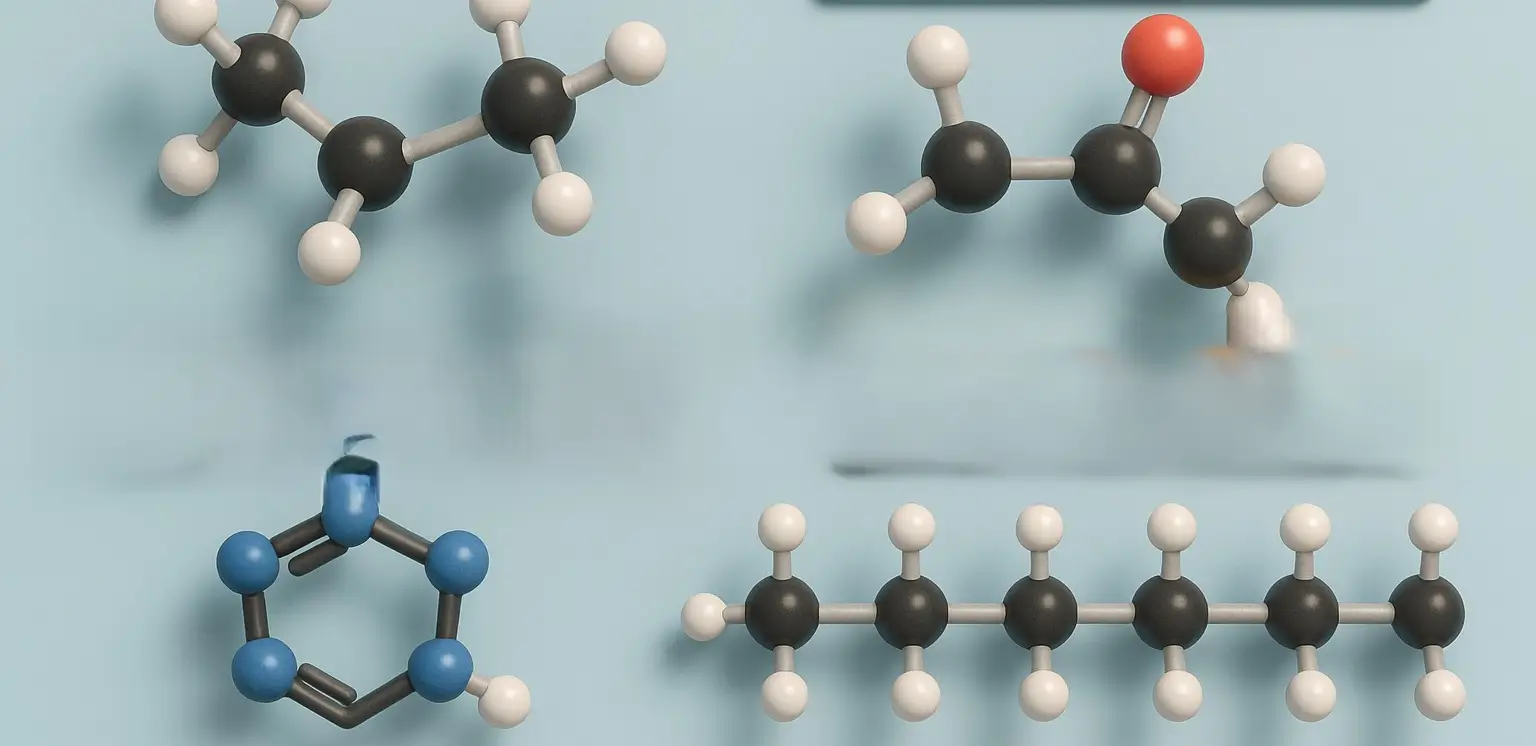
Organic Compounds Classification is a fundamental aspect of organic chemistry, facilitating the organization, study, and understanding of the vast array of organic molecules. Organic compounds classification are primarily made up of carbon atoms along with hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and halogens. The classification is based on the structure, functional groups, and the type of bonding … Read more