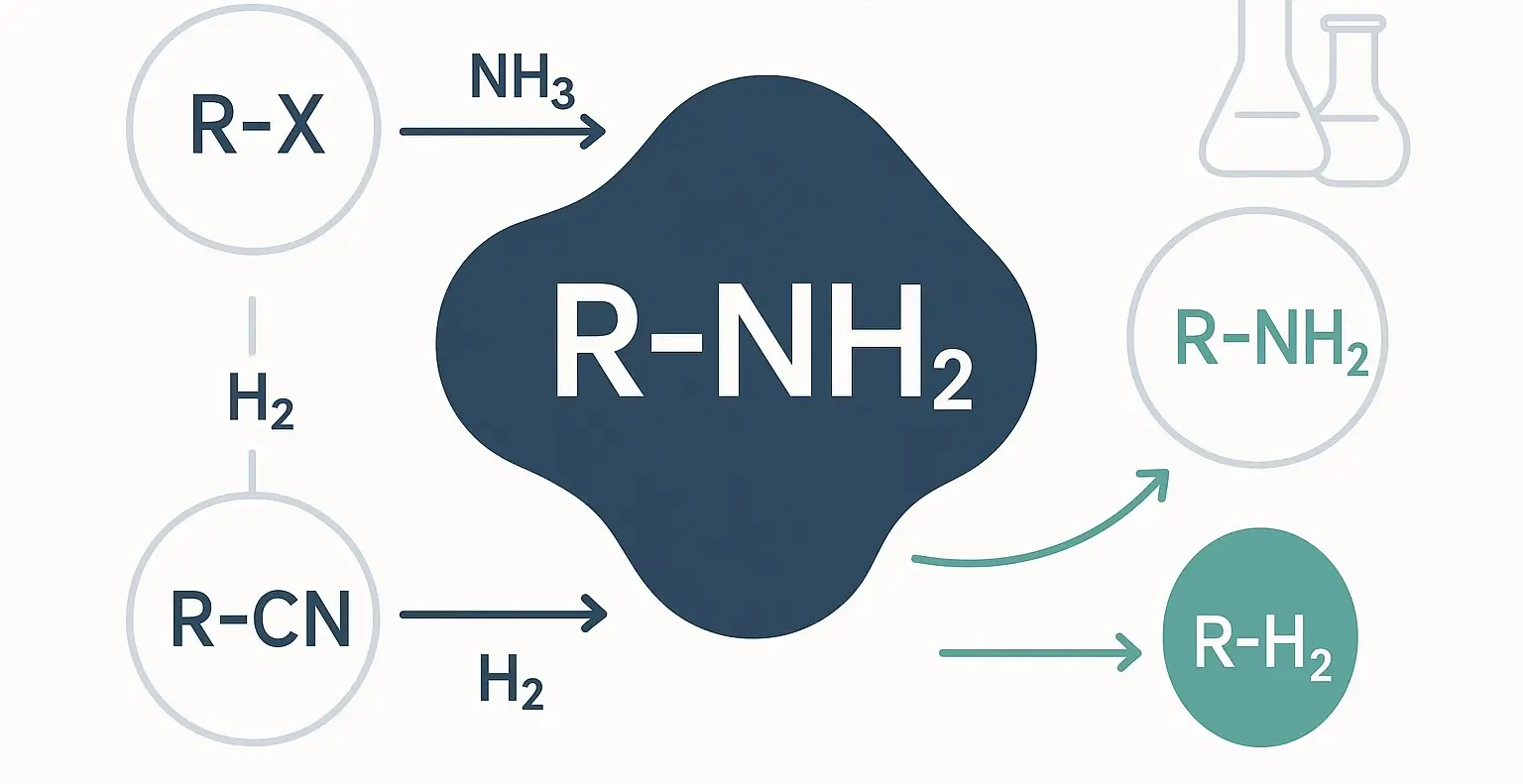
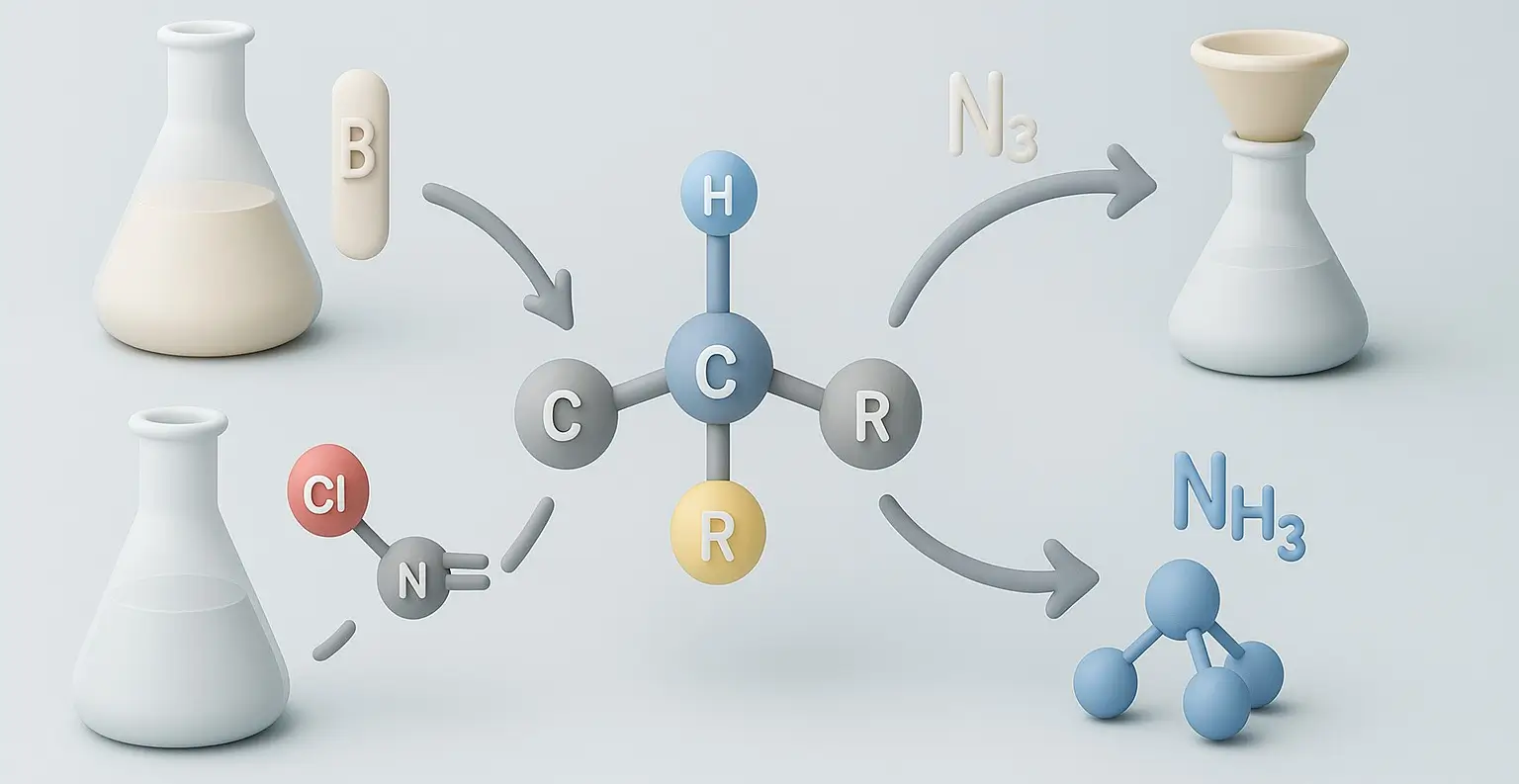
Qualitative test of Aliphatic amines
Qualitative test of Aliphatic amines can be distinguished as primary, secondary, or tertiary through various qualitative tests based on their solubility and reactivity. Below are the key tests used to identify the Qualitative test of Aliphatic amines and differentiate between these types of amines: Solubility Test Primary and Secondary Amines: Generally soluble in water and … Read more