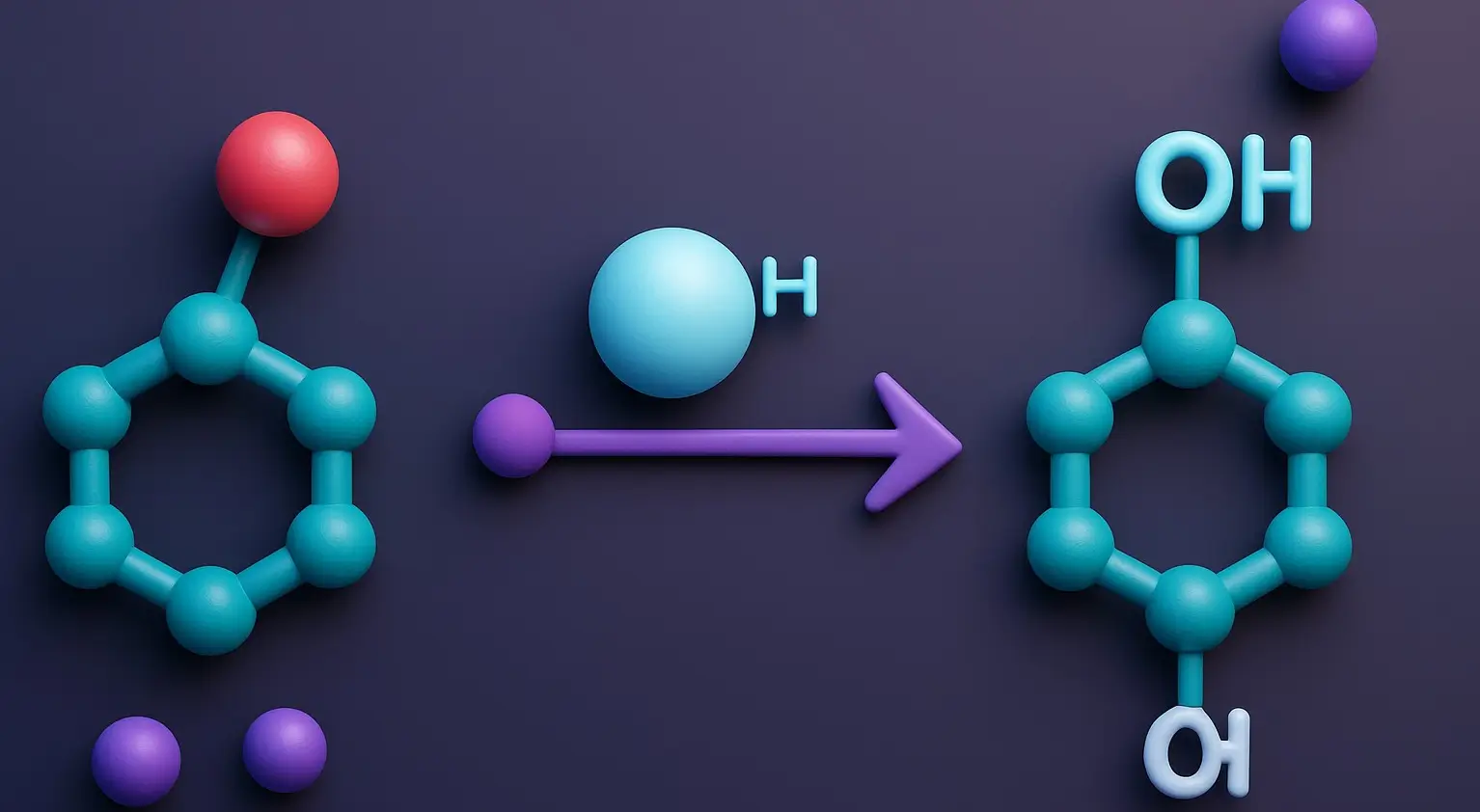
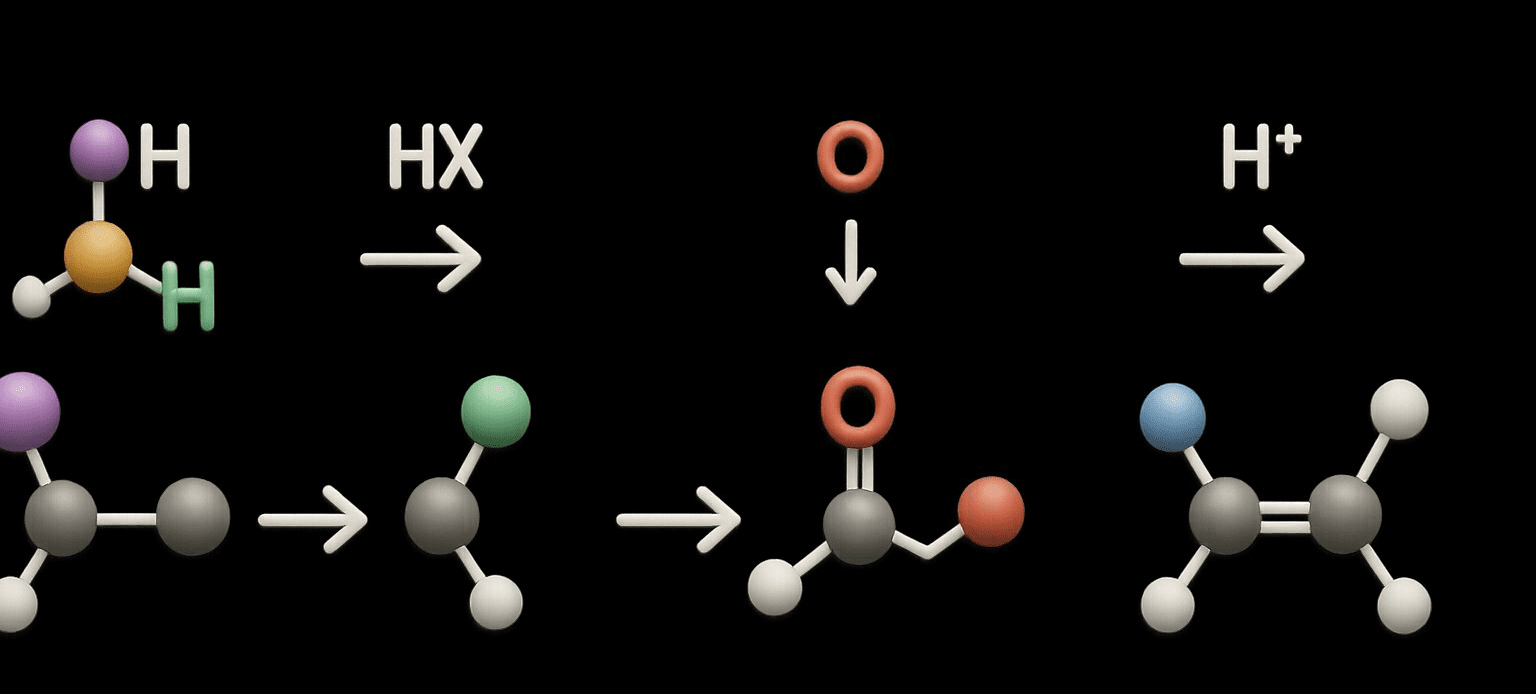Qualitative Tests for Alcohol
Qualitative tests for alcohol are analytical methods used to confirm the presence or type of alcohol in a sample. Qualitative Tests for Alcohol are important in fields like forensic science, the food and beverage industry, pharmaceuticals, and environmental monitoring. These tests do not measure the quantity of alcohol but confirm its existence or identify its … Read more