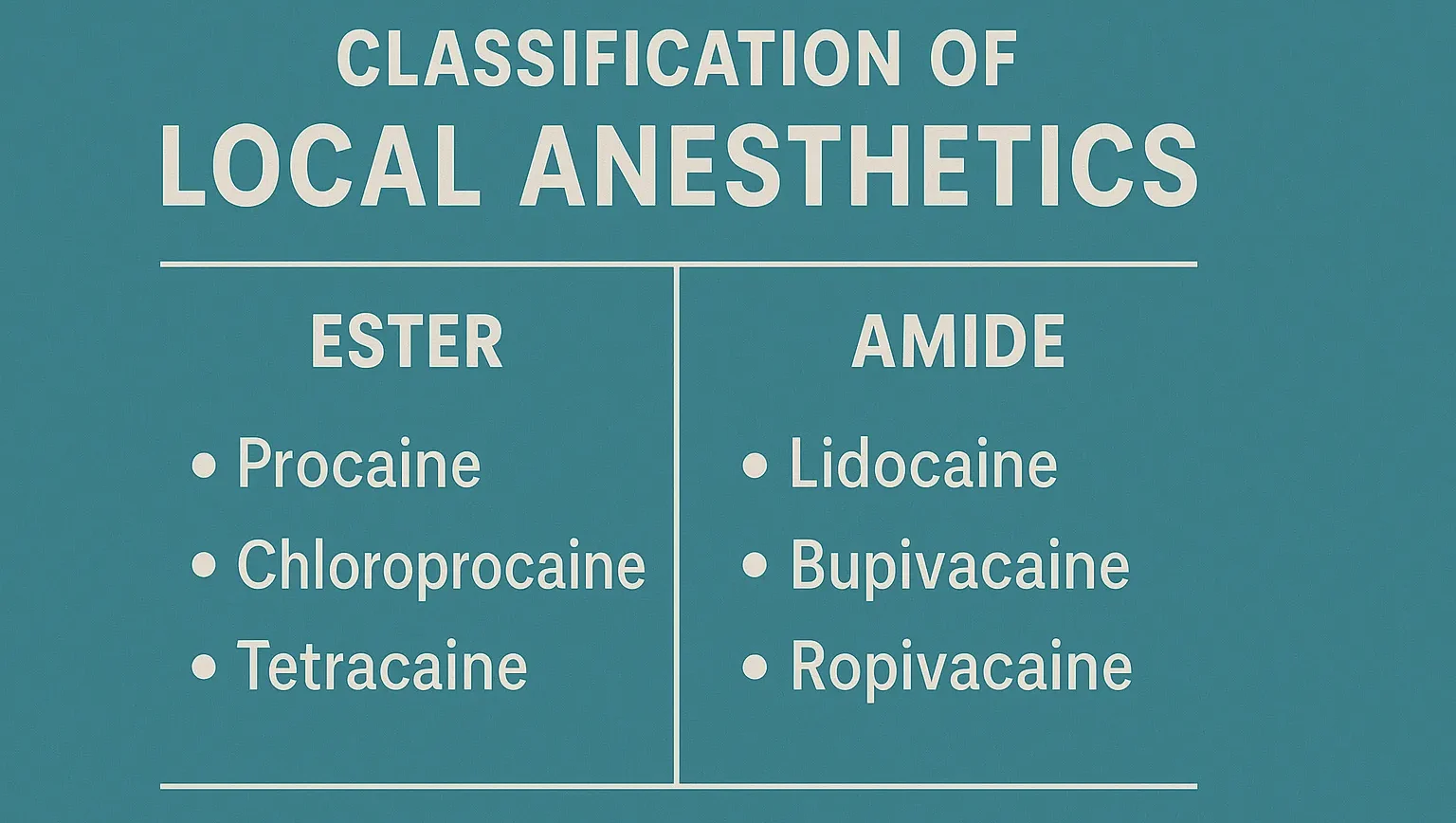
Classification of Local Anesthetics is based on their chemical structure, mainly ester-linked and amide-linked agents, with differing duration and use.
Classification of Local Anesthetics
- Local anesthetics are categorized based on their chemical structure.
- Each class shares a common mechanism of action, primarily involving the inhibition of nerve impulse transmission.
- Below is the classification along with the mechanism of action for each class:
-
Benzoic Acid Derivatives
- Mechanism of Action: Block sodium channels by binding to the intracellular portion of the channel, preventing depolarization and nerve impulse conduction.
- Examples: Cocaine, Hexylcaine, Meprylcaine, Cyclomethycaine, Piperocaine
-
Amino Benzoic Acid Derivatives
- Mechanism of Action: Inhibit sodium ion influx by binding to sodium channels, thereby blocking nerve impulse transmission.
- Examples: Benzocaine, Butamben, Procaine, Butacaine, Propoxycaine, Tetracaine, Benoxinate
-
Lidocaine/Anilide Derivatives
- Mechanism of Action: Stabilize neuronal membranes by blocking voltage-gated sodium channels, which inhibits the initiation and conduction of nerve impulses.
- Examples: Lignocaine (Lidocaine), Mepivacaine, Prilocaine, Etidocaine
-
Miscellaneous
- Mechanism of Action: Primarily block sodium channels to prevent the propagation of nerve impulses, with varying affinities and durations of action.
- Examples: Phenacaine, Diperodon, Dibucaine
Here is a shortened version of the table:
| Classification | Examples | Mechanism | Uses | Side Effects |
| Benzoic Acid Derivatives | Cocaine, Hexylcaine, Meprylcaine, Cyclomethycaine, Piperocaine | Block Na⁺ channels | Topical anesthesia, minor surgeries | Nervousness, tachycardia, hypertension, addiction risk |
| Amino Benzoic Acid Derivatives | Benzocaine, Butamben, Procaine, Butacaine, Propoxycaine, Tetracaine, Benoxinate | Block Na⁺ channels | Surface anesthesia, minor procedures | Methemoglobinemia, allergic reactions, systemic toxicity |
| Lidocaine/Anilide Derivatives | Lidocaine, Mepivacaine, Prilocaine, Etidocaine | Block Na⁺ channels | Dental work, surgeries, arrhythmias | CNS toxicity, cardiovascular issues, allergies |
| Miscellaneous | Phenacaine, Diperodon, Dibucaine | Block Na⁺ channels | Various anesthesia uses | Varies: CNS/cardio toxicity, allergies |