- Coenzymes are small, organic molecules that bind to enzymes and are essential for their catalytic activity.
- Derived from vitamins, they act as carriers for chemical groups or electrons in enzymatic reactions.
Structure and Examples of Coenzymes
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD⁺)
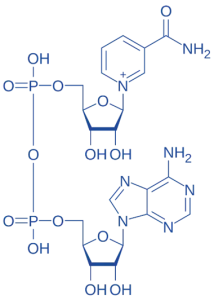
- Structure: Two nucleotides (adenine and nicotinamide) joined by phosphate groups.
- Function: Electron carrier in redox reactions.
- Example: NAD⁺ to NADH in cellular respiration.
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (FAD)
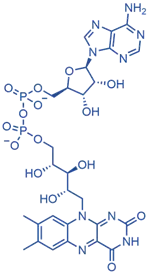
- Structure: Riboflavin bound to an adenine nucleotide.
- Function: Electron carrier.
- Example: FAD to FADH₂ in the citric acid cycle.
Coenzyme A (CoA)
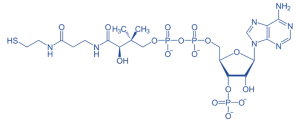
- Structure: Pantothenic acid, cysteamine group, and adenine nucleotide.
- Function: Transfers acyl groups.
- Example: Acetyl-CoA in the citric acid cycle.
Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TPP)
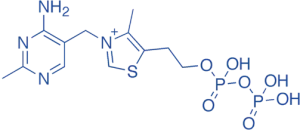
- Structure: Thiazole and pyrimidine rings with two phosphate groups.
- Function: Decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids.
- Example: Pyruvate to acetyl-CoA.
Pyridoxal Phosphate (PLP)
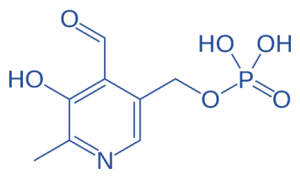
- Structure: Aldehyde group, pyridine ring, and phosphate group.
- Function: Amino acid metabolism.
- Example: Aminotransferases in transamination reactions.
Biotin
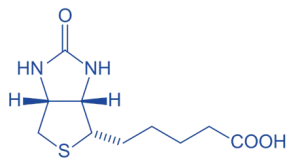
- Structure: Bicyclic molecule with ureido and tetrahydrothiophene rings.
- Function: Carboxylation reactions.
- Example: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase in fatty acid synthesis.
Tetrahydrofolate (THF)
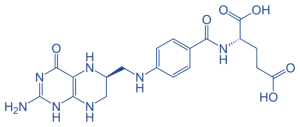
- Structure: Pteridine ring, para-aminobenzoic acid, and glutamic acid.
- Function: Transfers one-carbon units.
- Example: Nucleotide synthesis.
Biochemical Functions
- Electron Transfer: NAD⁺ and FAD in redox reactions (e.g., cellular respiration).
- Group Transfer: CoA and TPP in metabolic pathways (e.g., citric acid cycle).
- Carboxylation and Decarboxylation: Biotin and TPP in metabolism.
- One-Carbon Transfer: THF in nucleotide synthesis.
- Amino Acid Metabolism: PLP in transamination and other amino acid reactions.
- Coenzymes ensure the proper functioning of metabolic pathways and cellular health by facilitating various biochemical processes.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos