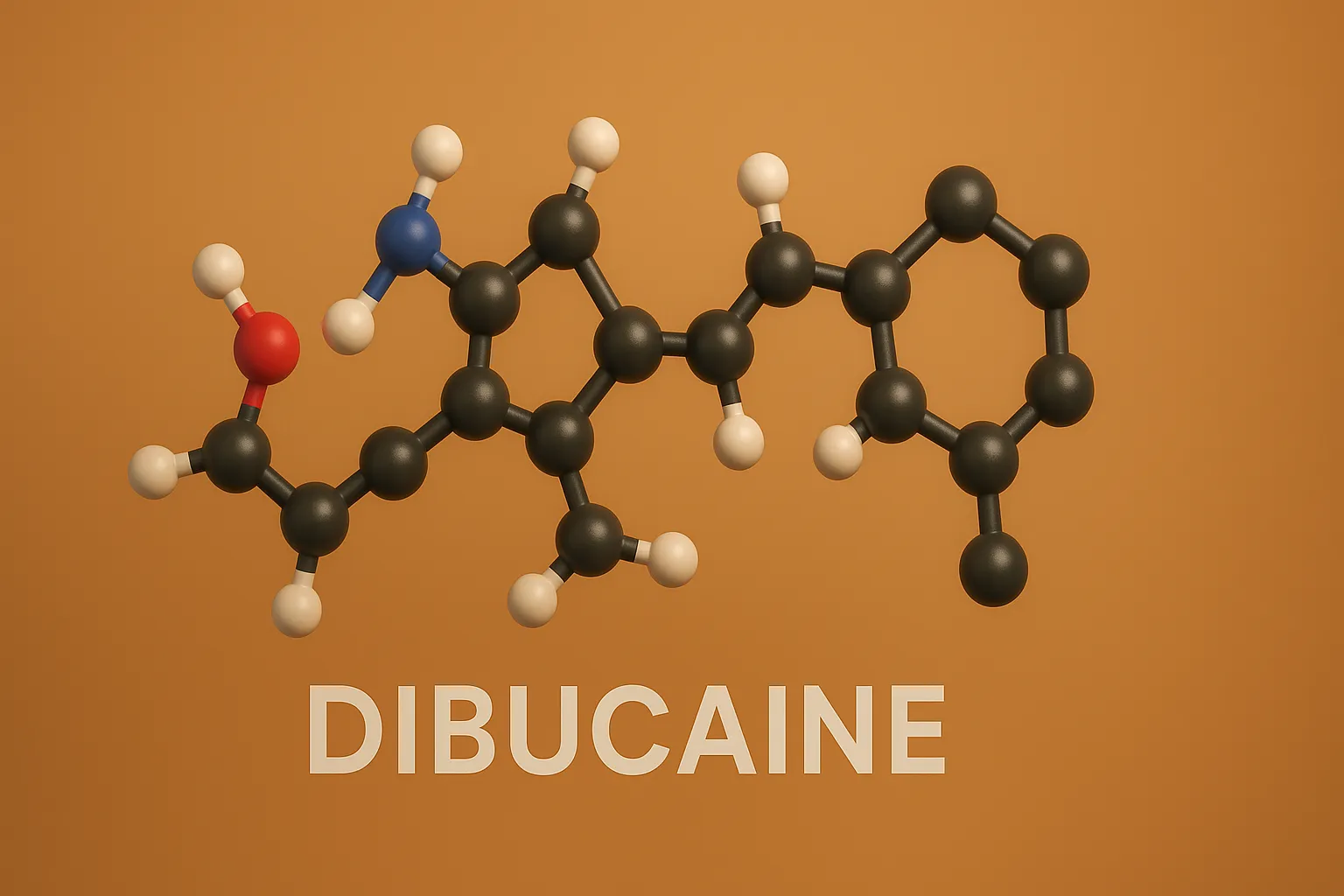
Dibucaine is a potent amide local anesthetic used topically for pain relief and hemorrhoid treatment.
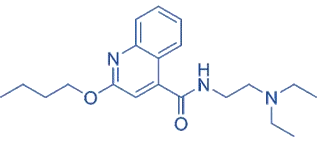
Structure of Dibucaine
- It is a potent amino benzoic acid derivative with a butyl ester group, providing long-lasting local anesthetic effects.
- Chemical Formula: C₁₀H₂₀N₂O₂
Mode of Action
- Sodium Channel Blockade: Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing nerve impulse conduction.
- Membrane Stabilization: Enhances nerve membrane stability, reducing excitability.
Uses
- Topical Anesthesia: Applied in rectal preparations, hemorrhoid treatments, and skin procedures for prolonged numbing.
- Local Anesthesia: Used in minor surgical procedures requiring extended anesthesia.
- Dermatological Applications: Employed in creams and ointments for skin conditions requiring local pain relief.
Side Effects
- Local Irritation: Redness, swelling, or discomfort at the application site.
- Systemic Toxicity: CNS excitation (e.g., seizures) and cardiovascular disturbances in high doses.
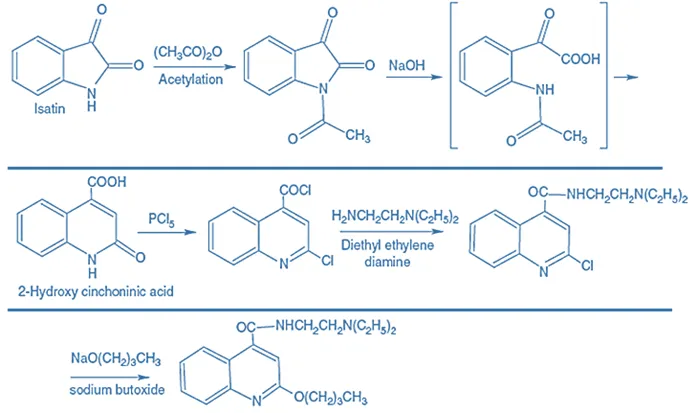
Synthesis of Dibucaine