Dipyridamole is an anti-anginal and antiplatelet drug that improves coronary blood flow and prevents blood clots.
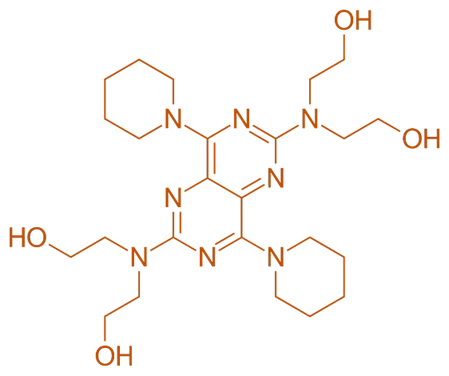
Structure of Dipyridamole
- Dipyridamole is a bis(pyrrolidine) derivative linked by a central ethylene bridge with two methanol side groups.
- Chemical Formula: C₂₀H₂₂N₄O₂
Advertisements
Mode of Action
- Phosphodiesterase Inhibition: Inhibits the enzyme responsible for breaking down cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP, increasing their intracellular levels.
- Vasodilation: Enhances nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation.
- Antiplatelet Effects: Inhibits platelet aggregation by increasing cyclic AMP in platelets.
- Inhibition of Adenosine Reuptake: Prolongs the action of adenosine, leading to vasodilation and anti-inflammatory effects.
Advertisements
Advertisements
Uses
- Stroke Prevention: Reduces the risk of stroke in patients with a history of transient ischemic attacks or ischemic strokes.
- Thrombosis Prevention: Used in combination with other antiplatelet agents to prevent clot formation.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Enhances blood flow and reduces platelet aggregation.
- Peripheral Arterial Disease: Improves blood circulation in affected limbs.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements

