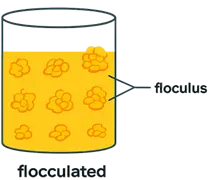
- Flocculated Suspensions are agents (like electrolytes, polymers) are used.
- Flocculated Suspensions Particles form loosely bound clusters called flocs.
- Flocs are light and settle rapidly but form a loose sediment that is easily redispersed.
- Zeta potential is reduced (but not too low) to promote controlled aggregation.
Advantages:
- No caking
- Easy redispersion
- Uniform dose upon shaking
Advertisements
Disadvantages:
- Settling is faster (but acceptable due to easy redispersion)
Formulation Strategy:
| Component | Function |
| Flocculating agent | Induces floc formation by reducing zeta potential (e.g., electrolytes: NaCl, KCl, AlCl₃) |
| Wetting agent | Promotes particle dispersion in vehicle (e.g., polysorbates, glycerin) |
| Suspending agent | Increases viscosity to slow sedimentation (e.g., xanthan gum, methylcellulose) |
| Buffer | Maintains pH for stability |
| Preservative | Prevents microbial growth |
| Vehicle | Typically, water or an aqueous medium |
Example Approach:
- Wet solid particles with surfactant.
- Disperse in vehicle.
- Add flocculating agent to induce loose aggregates.
- Add suspending agent to slow down sedimentation.
Advertisements