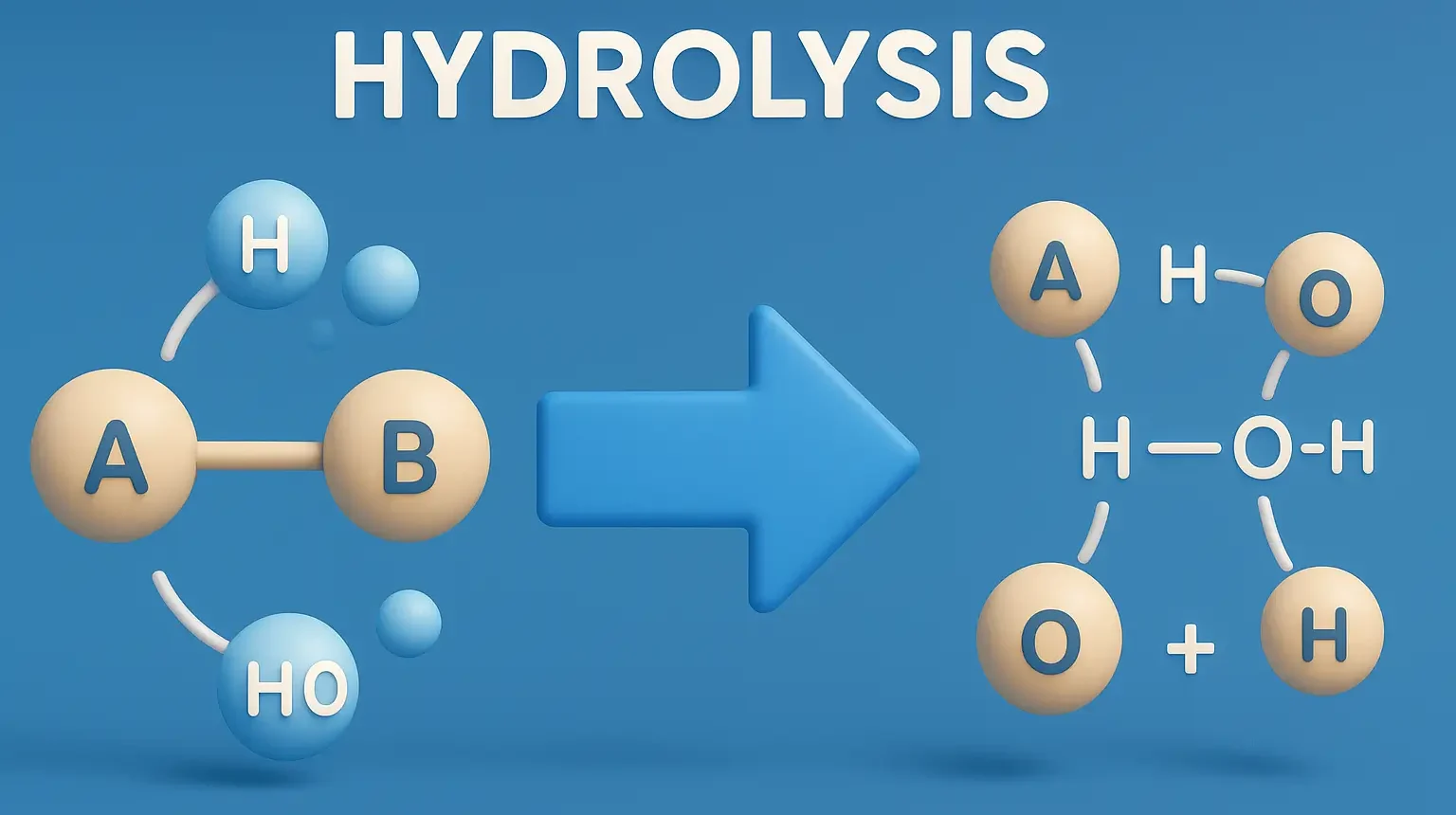
Definition of Hydrolysis:
- Hydrolysis is the decomposition or breakdown of a compound due to its reaction with water.
- It is the most common form of chemical degradation in pharmaceuticals, especially for drugs containing esters, amides, lactones, and lactams.
Mechanism:
The drug molecule reacts with water, leading to cleavage of chemical bonds (e.g., ester bonds) and formation of degradation products.
-
Example Reaction (Ester Hydrolysis):
- RCOOR’ + H2O →[H+ or OH−] RCOOH + R’OH
- RCOOR’ + H2O →[H+ or OH−] RCOOH + R’OH
-
Example Reaction (Amide):
- RCONH2 + H2O →[H+ or OH−] RCOOH + NH3
Prevention Strategies:
-
- Use of buffers to maintain optimal pH.
- Incorporation of anhydrous solvents.
- Packaging in moisture-proof containers (e.g., blister packs).
- Addition of desiccants to adsorb moisture.