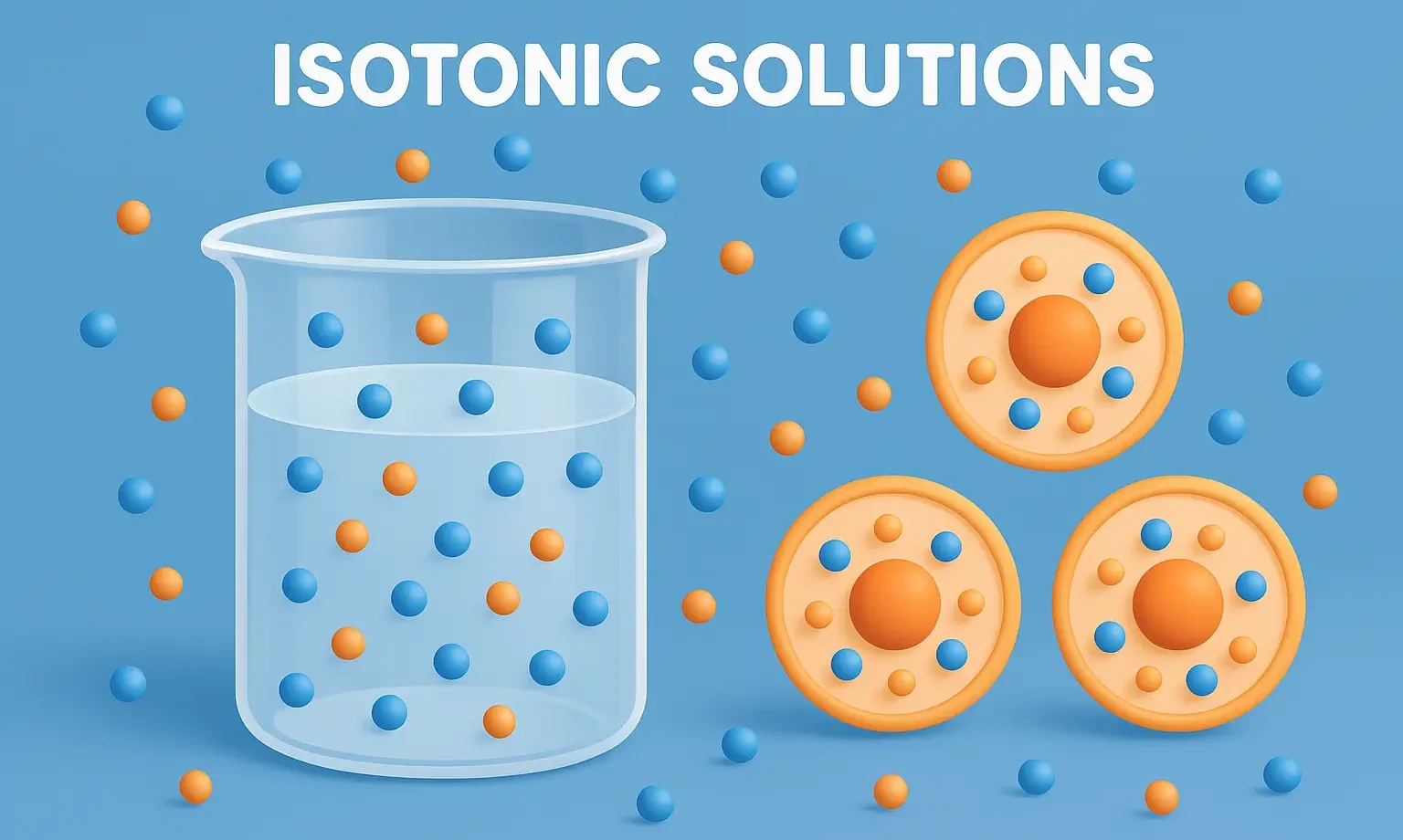
- An Isotonic Solutions has the same osmotic pressure as body fluids, preventing cell damage by maintaining balance between fluids.
Isotonicity and Freezing Point Depression
- Isotonic solutions match the freezing point depression of body fluids, around -0.52°C.
- Example: 9 Percent NaCl solution is isotonic with blood (normal saline).
Isotonicity and Molecular Weight
- The osmotic pressure depends on the number of particles, not their mass.
- Formula for freezing point depression:
- $\Delta T_f = i \times K_f \times m$
- Where:
- i= Van’t Hoff factor (dissociation particles).
- Kf = Freezing point depression constant.
- m = Molality.
E-value (NaCl Equivalent)
- The E-value helps compare other solutes to NaCl for isotonic solutions:
- $E = \frac{17}{i \times MW}$
Where MW = Molecular weight and i = Van’t Hoff factor
Advertisements
Example: To make an isotonic solution with dextrose (C₆H₁₂O₆), calculate based on molecular weight and freezing point depression.
Key Points:
- 9 Percent NaCl has a freezing point depression of 0.52°C.
- Use molecular weight, Van’t Hoff factor, and E-value to calculate the isotonic concentration of other solutes.