- Measurements of Tonicity can be assessed by measuring osmolality or osmolarity, which indicate the concentration of solute particles in a solution.
- Two common methods for measuring osmolality, and subsequently assessing tonicity, are the haemolytic method and the cryoscopic method.
Haemolytic Method of Measurements of tonicity:
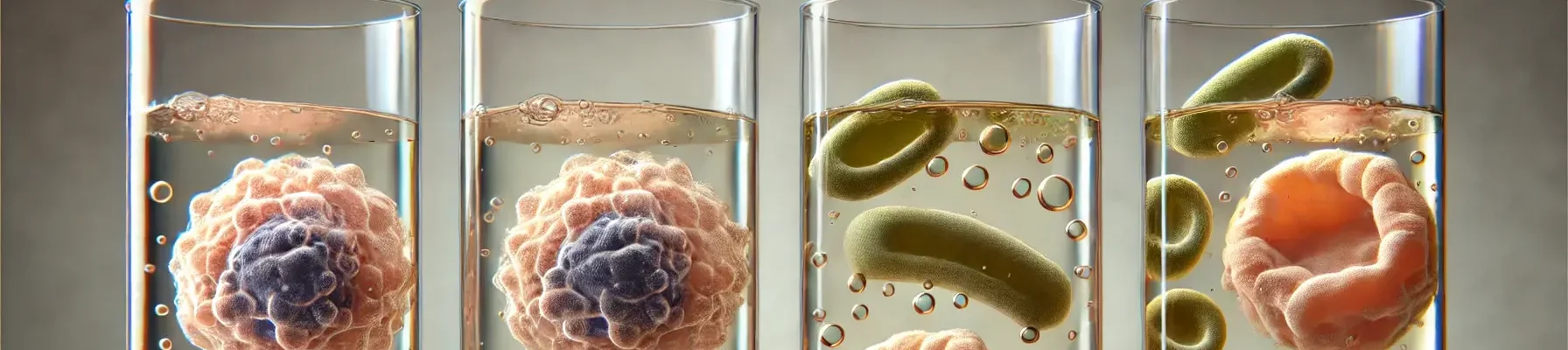
- A biological technique that assesses the tonicity of a solution by observing its effect on red blood cells (RBCs).
Procedure:
- RBCs are exposed to the test solution, and the degree of haemolysis (rupture of RBCs) is monitored.
- In an isotonic solution, RBCs maintain their normal shape with no net water movement.
- In a hypotonic solution, water enters the RBCs, causing them to swell and burst.
- In a hypertonic solution, water leaves the RBCs, causing them to shrink and crenate (shrink).
Advertisements
Conclusion:
- By comparing the haemolysis in the test solution with known solutions, you can determine the tonicity of the test solution.
Cryoscopic Method of Measurements of tonicity:
- Also known as freezing point depression osmometry, this method measures the decrease in freezing point of a solution relative to pure solvent.
Procedure:
- The freezing point of a solution is lower than that of a pure solvent due to the presence of solute particles.
- The amount of freezing point depression correlates with the osmolality of the solution.
Conclusion:
- By calculating the osmolality and comparing it with the osmolality of a reference solution (e.g., blood plasma), the tonicity can be determined.
- Isotonic solutions have similar osmolality to the reference, hypotonic solutions have lower osmolality, and hypertonic solutions have higher osmolality.
Click Here to Watch the Best Pharma Videos
Advertisements