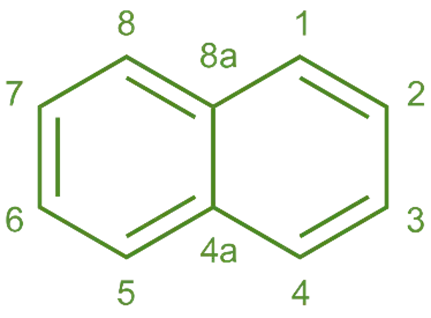
Structure of Naphthalene:
- It is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of two fused benzene rings.
- The molecular formula is C10H8.
- The structure is planar, and it has alternating double and single bonds, which are characteristic of aromatic compounds.
Synthesis of Naphthalene:
-
From Coal Tar:
- Naphthalenes are primarily obtained from coal tar, which is distilled to separate it from other components.
-
Laboratory Synthesis (Haworth Reaction):
- Formation of 1-Tetralone: Benzene is first reacted with succinic anhydride to form 1-tetralone via the Friedel-Crafts acylation.
- Cyclization: The intermediate is cyclized to form naphthol.
- Dehydration and Aromatization: Finally, dehydration and aromatization produce naphthalenes.
-
Benzene + Succinic anhydride → AlCl3 (reagents) → 1-Tetralone → Cyclization Naphthalenes
Reactions of Naphthalene:
-
Electrophilic Substitution:
- Nitration: Naphthalenes react with nitric acid (HNO3 HNO_3HNO3) to form nitronaphthalene.
-
C10H8 + HNO3 → H2SO4 (reagents) C10H7NO2 + H2O
-
- Sulfonation: Naphthalenes react with sulfuric acid (H2SO4H_2SO_4H2SO4) to form naphthalenes sulfonic acid.
-
C10H8 + H2SO4 → C10H7SO3H + H2O
-
- Nitration: Naphthalenes react with nitric acid (HNO3 HNO_3HNO3) to form nitronaphthalene.
-
Oxidation:
- It can be oxidized to phthalic anhydride using oxidizing agents like vanadium pentoxide (V2O5).
-
C10H8+4O2→V2O5C6H4(CO)2O+2H2O
-
- It can be oxidized to phthalic anhydride using oxidizing agents like vanadium pentoxide (V2O5).
Advertisements
Derivatives:
- Naphthols (1-Naphthol, 2-Naphthol): These are important derivatives used in dye manufacture.
- Naphthylamines (1-Naphthylamine, 2-Naphthylamine): These are precursors to various azo dyes.
Medicinal Uses:
- Mothballs: It is used in mothballs due to its insect-repellent properties.
- Derivatives: Some derivatives of naphthalene, such as naphthoquinones, have antibacterial and antifungal properties. However, the direct medicinal use of naphthalene is limited due to its toxic nature.